Rep:Mod:PES26
NH3 molecule
NH3 molecule |
The optimisation file is liked to here
Calculation method:
FREQ
Basis set:
6-31G(d.p)
Final energy:
-56.55776873 a.u.
RMS gradient:
0.00000485 a.u.
Point group:
C3V
Optimised N-H bond length:
1.01798 Å
Optimised H-N-H bond angle:
105.741 degrees
| Item | Value | Threshold | Converged? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum Force | 0.000004 | 0.000450 | YES |
| RMS Force | 0.000004 | 0.000300 | YES |
| Maximum Displacement | 0.000072 | 0.001800 | YES |
| RMS Displacement | 0.000035 | 0.001200 | YES |
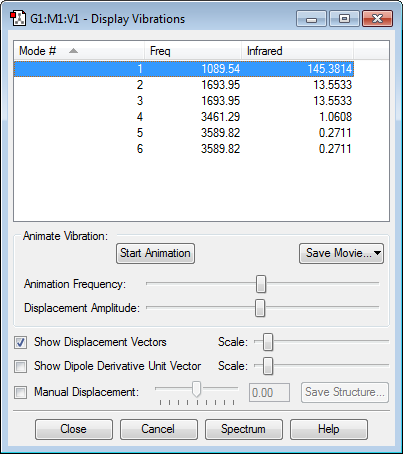
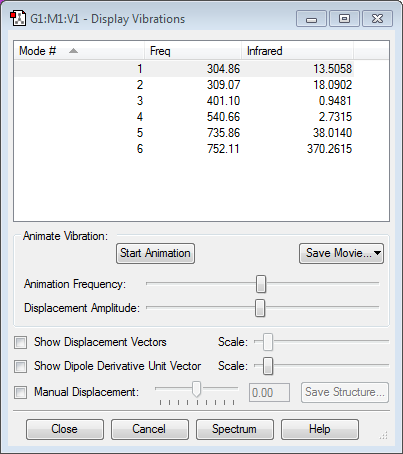
Vibrations:
As there are 4 atoms on an NH3 molecule, the 3N-6 rule suggests that the molecule has 6 modes of vibration. Of the different vibrational modes shown above, 2 and 3 are degenerate and so are 5 and 6. Modes 1,2 and 3 are are bending vibrations but 4,5 and 6 are stretching vibrations. Mode 4 is very symmetric. Mode 1 is the umbrella mode. On an experimental spectrum for gaseous ammonia, mode 4 will not produce a peak, as there is no change in dipole moment for that vibration. Therefore on an experimental spectrum for gaseous ammonia, there will be 3 peaks.
Charges:
Nitrogen: -1.125
Hydrogen: +0.375
It would be expected that nitrogen has a negative charge, as it is the most electronegative of the two elements in ammonia, so will draw the electron density to itself, leaving the hydrogen atoms with a slight positive charge.
N2 molecule
N2 molecule |
The optimisation file is liked to here
Calculation method:
FREQ
Basis set:
6-31G(d.p)
Final energy:
-109.52412868 a.u.
RMS gradient:
0.00000365 a.u.
Point group:
D*H
Optimised N-N bond length:
1.10550 Å. This is very close to the experimentally observed bond length for N2, which is 1.10Å [1].
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000006 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000006 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000002 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000003 0.001200 YES
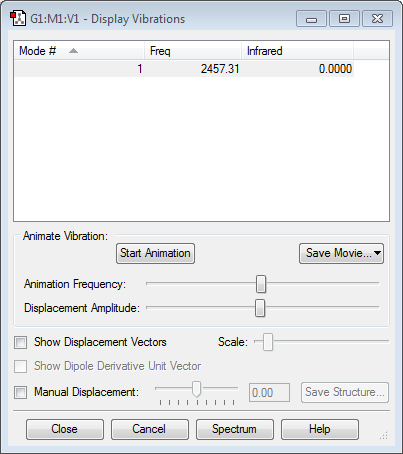
This shows that the vibrational frequency for the optimised N2 molecule is positive.
H2 molecule
H2 molecule |
The optimisation file is liked to here
Calculation method:
FREQ
Basis set:
6-31G(d.p)
Final energy:
-1.1785393 a.u.
RMS gradient:
0.00012170 a.u.
Point group:
D*H
Optimised H-H bond length:
0.74309 Å
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000211 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000211 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000278 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000393 0.001200 YES
This shows that the vibrational frequency for the optimised H2 molecule is positive.
Reaction energies:
E(NH3)= -56.55776873 a.u.
2*E(NH3)= -113.1155375 a.u.
E(N2)= -109.52412868 a.u.
E(H2)= -1.1785393 a.u.
