Rep:Mod:Mx4417
NH3 Molecule
- calculation method: RB3LYP
- the basic set: 6-31G(d,p)
- final energy E(RB3LYP): -56.55776873au
- RMS gradient: 0.00000485au
- the point group : C3V
- bond length:1.01798Å
- bond angle:105.741º
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
test molecule |
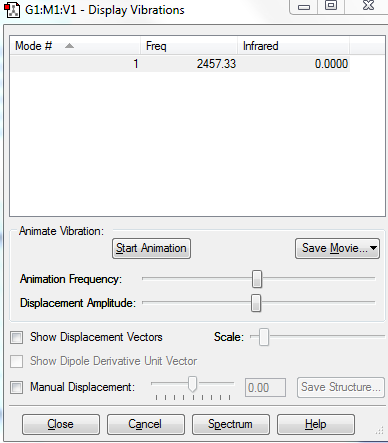
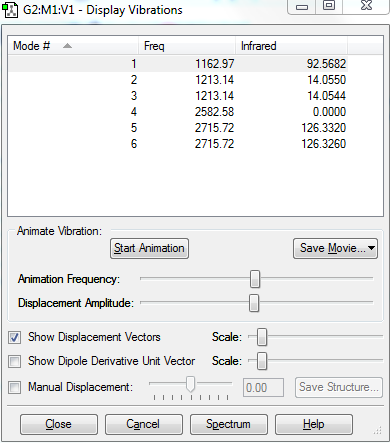
- how many modes do you expect from the 3N-6 rule?: 3
- which modes are degenerate? mode2,3 and mode5,6
- which modes are "bending" vibrations and which are "bond stretch" vibrations? mode456 are stretch, mode 123 are bending.
- which mode is highly symmetric? bond stretch
- one mode is known as the "umbrella" mode, which one is this? mode 1bending
- how many bands would you expect to see in an experimental spectrum of gaseous ammonia? 4
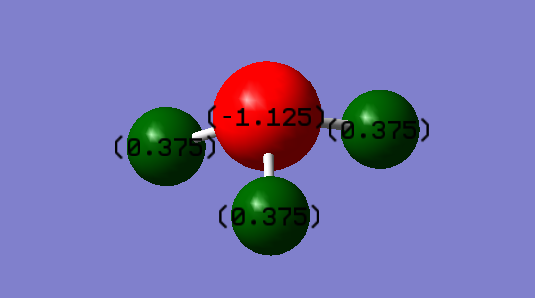 The charge on the N will be partial negative as N is more electronegative than H atom. The H atoms will be partial positive.
The charge on the N will be partial negative as N is more electronegative than H atom. The H atoms will be partial positive.
N2 Molecule
- calculation method: RB3LYP
- the basic set: 6-31G(d,p)
- final energy E(RB3LYP): -109.52359111au
- RMS gradient: 0.02473091au
- the point group : D∞h
- bond length:1.0550Å
- bond angle:180º
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-3.401071D-13
test molecule |
The charge on each N atom is 0, as it is a linear diatomic molecule.
H2 molecule
- calculation method: RB3LYP
- the basic set: 6-31G(d,p)
- final energy E(RB3LYP): -1.17853936au
- RMS gradient: 0.00000017au
- the point group : D∞h
- bond length:0.74279Å
- bond angle:180º
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-1.164080D-13
test molecule |
The charge on each H atom is 0, as it is a linear diatomic molecule.
Reaction energy of of N2 + 3H2 -> 2NH3
- E(NH3)=-56.55776873au
- 2*E(NH3)=-113.115537au
- E(H2)=-1.17853936au
- E(N2)=-109.52412868au
- 3*E(H2)=3.53561808au
- ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]=-0.0557907au==-146.48 KJ/mol
The ΔE energy was negative, so the ammonia product has lower energy and is more stable.
BH3 molecule
- calculation method: RB3LYP
- the basic set: 6-31G(d,p)
- final energy E(RB3LYP): -26.61532364au
- RMS gradient: 0.00000211au
- the point group : D3h
- bond length:1.19232Å
- bond angle:120º
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000003 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000017 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000011 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-1.053675D-10
test molecule |
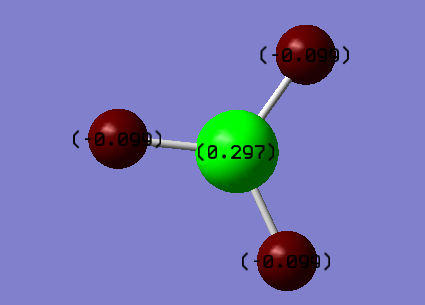 Boron was more electropositive than H atom.
Boron was more electropositive than H atom.
