Rep:Mod:POLS
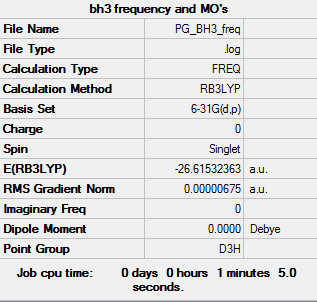
BH3
BL3LYP/6-31G
Item Table
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000014 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000007 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000053 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000027 0.001200 YES
Frequency analysis log file:PG_BH3_FREQ.LOG
Frequencies
Low frequencies --- -7.5936 -1.5614 -0.0055 0.6514 6.9319 7.1055
Low frequencies --- 1162.9677 1213.1634 1213.1661
Image of BH3
test molecule |
Vibrational spectrum for BH3
| wavenumber (cm-1) | Intensity (arbitrary units) | symmetry | IR active? | type |
| 1163 | 93 | A2" | yes | out-of-plane bend |
| 1213 | 14 | E' | yes | symmetric bend |
| 1213 | 14 | E' | yes | asymmetric bend |
| 2582 | 0 | A1' | no | symmetric stretch |
| 2716 | 126 | E' | yes | asymmetric stretch |
| 2716 | 126 | E' | yes | symmetric stretch |
There are 3 peaks in the IR spectrum but six actual vibrations picked up. This is because there are two sets of degenerate vibrations, with two vibrational modes at 1213 and 2716. They will appear as only one peak in the IR spectrum for each of these two vibrations. Lastly the vibrational mode at 2582 is not IR active as it does not cause a change in dipole moment so will not appear in the spectrum.
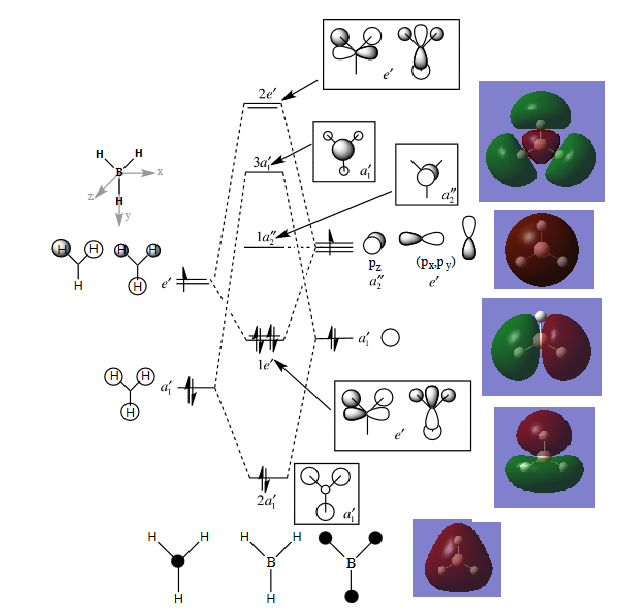
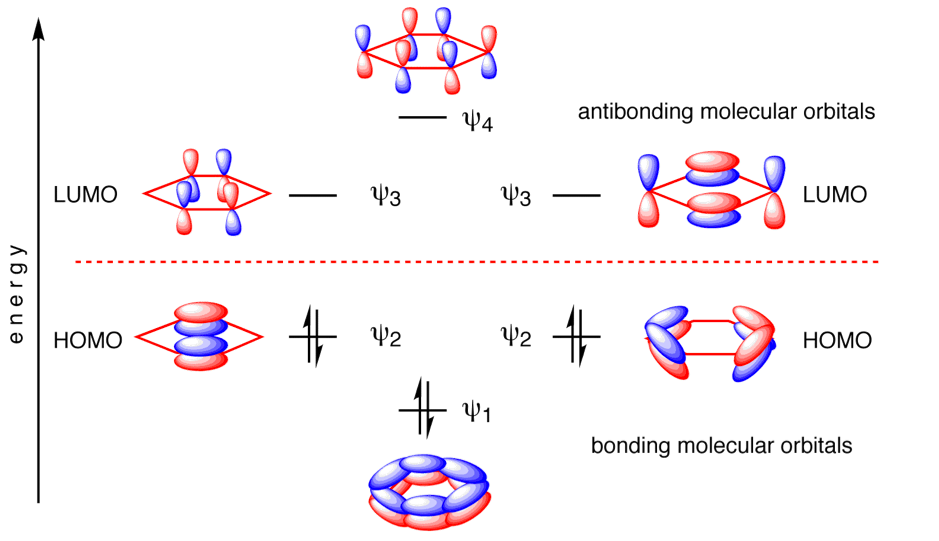
MO diagram for BH3
The actual molecular orbitals are a lot more diffuse and cover more of the molecule than those formed from LCAO.For example the 3A1'actual orbital has a much larger relative contribution from the hydrogens compared to the ones qualitatively determined. This shows that qualitative MO is useful to give you an idea of the molecular orbitals involved and the general shape of them but it does not show you the whole scope of the orbital. http://www.huntresearchgroup.org.uk/teaching/teaching_MOs_year2/P1_BH3_MO_diagram.pdf From Dr Tricia Hunt's notes
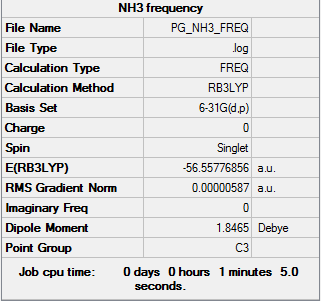
Ammonia
BL3LYP/6-31G
Item Table
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000013 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000006 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000039 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000013 0.001200 YES
Frequency analysis log file:PG_NH3_FREQ.LOG
Low frequencies --- -8.5646 -8.5588 -0.0047 0.0454 0.1784 26.4183 Low frequencies --- 1089.7603 1694.1865 1694.1865
Image of NH3
test molecule |
NH3BH3
BL3LYP/6-31G
Item table
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000222 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000059 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.001102 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000414 0.001200 YES
Frequency analysis log file:PG_NH3BH3_FREQ.LOG
Low frequencies --- -23.3831 -0.3116 -0.0273 0.0386 12.7226 12.8172 Low frequencies --- 261.8470 631.2544 637.6402
Image of NH3BH3
test molecule |
