Rep:Mod:SPA2416
NH3 molecule
Molecule: NH3
Calculation method: RB3LYP
Basis set: 6-31G(d,p)
Final energy E(RB3LYP): -56.55776873 au
RMS Gradient: 0.00000485
Point group of NH3: C3V
Optimised N-H bond distance: 1.01798 angstroms
Optimised H-N-H bond angle: 105.741 degrees
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-5.986283D-10
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R2 R(1,3) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R3 R(1,4) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A1 A(2,1,3) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(2,1,4) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(3,1,4) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(2,1,4,3) -111.8571 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
Ammonia Molecule |
The optimisation file is liked to here
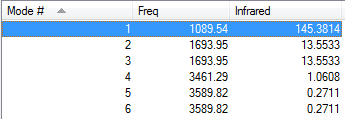
There are no negative frequencies
How many modes would you expect from the 3N-6 rule? 6
Which modes are degenerate? Modes 2 and 3, 5 and 6
Which modes are 'bending' vibrations and which are 'bond stretch vibrations? Bending: 1, 2, 3
Bond stretch: 4, 5, 6
Which mode is highly symmetric? 1
One mode is known as the 'umbrella' mode, which one is it? 1
How many bands would you expect to see in an experimental spectrum of gaseous ammonia? 3 as these are the only ones which are IR active as they have a change in the dipole moment
Charge on N atom: -1.125
Charge on H atoms: 0.375 on each one
Nitrogen is more electronegative than hydrogen so it bears the negative charge
N2
SUMMARY INFORMATION
What is the molecule? N2
What is the calculation method? RB3LYP
What is the basis set? 6-31G(d,p)
What is the final energy E(RB3LYP)? -109.52412868 au
What is the RMS gradient? 0.00000060 au
What is the point group of the molecule? D*H
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-3.401103D-13
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.1055 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
There are no negative frequencies
The optimisation file is liked to here
H2
SUMMARY INFORMATION
What is the molecule? H2
What is the calculation method? RB3LYP
What is the basis set? 6-31G(d,p)
What is the final energy E(RB3LYP)? -1.17853936 au
What is the RMS gradient? 0.00000017 au
What is the point group of the molecule? D*H
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.164080D-13
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 0.7428 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
There are no negative frequencies
The optimisation file is liked to here
Energies in atomic units
E(NH3)= -56.55776873
2*E(NH3)= -113.11553750
E(N2)= -109.52412868
E(H2)= -1.17853936
3*E(H2)= -3.53561808
ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]= -0.05579074 au
ΔE= -146.48 kJ/mol
The ammonia is more stable than the gaseous reactants
N2 + 3 H2 ⇌ 2 NH3
The standard enthalpy change of the Haber process is found to be -45.8 kJ/mol. [1]
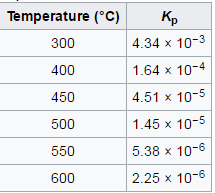
This reaction is an equilibrium reaction where the optimum temperature is 300oC. As the temperature where the reaction happens increases above 300oC, KP decreases meaning that the equilibrium shifts to the left and less ammonia is produced.[1]
- ↑ Brown, Theodore L.; LeMay, H. Eugene, Jr; Bursten, Bruce E (2006). "Table 15.2". Chemistry: The Central Science (10th ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson. ISBN 0-13-109686-9.
F2 molecule
Summary Information
What is the molecule? F2
What is the calculation method? RB3LYP
What is the basis set? 6-31G(d,p)
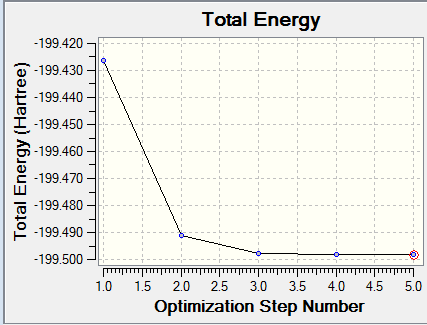
What is the final energy E(RB3LYP)? -199.49825218 au
What is the RMS gradient? 0.00007365 au
What is the point group of the molecule? D*H
F2 Optimisation Plot
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000128 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000128 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000156 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000221 0.001200 YES
The optimisation file is liked to here
Fluorine Molecule |
Vibrations
F2 is not IR active since it is a linear molecule with no change in dipole
Charges
There are no charges in the molecule since the atoms are identical and hence have identical electronegativity and sharing of the electrons is equal
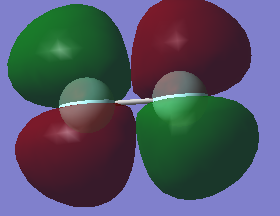
Molecular Orbitals
The atomic orbitals that contribute to the molecular orbitals are the 1s, 2s, and 2p for each of the fluorine atoms, as each fluorine atom has an electronic configuration of: 1s22s22p5.
The molecular orbitals in the fluorine molecule are a mixture of bonding and antibonding orbitals
The molecular orbitals are very low in energy, especially the 1s bonding and the 1s antibonding with -24.79 au. As we move to the 2s orbitals their energy is much higher (-1.34 au).
The molecular orbitals are occupied since they have electrons in them