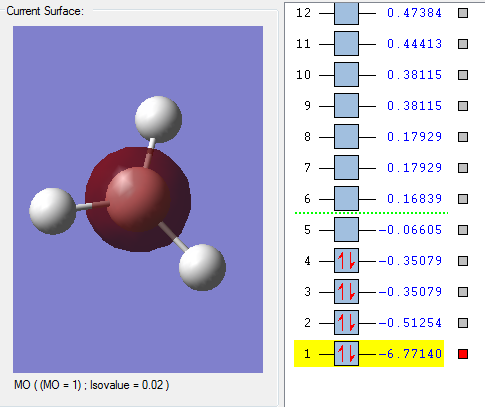
MOs of BH3
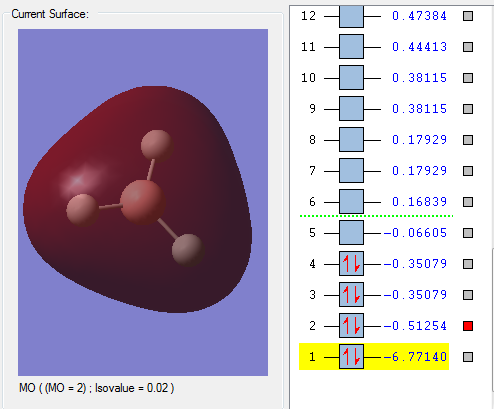
MO1 The red shaded region is the occupied, non-bonding 1s AO of Boron, since electrons in the hydrogen atom doesn't contribute anything It has very deep in energy(-6.77140au) compare to other since 1s orbital is in the core AOs.
MO2
The red region is the MO that is occupied, overlapped by three 1s AOs of H atoms and one 2s AO of B atom.
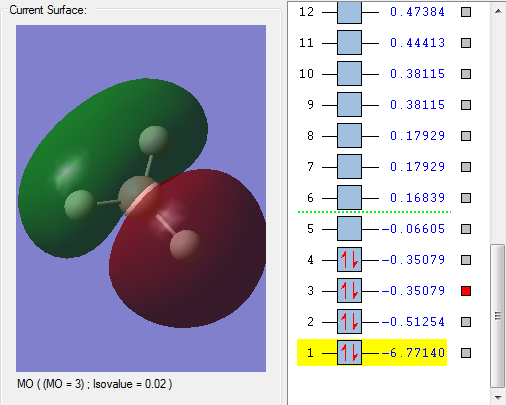
MO3
This occupied MO
The 2PX AO overlapped with part of the 1s and 2s the third H atom in phase. The 2PX AO overlapped with part of the 1s and 2s the second H atom out of phase.
MO3 is in the HOMO region as it has the one of the highest energy within all the occupied orbitals as shown on the picture.
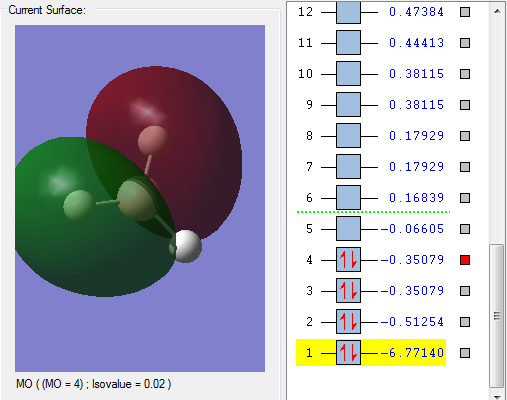
MO4
This MO has the same energy value with MO3 so it is the same type of MO just different 2P N atom, which is 2PY AO of the B atom.
The red part forms from overlapping 1s and 2s AOs with the first H atom in phase. The green part forms from overlapping the 1s and 2s AOs of the second and the third H atoms.
MO4 is in the HOMO region as it has the one of the highest energy within all the occupied orbitals as shown on the picture.
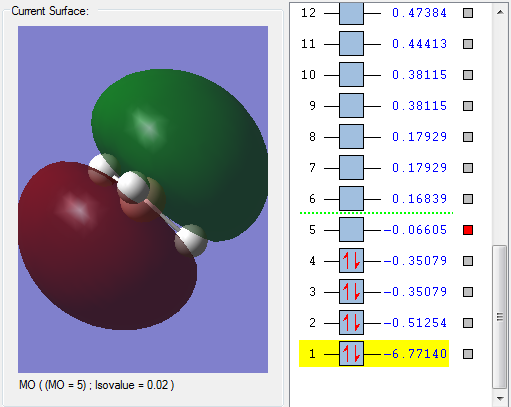
MO5
This MO is unoccupied and is in the LUMO region.
It is a combination of 2PZ and 3PY AOs of the B atom overlap with 3PZ AOs of three H atoms.