3*E(H2)= -3.5356179 a.u.
ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]= -0.05579092 a.u.
ClF3 molecule:
ClF3 molecule |
The optimisation file is liked to here
Calculation method:
FREQ
Basis set:
6-31G(d.p)
Final energy:
-759.44149520 a.u.
RMS gradient:
0.00014109 a.u.
Point group:
D3H
Optimised Cl-F bond length:
1.75620 Å
Optimised F-Cl-F bond angle:
120.000 degrees
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000282 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000185 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.001250 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000819 0.001200 YES
Vibrations:
Charges:
Fluorine: -0.396
Chlorine: +1.188
Structure:
The structure which the optimised ClF3 molecule has is trigonal planar. However, ClF3 molecules are most stable when they are in a T-shape.[2] The vibration table shows 2 modes of vibrations which show a peak at a negative frequency. This suggests that the optimisation is not complete. Thus, the optimisation needs to be redone to get the most stable structure of ClF3.
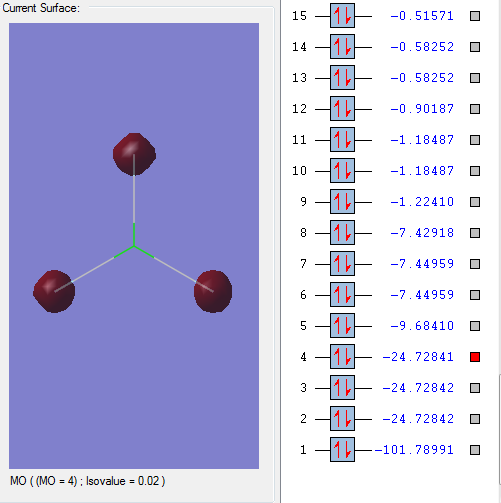
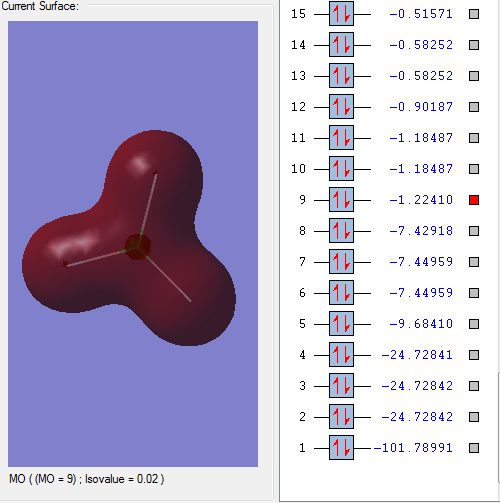
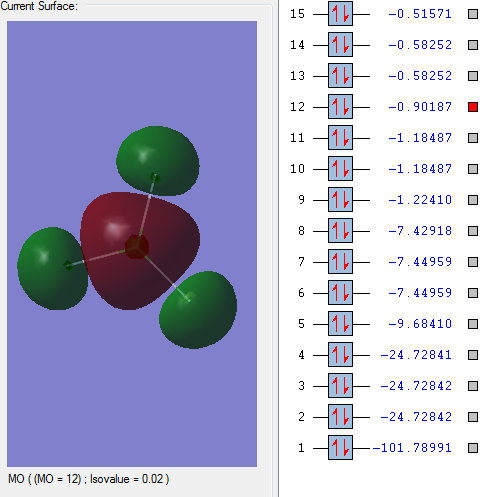
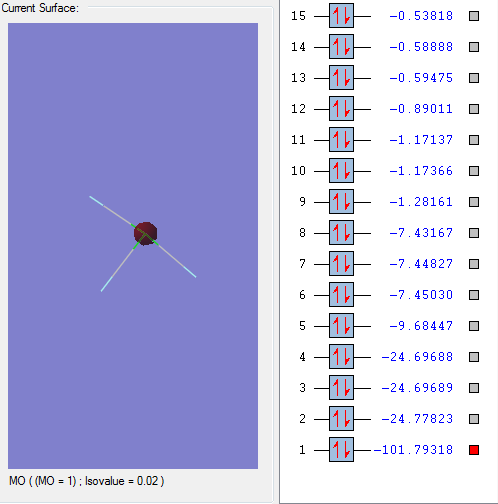
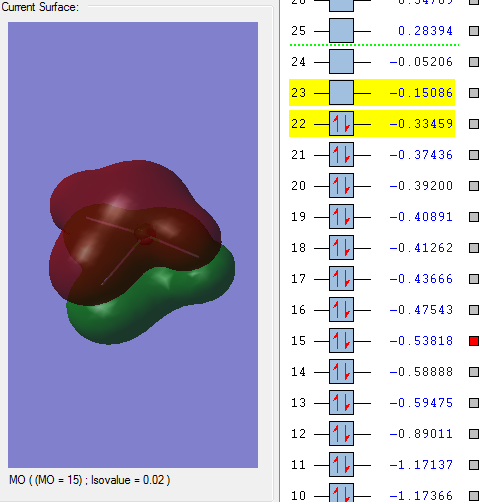
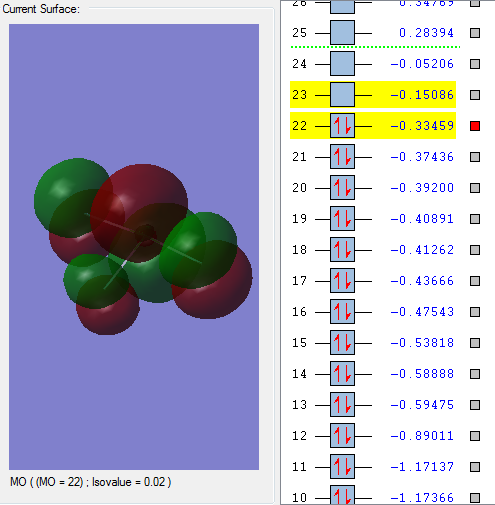
Molecular orbitals:
This molecular orbital is a non-bonding orbital which is the deepest in energy. It is comprised of the 1s orbital from the chlorine atom. It is occupied, but has no effect on the bonding of the molecule.
This molecular orbitals is a non-bonding orbital which is made up of the 1s orbital from each of the fluorine atoms. It has a deep energy and has no effect on bonding. It is occupied.
This is the first bonding molecular orbital. The orbitals which make it up are s orbitals from the chlorine and fluorine molecules. It has a higher energy than the two non-bonding orbitals previously seen. This orbital is occupied by valence electrons but doesn't have a large effect on bonding.
This bonding orbital is comprised of p orbitals from the 3 fluorine atoms and an s orbital from the chlorine atom. It is occupied and it quite close to the HOMO.
