Rep:Mod:TPD17 01356675
NH3 Optimisation
Molecule: Ammonia, NH3
Calculation Method: RB3LYP
Basis Set: 6-31G(d,p)
E(RB3LYP): -56.55776873 a.u.
RMS Gradient Norm: 0.00000485 a.u.
Point Group: C3V
Bond Length: 1.01798
Bond Angle: 105.741
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-5.986274D-10 Optimization completed.
Ammonia |
File:TORIN DE GROOT NH3 OPT 01356675.LOG
NH3 Vibrations
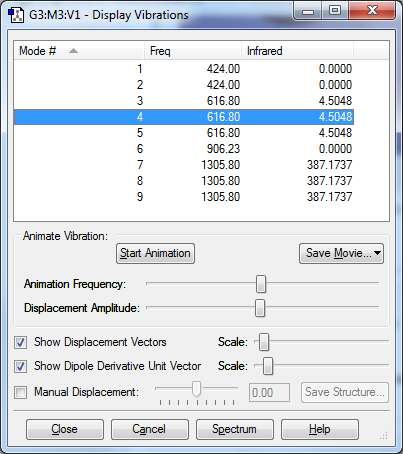
How many modes do you expect from the 3N-6 rule? 6 Which modes are degenerate (ie have the same energy)? 2&3 and 5&6 Which modes are "bending" vibrations and which are "bond stretch" vibrations? Bend:1,2,3 Stretch:4,5,6 Which mode is highly symmetric? 4 One mode is known as the "umbrella" mode, which one is this? 1 How many bands would you expect to see in an experimental spectrum of gaseous ammonia? 2 Charge on Nitrogen:-1.125 Charge on Hydrogens 0.375 Nitrogen is expected to have a negative charge and the hydrogens are expected to be positive because nitrogen is more electronegative than hydrogen.
N2 Optimisation
Molecule: Nitrogen, N2
Calculation Method: RB3LYP
Basis Set: 6-31G(d,p)
E(RB3LYP): -109.52412868 a.u.
RMS Gradient Norm: 0.00000003 a.u.
Point Group: D*H
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
N2 Vibrations
Vibrations:1 at 2457.33
Nitrogen |
H2 Optimisation
Molecule: Hydrogen, H2
Calculation Method: RB3LYP
Basis Set: 6-31G(d,p)
E(RB3LYP): -1.17853936 a.u.
RMS Gradient Norm: 0.00000017 a.u.
Point Group: D*H
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES
Vibrations:1 at 4465.68
Hydrogen |
Energy calculation
E(NH3)= -56.55776873 a.u 2*E(NH3)=-113.11553746 a.u E(N2)=-109.52412868 a.u E(H2)=-1.17853936 a.u 3*E(H2)=-3.53561808 a.u ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]=-0.05579069999998865 a.u = -146.47849400811018 kJ/mol ΔE=-146.48kJ/mol so Ammonia is more stable than its gaseous reactants
HCl analysis
Molecule: HCl
Calculation Method: RB3LYP
Basis Set: 6-31G(d,p)
E(RB3LYP): -460.80077875 a.u.
RMS Gradient Norm: 0.00005211 a.u.
