Rep:Mod:MS8017
NH3 Molecule
NH3 Molecule Calculation parameters
Calculations for an ammonia molecule (NH3). Following parameters were used to carry out the optimisation
- Calculation Method = RB3LYP
- Calculation Type = OPT+FREQ
- Basis Set = 6-31G(d,p)
GaussView .log files can be found here
NH3 Molecule results
- E(RB3LYP) = -56.55776873 a.u.
- RMS Gradient Norm = 0.00000485 a.u.
- Point Group = C3V
N-H bond length 1.01798 angstroms
H-N-H bond angle 105.741 degrees
The bond length and bond angles are close to experimental numbers. The differences are due to approximations in the calculation process[1]
NH3 Jmol picture
NH3 Molecule |
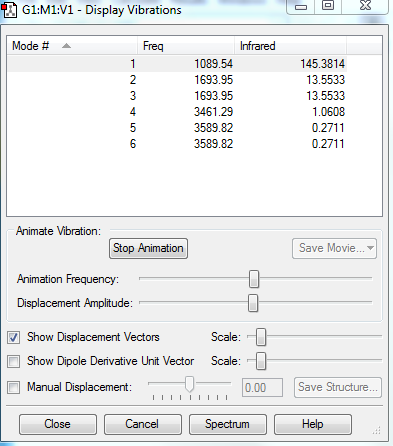
NH3 Vibrations
6 Vibrational modes were expected according to the 3n-6 rule (4 atoms).
4 vibrational modes were found to be degenerate (2 bending modes and 2 stretching modes).
Bending modes are numbere 1,2 and 3. Stretching modes are numbered 4,5 and 6.
The modes with highest symmetries were 1 (bending) and 4 (stretching). Hydrogen atoms in these cases were performing the same motion relative to the nitrogen atom.
The vibrational mode designated as 1 is the "umbrella" mode as it is mimicking the folding and unfolding of an umbrella.
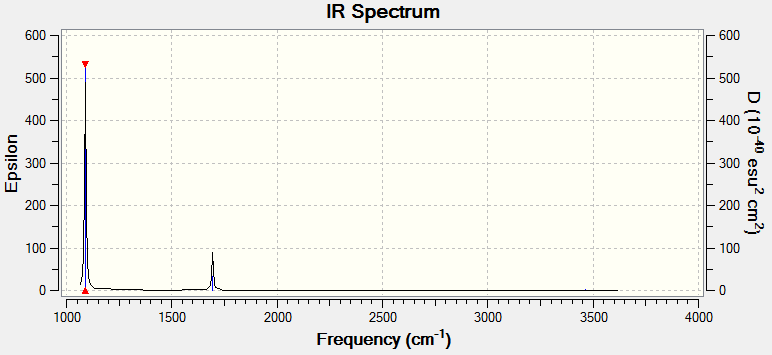
4 IR active vibrational modes are present, however only 2 are distinguishable in an experimental measurements. Modes 4,5 and 6 would be indistinguishable form noise
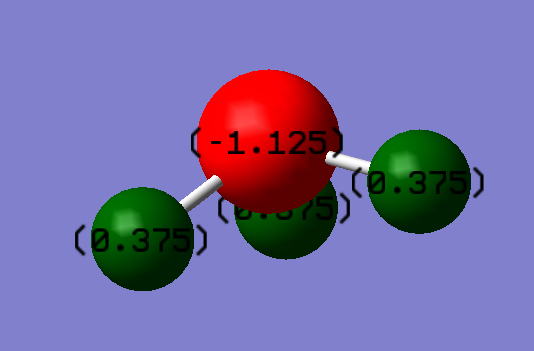
NH3 Charge distribution
Nitrogen is known to have higher electronegativity compared to hydrogen therefore we expect to see more electrons on the nitrogen atom. A negative number higher in magnitude is expected on the nitrogen atom compared to the hydrogen atoms.
Haber-Bosch process

- E(NH3)=-56.55776873 a.u.
- 2*E(NH3)=-113.11553746 a.u.
- E(N2)=-109.52412868 a.u.
- E(H2)=-1.17853936 a.u.
- 3*E(H2)=-3.53561808 a.u.
- ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]=-0.0557907 a.u. = -146.45 kJ.mol-1
This reaction tells us that the ammonia gas is more stable as thermodynamically it is an exothermic reaction. This number is however different from measured values. This is due to it being a calculated value using approximations and not an empirically measured value.
Molecule of choice PH5
- Charge = 0
- E(RB3LYP) = -344.25491049 a.u.
- RMS Gradient Norm = 0.00000471 a.u.
