Rep:Mod:MSS3117IL
Revision
BH3
Basis Set: 6-31G(d,p)
Method: RB3LYP
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000003 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000017 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000011 0.001200 YES
DOI:https://wiki.ch.ic.ac.uk/wiki/images/a/af/MSS_BH_FREQUENCY_621G_DP.LOG
Low frequencies --- -0.7437 -0.4573 -0.0054 10.8204 14.8992 14.9177 Low frequencies --- 1163.0234 1213.2008 1213.2035
test molecule |
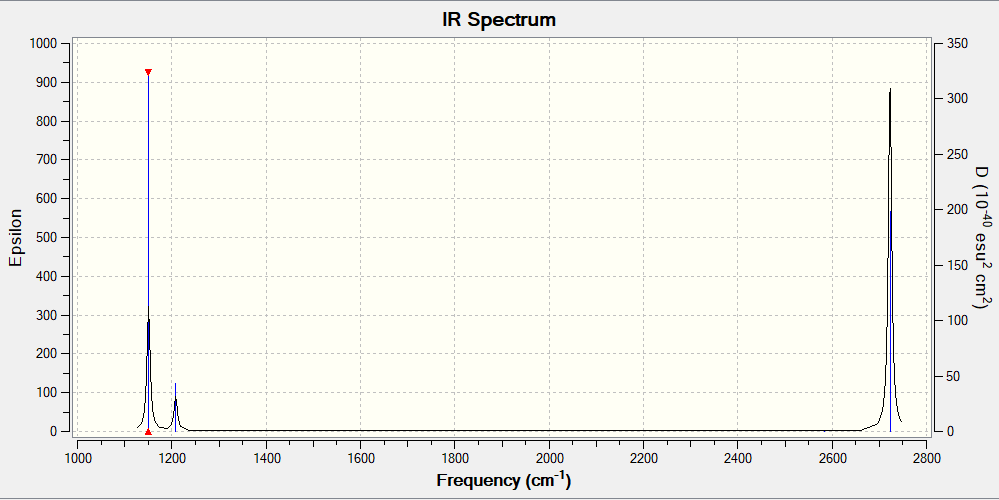
| Mode Number | Intensity (Arbitrary Units) | Frequency (cm-1) | Symmetry | IR Active> | Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 93 | 1163 | A2' | Yes | Out of Plane Bend |
| 2 | 14 | 1213 | E' | No | Bend |
| 3 | 14 | 1213 | E' | No | Bend |
| 4 | 0 | 2582 | A' | Yes | Symmetric Stretch |
| 5 | 126 | 2715 | E | Yes | Asymmetric Stretch |
| 6 | 126 | 2715 | E | Yes | Asymmetric Stretch |
BH3 IR Spectrum
The IR Spectrum shows only three peaks although there are six modes. This is because the mode 2 and mode 3 have frequencies very close to one another. This is because they have the same symmetry and so the peaks overlap which in the IR Spectrum is observed as a single peak. This leaves four modes of which one is IR Inactive. Modes 5 and 6 have the same symmetry which in the IR Spectrum is observed as one peak. The remaining first mode is then the third peak in the IR Spectrum.
