Rep:Mod:MLW115
NH3 Molecule.
I have created and optimised NH3 this is the analysis of the molecule.
Analysis
| Molecule | NH3 |
| Calculation method | RB3LYP |
| Basis set | 6-31G(d.p) |
| Final energy | -56.55776835 a.u |
| RMS gradient | 0.00019033 a.u |
| Point Group | C3v |
| Bond length | 1.01756 Å |
| Bond angle | 105.782° |
Item Table
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000301 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000198 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.001000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000471 0.001200 YES
NH3 Image
NH3 |
The optimisation file is linked to here
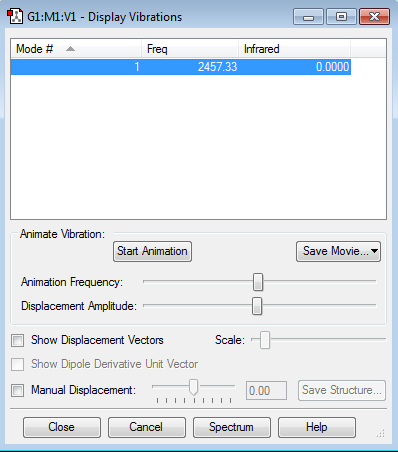
Molecular Vibrations
I have analysed the vibrational modes.
Number of modes expected: 6 Degenerate modes: 2,3 and 5,6 are degenerate. Bending vibrations:2,3 Stretching vibrations:1,4,5,6 Symmetric mode:1,4 Umbrella mode:1 Bands expected:2
Charges
I looked at the charges on each atom.
Charge on N atom: -1.125 a.u
Charge on H atom: 0.375 a.u
N2 Molecule
Analysis and optimisation of the N2 molecule.
The optimisation file is linked to here
Analysis
| Molecule | N2 |
| Calculation method | RB3LYP |
| Basis set | 6-31G(d.p) |
| Final energy | -109.52412868 a.u |
| RMS gradient | 0.00000060 a.u |
| Point Group | D∞h |
| Bond length | 1.10550 Å |
| Bond angle | 180° |
Item Table
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
Molecular Vibrations
Charges
Because the atoms in the molecule are both the same there is no charge.
H2 Molecule
Analysis and optimisation of the H2 molecule.
The optimisation file is linked to here
Analysis
| Molecule | H2 |
| Calculation method | RB3LYP |
| Basis set | 6-31G(d.p) |
| Final energy | -1.17853936 a.u |
| RMS gradient | 0.00000017 a.u |
| Point Group | D∞h |
| Bond length | 0.74279 Å |
| Bond angle | 180° |
Item Table
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES
Molecular Vibrations
Charges
Because the atoms in the molecule are both the same there is no charge.
Energy Calculation
Here I calculate the energy change for this reaction:
N2 + 3H2 -> 2NH3
E(NH3)= -56.55776835 a.u 2*E(NH3)= -113.1155367 a.u E(N2)= -109.52412868 a.u E(H2)= -1.17853936 a.u 3*E(H2)= -3.53561808 a.u ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]= -0.05578994 a.u ΔE=-146.476 kJ/mol The product is more stable than the gaseous reactants.
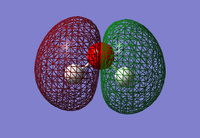
Molecular Orbitals
Here I look at the molecular orbitals in the N2 molecule.
 |
 |
H2O Molecule Analysis
Optimisation and analysis of the H2O molecule.
The optimisation file is linked to here
Analysis
| Molecule | H2O |
| Calculation method | RB3LYP |
| Basis set | 6-31G(d.p) |
| Final energy | -76.41973740 a.u |
| RMS gradient | 0.00006276 a.u |
| Point Group | C2V |
| Bond length | 0.96522 Å |
| Bond angle | 103.745° |
Item Table
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000099 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000081 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000115 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000120 0.001200 YES
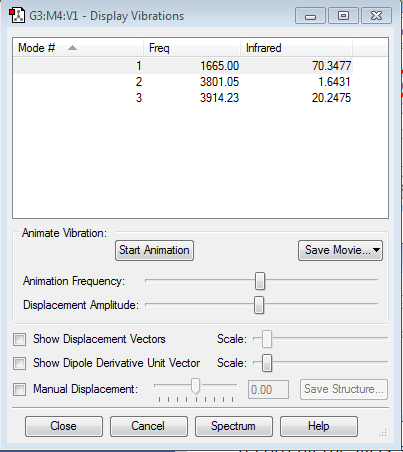
Molecular Vibrations
| 1 | Bend |
| 2 | Symmetric stretch |
| 3 | Asymmetric stretch |
Charges
Here I look at the charge distribution in the water molecule.
Charge on hydrogen: 0.472
Charge on oxygen atom: -0.944
This shows that water is polar because the oxygen is electronegative. The oxygen is partially negative and the hydrogen is partially positive. Overall the charges balance and the molecule is neutral.
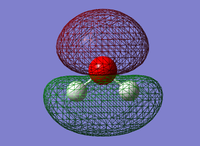
Molecular Orbitals
Here I look at the molecular orbitals of the H2O.