Rep:Mod:TKZC2018
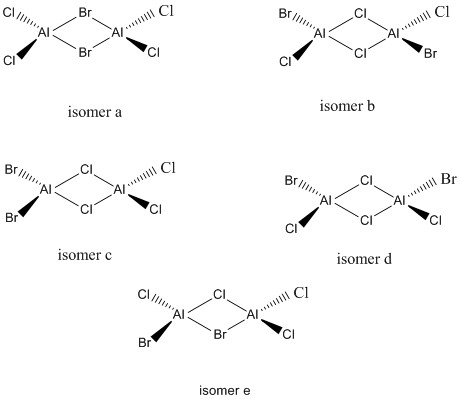
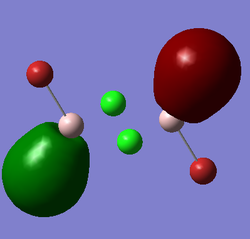
All the possible isomers of Al2Cl4Br2
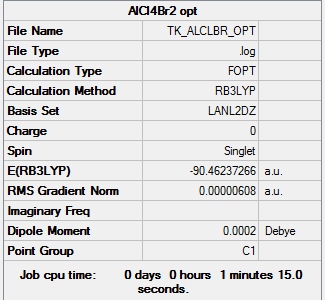
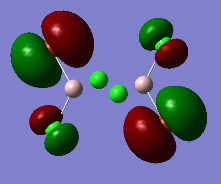
Al2Cl4Br2 isomer (a) bridging Br atoms
B3LYP/LanL2DZ
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000010 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000159 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000080 0.001200 YES
optimised AlClBr isomer (a) |
Ng611 (talk) 21:04, 20 May 2018 (BST) Your frequency log file and low-frequency modes should also be included here.
Comparison of the energies of isomers a and b:
E(isomer a)= -90.46237 a.u. E(isomer b)= -90.47287 a.u.
ΔE= 30 kJ/mol
Isomer b is approximately 30 kJ/mol lower in energy than isomer a and thus more stable. This mostly due to the large steric effects, the 2 bulky bromine atoms experience some strain in between the aluminum atoms.
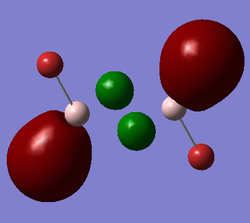
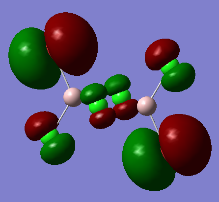
Al2Cl4Br2 isomer (b) with bridging Cl atoms and trans terminal Br atoms
B3LYP/LanL2DZ
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000047 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000025 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.001182 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000522 0.001200 YES
optimised AlClBr isomer (b) |
Vibrational spectrum for Al2Cl4Br2 isomer (b)
| wavenumber (cm-1 | Intensity (arbitrary units) | IR active? | type |
| 102 | 12 | slightly | bend |
| 106 | 20 | slightly | bend |
| 144 | 15 | slightly | bend |
| 251 | 43 | yes | stretch |
| 346 | 135 | yes | bend |
| 389 | 440 | yes | bend |
| 543 | 235 | yes | asymmetric stretch |
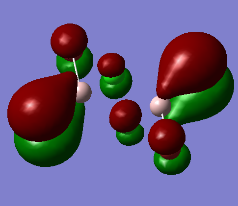
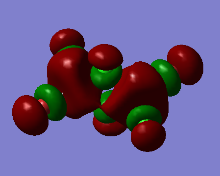
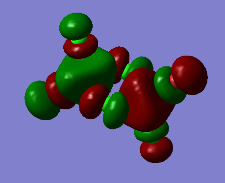
MO analysis
Ng611 (talk) 21:14, 20 May 2018 (BST) It's nice that you've analysed seemingly all of the MOs here, but it was completely unnecassry. The lab script only asked for 3.