Association Energy
E[BH3]= -26.61532
E[NH3]= -56.55777
E[NH3BH3] = -83.22469
ΔE=E(NH3BH3)-[E(NH3)+E(BH3)] ΔE= -0.0516au = -129 kjmol
This is a fairly low bond energy as the energy for a c-c bond is 348 kjmol. I chose this comparison as NH3BH3 is isoelectronic to ethane that contains the c-c bond.
Smf115 (talk) 18:46, 23 May 2018 (BST)Corrrect calculation method however, the conversion from a.u. to kJ/mol isn't right resulting to an incorrect answer. The comprison used lacks a reference for the literature value, although good choice of comparison.
BBr3
The optimized molecule can be found from this DOI link
Link to file: DOI:10042/202394
Smf115 (talk) 18:49, 23 May 2018 (BST)Shame to see an incomplete section and the calculation linked too didn't run due to an error, I believe this is because the pseudopotential wasn't reentered for the freqeuncy calculation.
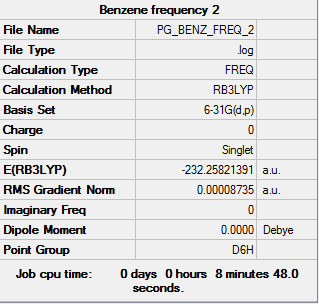
Benzene
BL3LYP/6-31G
Item table
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000198 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000087 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000757 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000321 0.001200 YES
Low frequencies --- -2.1422 -2.1422 -0.0089 -0.0042 -0.0042 10.4842 Low frequencies --- 413.9768 413.9768 621.1389
Frequency analysis log file:PG_BENZ_FREQ_2.LOG
Image of Benzene
test molecule |
Borazine
BL3LYP/6-31G
Item table
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000201 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000067 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000448 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000180 0.001200 YES
Low frequencies --- -11.1653 -10.4477 -10.4477 -0.0238 -0.0238 -0.0188 Low frequencies --- 289.1429 289.1429 403.9762
Frequency analysis log file:PG_BOR_FREQ_2.LOG
Image of Benzene
test molecule |
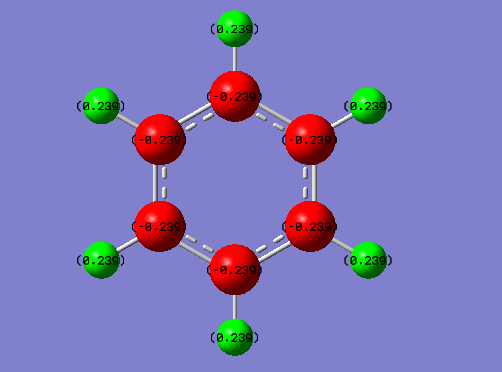
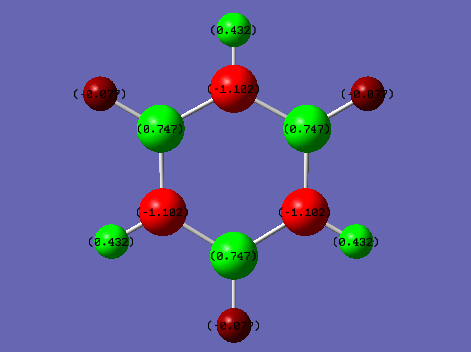
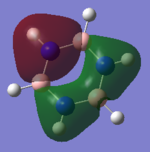
NBO charge comparison
Comparing the two NBO's of Benzene and Borazine, it can be seen on benzene that the carbons are negative and hydrogens are positive as carbon is more electronegative than hydrogen. The difference isn't by much however due the fact carbon and hydrogen are of fairly similar eledtronegativity. So you get an overall positive charge on the outside of the ring and negative inside the ring. Borazine however contains nitrogen and boron in the ring, nitrogen is more electronegative then boron and so you can alternating positive and negative charge distribution in the ring. The hydrogen's are more electronegative than the boron and so the ones that are attached to boron are negative but the hydrogen's that are attached to the nitrogen have a positive charge as they are less electronegative than nitrogen. Therefore, even though they have similar aromaticity and energy and very different NBO's due to the differences in electronegativity.
