Rep:Mod:TAW1234
NH3 Molecule
Key Information
Calculation Type - OPTF
Calculation Method - B3LYP
Basis Set - 6-31(d,p)
Final Energy - - 56.55776873 a.u.
Point Group - C3v
RMS Gradient - 0.00000485
Optimised NH3 Bond Length - 1.01798 Å
Optimised NH3 Bond Angle - 105.741°
Item Table
Item. Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-5.986284D-10
The optimisation file is liked to here
Jmol Dynamic Image
test molecule |
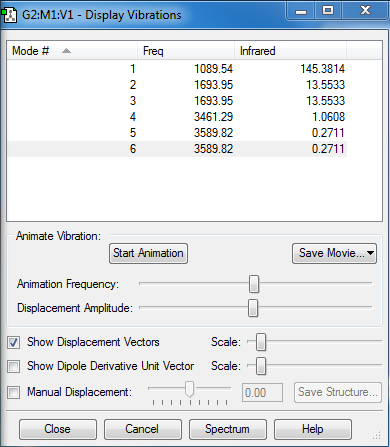
Vibrations
How many modes do you expect from the 3N-6 rule?
There are four atoms and therefore N=4. As a result, there are 6 modes.
Which modes are degenerate (ie have the same energy)?
The 2nd and 3rd modes are degenerate. The 5th and 6th modes are also degenerate too.
Which modes are "bending" vibrations and which are "bond stretch" vibrations?
The first three modes are bending vibrations and the last three modes are bond stretch vibrations.
Which mode is highly symmetric?
Mode 4 is highly symmetric.
One mode is known as the "umbrella" mode, which one is this?
Mode one is known as the umbrella mode.
How many bands would you expect to see in an experimental spectrum of gaseous ammonia?
2. This is because the intensity of some of the peaks is so small and would not show up in an experimental spectrum, especially with noise. This is because they are symmetric vibrations and only lead to a small change in dipole moment.
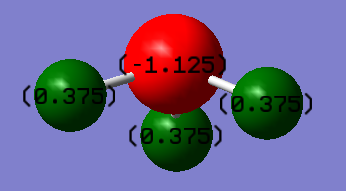
Charges in Ammonia
The charge on N atom is -1.125 and the charge on all the H atoms is 0.375. We would expect the hydrogen atoms to have a positive charge and the nitrogen atom to have a negative charge due to the difference in electronegativity between the two elements (nitrogen is more electronegative). More electronegative atoms attract electron density more easily.
H2 Molecule
Key Information
Calculation Type - OPTF
Calculation Method - B3LYP
Basis Set - 6-31(d,p)
Final Energy - -1.17853936 a.u.
Point Group - D∞h
RMS Gradient - 0.00000017
Optimised H2 Bond Length - 0.74279 Å
Item Table
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-1.164080D-13
The optimisation file is liked to here
Jmol Dynamic Image
test molecule |
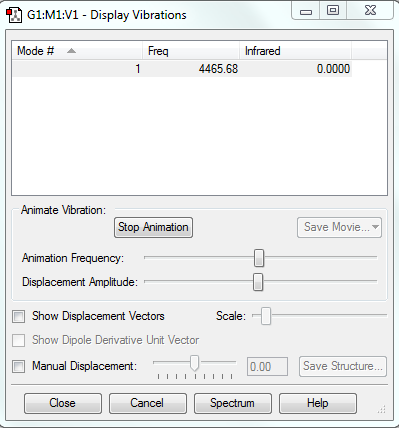
Vibrations
There is only one vibration. This is because in linear molecules there are 3N-5 vibrations.
N2 Molecule
Key Information
Calculation Type - OPTF
Calculation Method - B3LYP
Basis Set - 6-31(d,p)
Final Energy - -109.52412868 a.u.
Point Group - D∞h
RMS Gradient - 0.00000060
Optimised N2 bond Length - 1.10550 Å
Item Table
Item. Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-3.400948D-13
The optimisation file is liked to here
Jmol Dynamic Image
test molecule |
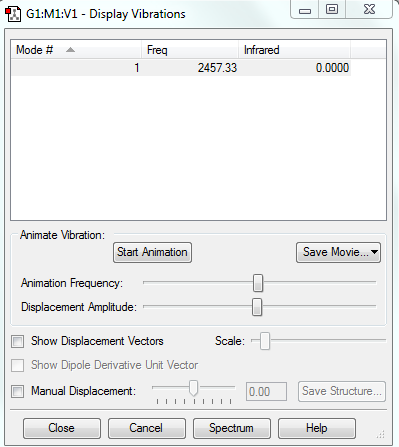
Vibrations
There is only one vibration. This is because in linear molecules there are 3N-5 vibrations.