Well presented and complete vibrational information with consideration given to the accuracy of the reported figures. You've correctly identified the reason for the IR inactive peak not appearing in the spectrum and while you're close with the second reason, the peaks overlap due to degeneracy in terms of the energy and not the symmetry. Smf115 (talk) 20:51, 17 May 2019 (BST)
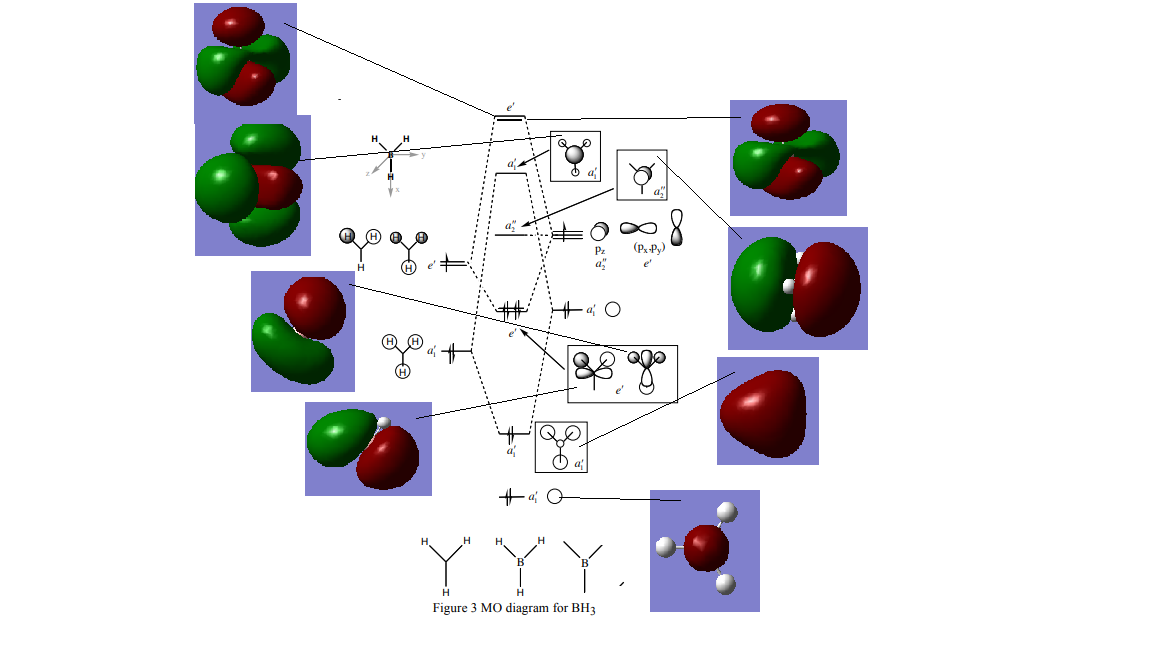
BH3 Molecular Orbital Diagram
Reference: Hunt, P, 2018, Molecular Orbitals Problem Class
The real MOs are generally a good resemblance of the LCAO in the lower energy levels up to 2/3. Above these energy levels it is increasingly hard to interpret the real MOs and consequently generate the LCAOs without doing precise calculation.
Good attempt at including the calculated MOs on to the MO diagram and the majority of them are correct. However, the top e' LCAOs are missing and the real MOs that you've assigned to these are the same MO. To improve, your discussion needed to be a bit more developed and you should consider the differences between the calculated and LCAO MOs. Smf115 (talk) 21:08, 17 May 2019 (BST)
Day 1 New
NH3
Basis Set: 6-31G(d,p)
Method: RB3LYP
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000006 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000012 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000008 0.001200 YES
DOI:https://wiki.ch.ic.ac.uk/wiki/images/7/72/NH3_FREQUENCY.LOG
Low frequencies --- -0.0138 -0.0032 -0.0015 7.0783 8.0932 8.0937 Low frequencies --- 1089.3840 1693.9368 1693.9368
test molecule |
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000164 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000035 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000901 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000342 0.001200 YES
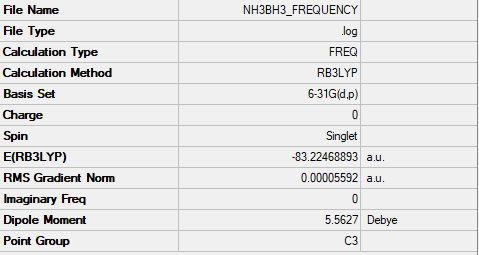
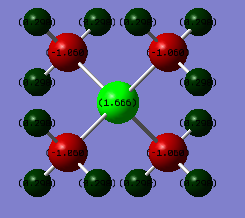
DOI:https://wiki.ch.ic.ac.uk/wiki/index.php?title=File:NH3BH3_FREQUENCY.LOG
Low frequencies --- -19.3099 -0.0315 -0.0057 0.0256 9.2849 9.2934 Low frequencies --- 262.4242 631.2240 637.8386
test molecule |
Determination of Association Energy
E(NH3) = -56.55776873
E(BH3) = -26.61532364
E(BH3E(NH3)) = -83.22468893
dE = -0.0515938 = -135.45 kJ/mol
This number indicates that the N-B bond is very weak.