- Dipole Moment = 0.0000 Debye
- Point Group = D3H
GaussView .log file cna be found here
PH5 Molecule |
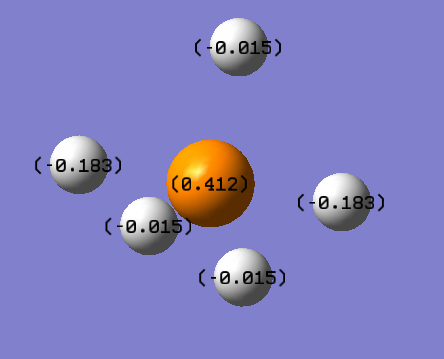
Charge Distribution on PH5
The values obtained form GaussView (their signs) are same as expected. Hydrogen should have a negative charge as it is more electronegative in comparison to phosphorus. As observed there is a discrepancy between the charge on the axial hydrogen copared to equatoreal charge. This is due to Jahn Teller distortion [2] and it can also be observed in bond lengths. H (axial) = 1.496Å and H (equatoreal) = 1.433Å
- P = 0.412e
- H (axial) = -0.183
- H (equatoreal) = -0.015
Vibrations within PH5
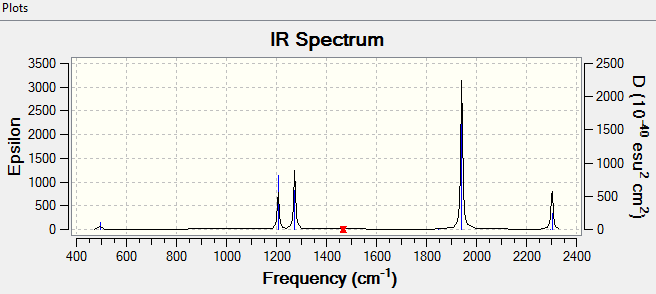
PH5 is not a linear molecule so we expect it to have 12 vibrational modes (3N-6).
File:MS8017 PH5 VIB.PNGthumb
4 vibrations (No. 6,7,8 and 10) do not produce any peaks in the IR spectra as they have no change in the dipole moment. These vibrations are highly symmetrical.
Multiple degenerate vibrational modes are present (No. 1 and 2, 4 and 5, 6 and 7, 11 and 12).
Only 4 peaks would be observed as multiple of these peaks are degenerate and some vibraitons are not IR active (No change in dipole)
PH5 Molecular orbitals
Orbitals 1-5 are non bonding that are found in the "core" level of this molecule. The bonding/anti bonding orbitals for this molecule are found in the HOMO/LUMO region
Optimisation, Log Files, Results
NH3
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-5.986279D-10
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R2 R(1,3) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R3 R(1,4) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A1 A(2,1,3) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(2,1,4) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(3,1,4) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(2,1,4,3) -111.8571 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
nh3 optimisation File Name = MS8017_NH3_OPTFRQ File Type = .log Calculation Type = FREQ Calculation Method = RB3LYP Basis Set = 6-31G(d,p) Charge = 0 Spin = Singlet E(RB3LYP) = -56.55776873 a.u. RMS Gradient Norm = 0.00000485 a.u. Imaginary Freq = 0 Dipole Moment = 1.8466 Debye Point Group = C3V
N2 Optimization
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-3.401057D-13
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.1055 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
N2 optimization File Name = MS8017_N2_OPTFRQ File Type = .log Calculation Type = FREQ Calculation Method = RB3LYP Basis Set = 6-31G(d,p) Charge = 0 Spin = Singlet E(RB3LYP) = -109.52412868 a.u. RMS Gradient Norm = 0.00000060 a.u. Imaginary Freq = 0 Dipole Moment = 0.0000 Debye Point Group = D*H
H2 Optimization
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.164080D-13
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 0.7428 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
H2 optimisation File Name = MS8017_H2_OPTFRQ File Type = .log Calculation Type = FREQ Calculation Method = RB3LYP Basis Set = 6-31G(d,p) Charge = 0 Spin = Singlet E(RB3LYP) = -1.17853936 a.u. RMS Gradient Norm = 0.00000017 a.u. Imaginary Freq = 0 Dipole Moment = 0.0000 Debye Point Group = D*H
PH5 Optimisation
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000009 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000055 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000022 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.032823D-09
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.4332 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R2 R(1,3) 1.4869 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R3 R(1,4) 1.4869 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R4 R(1,5) 1.4332 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R5 R(1,6) 1.4332 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A1 A(2,1,3) 90.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(2,1,4) 90.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(2,1,5) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A4 A(2,1,6) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A5 A(3,1,5) 90.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A6 A(3,1,6) 90.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A7 A(4,1,5) 90.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A8 A(4,1,6) 90.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A9 A(5,1,6) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A10 L(3,1,4,2,-1) 180.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A11 L(3,1,4,2,-2) 180.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(2,1,5,3) 90.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D2 D(2,1,6,3) -90.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D3 D(2,1,5,4) -90.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D4 D(2,1,6,4) 90.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D5 D(2,1,6,5) 180.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D6 D(3,1,6,5) -90.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D7 D(4,1,6,5) 90.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
PH5 optimisation File Name = MS8017_PH5_OPTFRQ File Type = .log Calculation Type = FREQ Calculation Method = RB3LYP Basis Set = 6-31G(d,p) Charge = 0 Spin = Singlet E(RB3LYP) = -344.25491049 a.u. RMS Gradient Norm = 0.00000471 a.u. Imaginary Freq = Dipole Moment = 0.0000 Debye Point Group = D3H
References
<references> [2]
[1] </refrences>
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 NIST Computational Chemistry Comparison and Benchmark Database , NIST Standard Reference Database Number 101, Release 18, October 2016, Editor: Russell D. Johnson III , https://cccbdb.nist.gov/exp2x.asp?casno=7664417
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Jahn, H.A., Teller, E. (1937). "Stability of polyatomic molecules in degenerate electronic states - I—Orbital degeneracy". Proc. R. Soc. A. 161 (A905): 220–235. DOI: 10.1098/rspa.1937.0142