Haber-Bosch Process
E(NH3)= -56.55776873 a.u.
2*E(NH3)= -113.1155375 a.u.
E(N2)= -109.52412868 a.u.
E(H2)= -1.17853936 a.u.
3*E(H2)= -3.53561808 a.u.
ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]= -0.05579074 a.u. = -146.48 kJ/mol (2 decimal places)
Since the enthalpy change is negative, this shows that the ammonia product is more stable than the gaseous reactants.
ClF Molecule
Key Information
Calculation Type - OPTF
Calculation Method - B3LYP
Basis Set - 6-31(d,p)
Final Energy - -559.94269578 a.u.
Point Group - C∞v
RMS Gradient - 0.00014211
Optimised ClF bond Length - 1.66434 Å
Item Table
Item. Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000246 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000246 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000433 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000613 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-1.066054D-07
The optimisation file is liked to here
Jmol Dynamic Image
test molecule |
Vibrations
There is only one vibration. This is because in linear molecules there are 3N-5 vibrations.
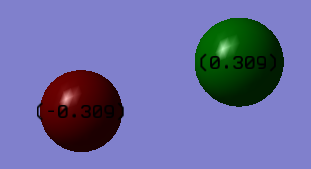
Charge Distribution
The charge on the fluorine atom is -0.309 and the charge on the chlorine atom is 0.309. This is because fluorine is more electronegative and more easily attracts electron density.
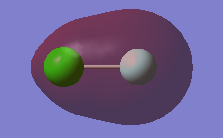
Molecular Orbitals
This molecular orbital is contributed to by the 2s atomic orbital on the Cl atom. It is a core orbital and is deep in energy. It is also non-bonding and occupied by two electrons. This MO will not have an affect on bonding.
Both the 2s atomic orbtial from the F atom and the 3s atomic orbital on the Cl atom contribute to this molecular orbital. It is an occupied bonding orbital and is quite deep in energy. This MO will strengthen the bonding however its contribution is cancelled out by the antibonding orbital below.
Both the 2s atomic orbtial from the F atom and the 3s atomic orbital on the Cl atom contribute to this molecular orbital. It is an occupied antibonding orbital and is quite deep in energy. This MO will weaken the bonding however its contribution is cancelled out by the bonding orbital above.
This molecular orbital is the HOMO and its energy is therefore in the HOMO/LUMO region. The 3p atomic orbital on the Cl atom and the 2p atomic orbital on the F atom both contribute to this molecular orbital. It is an occupied antibonding orbital. This MO weaken the bonding however its contribution is cancelled out by a bonding orbital.
This molecular orbital is the LUMO and its energy is therefore in the HOMO/LUMO region. The 3p atomic orbital on the Cl atom and the 2p atomic orbital on the F atom both contribute to this molecular orbital. It is an unoccupied antibonding orbital. This MO, since it is not filled, does not affect the bonding in this molecule.
H2O Molecule (Independence Section)
Key Information
Calculation Type - OPTF
Calculation Method - B3LYP
Basis Set - 6-31(d,p)
Final Energy - -76.41971755 a.u.
Point Group - C2v
RMS Gradient - 0.00201464
Optimised H2O Bond Length - 0.96211 Å
Optimised H2O Bond Angle - 104°
Item Table
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000099 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000081 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000115 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000120 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-1.939669D-08
The optimisation file is liked to here
Jmol Dynamic Image
test molecule |
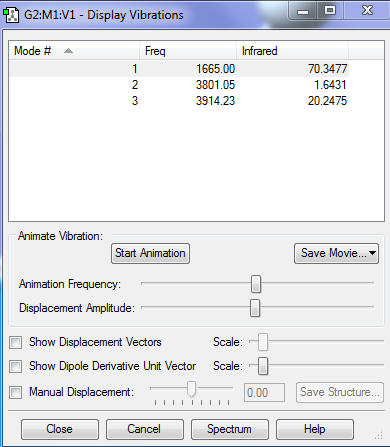
Vibrations
There are 3 vibrations. This is expected using 3N-6.