Rep:Mod:Scc215 MM2
NH3 Optimization
Summary
Calculation Method RB3LYP
Basis Set 6-31G(d,p)
Charge 0
Spin Singlet
E(RB3LYP) -56.55776873
RMS Gradient Norm 0.00000485
Imaginary Freq 0
Dipole Moment 1.8466
Point Group C3V
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-5.986282D-10
test molecule |
The optimisation file is linked to here
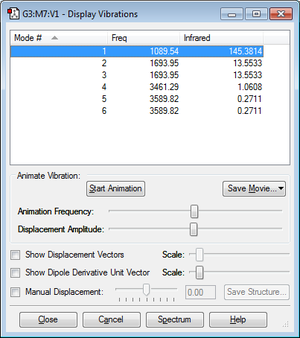
From the displayed vibration, it is expected to have 6 modes of vibration, which is identical to number of modes shown.
Vibration modes 2 and 3 are said to be a degenerated pair, while 5 and 6 are also said to be degenerated.
Vibration modes 1,2 and 3 are bending, while vibration modes 4,5 and 6 are bond stretch.
Vibration modes 1 and 4 are highly symmetric. Vibration mode 1 is the "umbrella mode". There are two sets of degenerated peaks, remaining four sets of peaks left.
Among these four peaks, absorption peaks of vibration modes 4 and 6 cannot be seen due to their low intensity.
N2 Optimization
Summary
Calculation Method RB3LYP
Basis Set 6-31G(d,p)
Charge 0
Spin Singlet
E(RB3LYP) -109.52412868
RMS Gradient Norm 0.00000060
Imaginary Freq 0
Dipole Moment 0.0000
Point Group D*H
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-3.401005D-13
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-1.164080D-13R1
H2 Optimization
Summary
Calculation Method RB3LYP Basis Set 6-31G(d,p) Charge 0 Spin Singlet E(RB3LYP) -1.17853936 RMS Gradient Norm 0.00000017 Imaginary Freq 0 Dipole Moment 0.0000 Point Group D*H
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-1.164080D-13R1
Haber-Bosch Process Enery Calculation
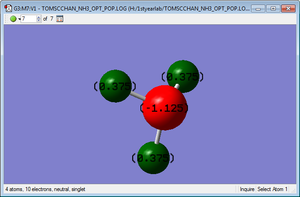
Energy related to the reaction : E(NH3)= -56.55776873 a.u.
2*E(NH3)= -113.1155375 a.u.
E(N2)= -109.52412868 a.u.
E(H2)= -1.17853936 a.u
3*E(H2)= -3.53561808 a.u.
ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]= -113.1155375-[(-109.52412868 + 3.5361808)] = -0.05522802 a.u. = -145.00 kJ mol-1
from above calculation, it was shown that the ammonia is having lower energy levels than the gaseous reactants, therefore ammonia is a more stable molecule in such reaction. The reaction is also said to be exothermic since the energy of product is lower than that of total of reactants
ClF Optimization
Summary
Calculation Method RB3LYP
Basis Set 6-31G(d,p)
Charge 0
Spin Singlet
E(RB3LYP) -559.94269578
RMS Gradient Norm 0.00014211
Imaginary Freq 0
Dipole Moment 0.9787
Point Group C*V
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000246 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000246 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000433 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000613 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-1.066055D-07
ClF molecule |
The optimisation file is linked to here
Frequency Analysis
How many modes do you expect from the 3N-5 rule?
i mode is expected as N is 2 for ClF.
Which modes are degenerate (ie have the same energy)?
There is only 1 mode, ie no degeneration will occur.
Which modes are "bending" vibrations and which are "bond stretch" vibrations?
Mode 1 is the stretching frequency.
Which mode is highly symmetric?
Mode 1 is highly symmetric
How many bands would you expect to see in an experimental spectrum of gaseous ammonia?
1 since the molecule is heterologous and difference of electronegativity is present between two atoms.
Charge Distribution

Cl atom : 0.309C
F atom : -0.309C
As shown from the diagram, Cl atom is said to carry a partial positive charge, while F atom is carrying partial negative charge, this is due to the differnce of electronegativity between Cl and F , and F atom is more electronegative than Cl atom
Molecular Orbital
Electron configuration of F : 1s22s22p5 Electron configuration of Cl : 1s22s22p63s235
Molecular Orbitals (MO) are formed when Atomic Orbitals (AO) ovedrlapped with each other. MO comes in different shapes and different energy levels due overlaps of various AO from both atoms. The six MO with lowest energy are AO of Cl and F without any overlap with other AO.
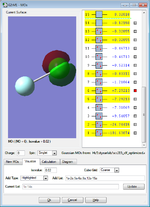
It was shown that only the 2nd orbital belongs to the F atom (1s orbital) and the other five orbitals belong to Cl atom.
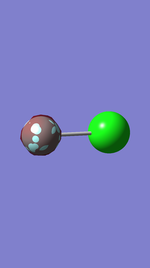
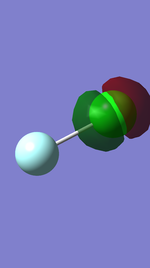
From the 7th orbital onwards, AO of both atoms start to overlap and MO start to contribute to the bonding character of ClF, the 7th and 8th orbital are the bonding orbital and anti-bonding orbital, formed by overlap of 3p orbital in Cl and 2p orbital in F, in ClF respectively.

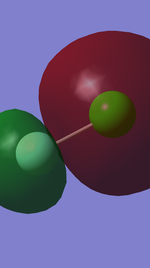
For the 9th to 11th orbital in the energy level diagram, the 9th MO is the 3p-2p sigma bonding orbital in ClF, while the 10th and 11th are pi bonding orbitals formed from overlap of 3p in Cl and 2p in F respectively.

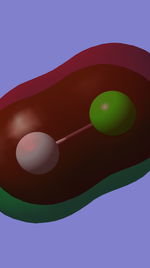
The last two occupied orbitals with highest energy levels are anti-bonding orbitals of pi orbital formed from 3p-2p overlap.
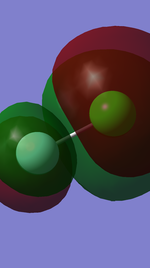
By cancelling out all bonding orbitals with their corresponding anti-bonding orbitals, bond order was shown to be 1, i.e. only a single bond of Cl-F is found.