Point Group: C*V
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000090 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000090 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000139 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000197 0.001200 YES
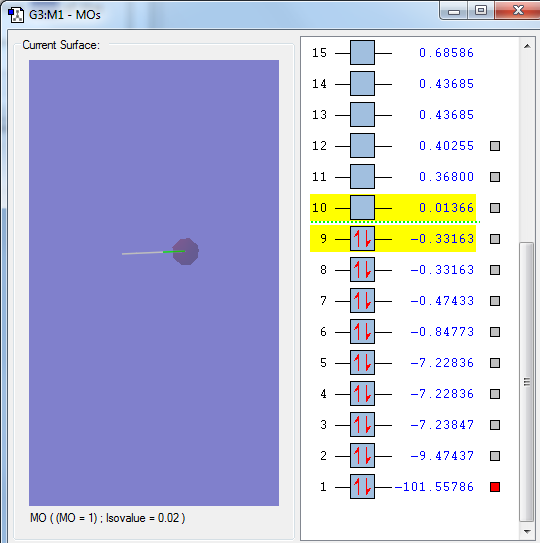
1 vibration at 2956.80 Charge on Cl atom:-0.284 Charge on H atom:0.284
HCl |
The 1s orbital of the Chlorine atom, a non bonding orbital
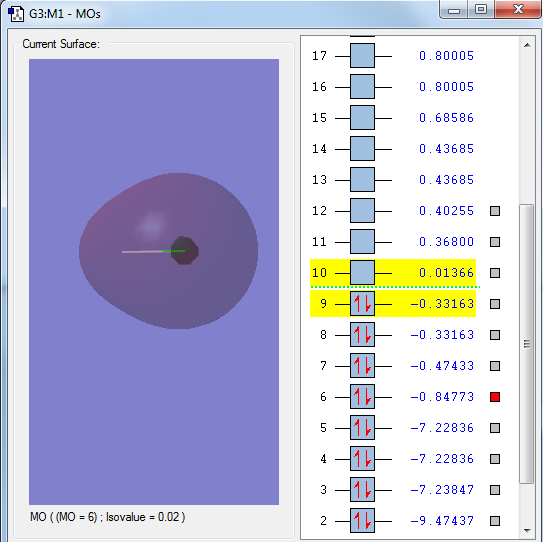
The 2px orbital of the Chlorine atom, a non bonding orbital
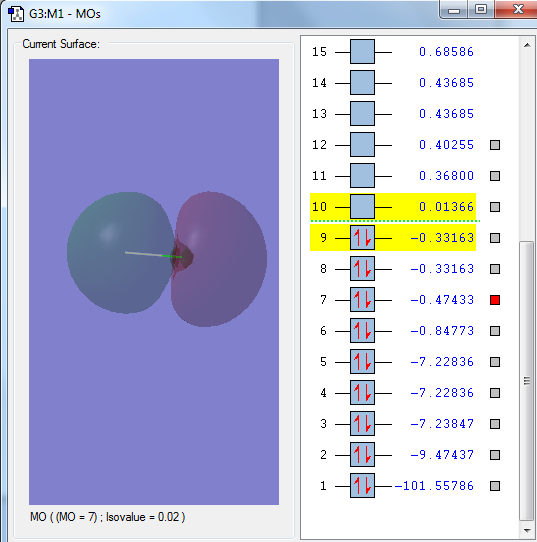
The sigma orbital of the hydrogen 1s orbital and the 3s orbital of the Chlorine atom, a bonding orbital
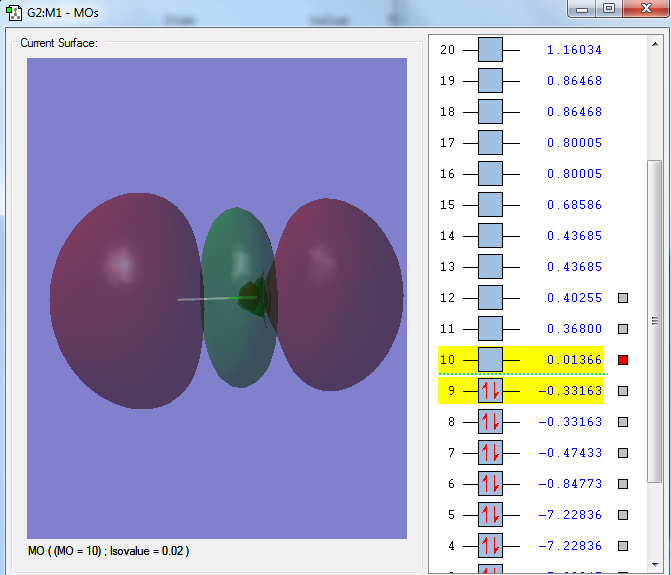
The sigma orbital of the HCl from the 1s orbital from the hydrogen atom and the 3pz orbital from the Chlorine atom, a bonding orbital
The sigma star orbital of the HCl, an out of phase combination of the hydrogen 1s orbital and chlorine 3pz orbital, an anti-bonding orbital, the LUMO
Extra molecule CF4 analysis
Molecule CF<sub>4</sub> Calculation Method RB3LYP Basis Set 6-31G(d,p) E(RB3LYP) -437.47627267 a.u. RMS Gradient Norm 0.00004048 a.u. Point Group TD
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000078 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000042 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000133 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000071 0.001200 YES
tetrafluoromethane |
The charge on the chlorine atom is 1.407. The charge on the fluorines is -0.352
One major IR peak,from vibrations 7,8 and 9 one very small one from 4 and 5