This is an anti-bonding molecular orbital. It is a pi orbital formed from p orbitals from the chlorine atom and the fluorine atom. It has a large effect on bonding. It is the HOMO.
Re-optimised ClF3 molecule:
Re-optimised ClF3 molecule |
The optimisation file is liked to here
Calculation method:
FREQ
Basis set:
6-31G(d.p)
Final energy:
-759.46531687 a.u.
RMS gradient:
0.00003698 a.u.
Point group:
CS
Optimised equitorial Cl-F bond length:
1.65142 Å
Optimised axial Cl-F bond length:
1.72872 Å
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000081 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000041 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000359 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000168 0.001200 YES
Vibrations:
There are no modes of vibration which give a negative frequency, suggesting that the molecule has now been completely optimised, so this is the most stable structure for ClF3.
Charges:
Equitorial fluorine: -0.316
Axial fluorine; -0.454
Chlorine: +1.224
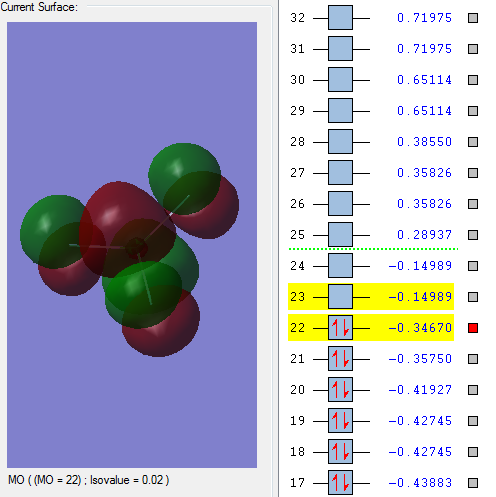
Molecular orbitals:
This molecular orbital is a non-bonding orbital which is the deepest in energy. It is comprised of the 1s orbital from the chlorine atom. It is occupied, but has no effect on the bonding of the molecule.
This is the first bonding molecular orbital. The orbitals which make it up are s orbitals from the chlorine and fluorine molecules. It has a higher energy than the two non-bonding orbitals previously seen. This orbital is occupied by valence electrons but doesn't have a large effect on bonding.
This is a bonding orbital made from a chlorine s orbital and fluorine p orbitals. It is occupied.
This is a bonding orbital which is formed from a p orbital on the chlorine and a p orbital on each of the fluorine atoms. It is a pi orbital which is quite high in energy.
This is the HOMO orbital for this molecule. It is comprised of one p orbital from each of the fluorine atoms and a p orbital from the chlorine atom. It is an anti-bonding orbital and is a pi orbital. The orbital has a large effect on bonding.