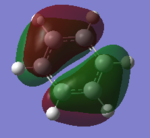
Molecular Orbital Theory
Smf115 (talk) 18:50, 23 May 2018 (BST)Nice range of MOs and correct description of the orbital types and character.
Aromatictiy
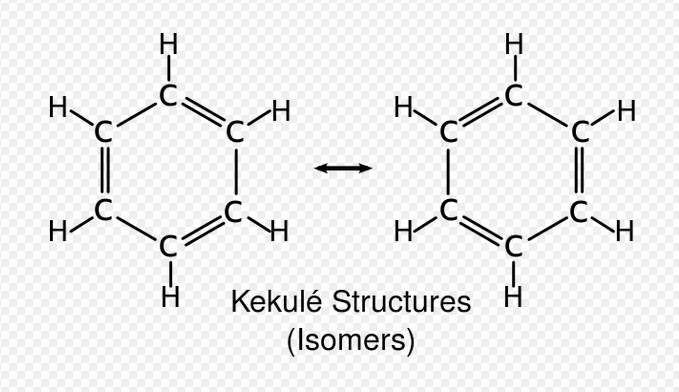
August Wilhelm Hofmann first coined the term aromatic to define a group of benzene derived compounds that had an 'aroma' unlike the other similar saturated hydrocarbons. Aromatic compounds have a high stability making them relatively nonreactive, predominantly only reacting in electrophilic substitution. Take Benzene, and compare it to the Kekule structure, it is resonance stabilized by around 150kjmol does not undergo addition reaction that you would expect if they were double bonds. Kekule theorized that benzene's structure was of three double bonds in constant rapid equilibrium. However evidence such as its resonance stabilization energy suggest that this was not occurring but in fact the pi electrons were delocalised throughout the molecule providing extra stabilization. MO theory suggested that compounds can be aromatic also when only the bonding orbitals are filled, not antibonding.
Aromatic compound compounds are traditionally defined through following Hückel's Rules:
1. Molecule is a cyclic ring of atoms
2. Molecule is Planar
3. Molecule is fully conjugated
4. The molecular has 4n + 2 pi electrons
However this was defined qualitatively. However once quantum mechanics was carried out on such structures it was discovered that the definition of aromaticity was not accurate and still is not absolutely defined.
It was found that all the molecular orbitals contribute to the aromatic character of compounds, not just the pi delocalisation interaction, but all of them, including sigma bonding interactions that are found in many of the bonding Mo's. The first quantitative approach to defining aromaticity was using bond alternation to determine bond length. Another approach to determine aromaticity is using NICS in NMR. From these new methods it has now been found that molecules do not necessarily have to follow these rules at all. There are many molecules that aren't planar for example benzene at 20k, it adopts the chair conformation due to intermolecular interactions in the lattice being strong enough.In addition, diphosphatriazo0late anion contains just nitrogen and phosphorous atoms is aromatic but contains electrons in the anti-boding orbital, it is still aromatic but less so than benzene. There is still not one conclusive way of defining aromaticity but what we do know that it isn't due to just one pi interaction but due to many complex reasons that are still being researched. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.1002/chem.200700250 |
Smf115 (talk) 18:45, 23 May 2018 (BST)Clear understanding of the main concepts of aromaticity shown and a really good range of points covered. Considering the MOs visualised and how they show how overalapping pZ AOs is a poor description of aromaticity would improve the answer, tieing in to the sigma-aromaticity point mentioned.
Smf115 (talk) 18:45, 23 May 2018 (BST)Overall a good report with a nice project section. Some mistakes were made throughout and some answers needed to be developed further.