Using a mixture of basis sets and pseudo potentials Example NI3
Basis Set: 6-31G(d,p)
Method: RB3LYP
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000067 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000017 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000252 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000081 0.001200 YES
DOI:https://wiki.ch.ic.ac.uk/wiki/images/c/c6/MSS_NI3_OPTIMISATION.LOG
Low frequencies --- -12.3847 -12.3783 -5.6131 -0.0040 0.0194 0.0711 Low frequencies --- 100.9307 100.9314 147.2333
test molecule |
The optimised N-I bond length is 2.18 angstrom
Good structure information is given throughout section 1 and correct implementation of the pseudopotential here (although the frequency file should have been submitted, not the optimisation). Smf115 (talk) 21:09, 17 May 2019 (BST)
Project
NMe4
Basis Set: 6-31G(d,p)
Method: RB3LYP
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000068 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000027 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000150 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000067 0.001200 YES
DOI:https://wiki.ch.ic.ac.uk/wiki/images/3/3f/OPTIMISATION_OF_NME4.LOG
Low frequencies --- -0.0005 0.0008 0.0010 22.7103 22.7103 22.7103 Low frequencies --- 189.1567 292.9980 292.9980
test molecule |
PMe4
Basis Set: 6-31G(d,p)
Method: RB3LYP
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000128 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000032 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000666 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000277 0.001200 YES
DOI:https://wiki.ch.ic.ac.uk/wiki/images/c/c6/MSS_NI3_OPTIMISATION.LOG
Low frequencies --- -0.0003 0.0023 0.0026 26.3157 26.3157 26.3157 Low frequencies --- 160.9744 195.4740 195.4740
test molecule |
https://wiki.ch.ic.ac.uk/wiki/images/5/54/PME4_FREQUENCY.LOG
Charge Distribution of PMe4 and NMe4
Charge Distribution for PMe4
Phosphorus: 1.67 Carbon: -1.060 H: 0.298
Carbon has a more negative charge distribution in comparison to phosphourus. This is simply because the phosphorus is less electronegative in comparison to carbon.
Charge Distribution for NMe4
NMe4 adduct adopts a formal positive charge. The formal charge arises due to the presence of a lone pair on the nitrogen. This lone pair is used to make a dative covalent bond with the electron deficient carbon. This specifically occurs by donation of the nitrogen lone pair onto the empty p-orbital on carbon. This results in a positive charge on nitrogen of which is shown by the presence of the four 4 electron domains. However, this positive charge is spread over electropostive atoms in the molecule.
Good attempt but you should have considered how the +1 actually arises from formal electron counting or Lewis Bonding. You also need to be more specific when discussing where the positive charge is actually located. Smf115 (talk) 20:26, 20 May 2019 (BST)
Nitrogen: -0.295 Carbon: -0.483 Hydrogen: 0.269
The nitrogen is seen as having a less negative charge distribution in comparison to the carbon. Where carbon is more electronegative in comparison to hydrogen, each carbon methyl withdraws electron density from three hydrogens. Nitrogen will withdraw electron density from carbon however where we have four carbons, in comparison to a single nitrogen, there is overall more electron density on carbon in comparison to nitrogen.
Correct calculation and good presentation of the NBO charges. To improve, your discussion should be developed further, specifically for [PMe4]+ where the Hydrogen atoms aren't even mentioned, and comparison between the two molecules should have been made. Smf115 (talk) 20:26, 20 May 2019 (BST)