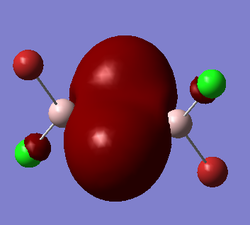
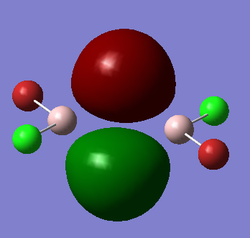
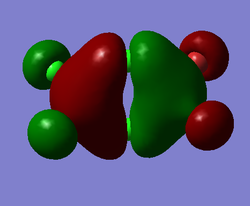
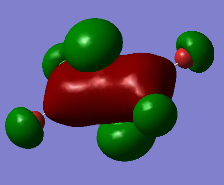
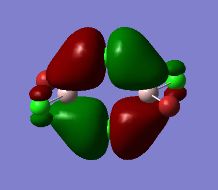
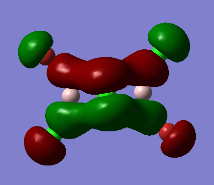
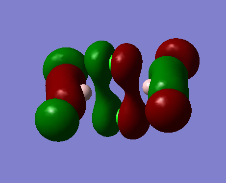
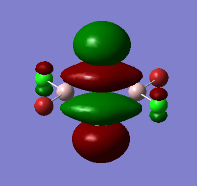
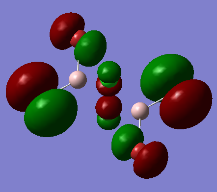
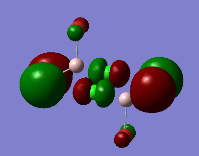
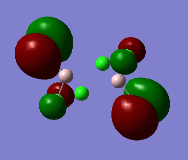
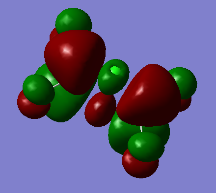
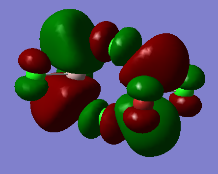
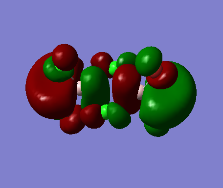
Representation of 3 MOs
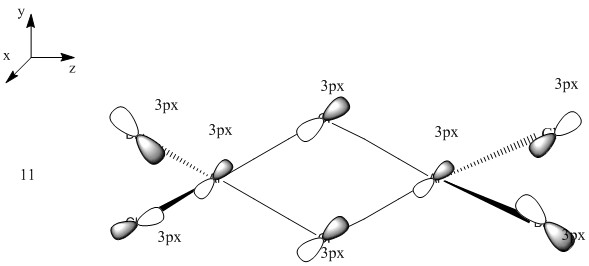
This MO is highly binding, it is one of the lowest energy valence MOs. There is good through-bond overlap of 3s aluminum orbitals with the 3pz orbitals of all the halogen atoms. All those overlaps are in-phase and increase the inter-nuclear electrical density. The bridging chlorine atoms have a worse overlap than the terminal halogen atoms as thy share the orbital with 2 different aluminum atoms and that bond distance is consequently longer. There is one nodal plane across the middle, across the 2 bridging chlorine atoms and then 4 more planes on the terminal halogen atoms. Those planes, that do not go through the bond are not as anti-bonding as across-bond would be. All this means that this MO is overall BONDING.
Ng611 (talk) 21:14, 20 May 2018 (BST) Good analysis. You could have saved yourself a lot of time by simply annotating the LCAO to show the major interactions though.
Ng611 (talk) 21:14, 20 May 2018 (BST) Good LCAO decomposition. In future, try to make it as easy as possible for the reader by orienting the molecule your LCAO diagram and the structure in the calculated MO diagram in the same way, for ease of comparison.
Practically all the orbitals involved in this MO bond through space and form a big cloud of pi bonds. There is one nodal plane across the central two chlorine atoms and the aluminum atoms and 4 nodal planes on the terminal halogen atoms. But since, the across-atom nodal planes aren't that anti-bonding, this MO is overall BONDING.
The MO 22 is one of the highest lying molecular orbitals. There are several nodal planes, across-bond and across-atom. There is some through space bonding from the cis terminal halogen atoms, but that is over a long distance and is week. Overall this MO is anti-bonding and most likely represents the lone pairs on the halogen atoms.
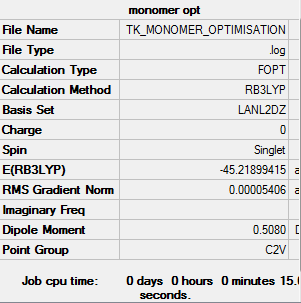
AlCl2Br monomer
B3LYP/LanL2DZ
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000199 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000093 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.001090 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000748 0.001200 YES
monomer |
Dissociation to the monomer
E(monomer)= -45.21899 a.u. E(isomer b)= -90.47287 a.u.
ΔE= 2[E(monomer)]-E(isomer b)= 0.03483 a.u. = 90 kJ/mol
The energy of dissociation is positive, which means that this reaction is energetically not spontaneous and unfavorable. The more stable is the dimer. The aluminum in the monomer is electron deficient and prefers having additional atoms bonded to it, to reduce that deficiency.
Ng611 (talk) 21:19, 20 May 2018 (BST) Some good bits to this report, although your let yourself down somewhat by missing out a lot of important information (e.g.: low frequency modes, log files, etc.). A very good LCAO and bonding analysis in both the first and second sections though.