Rep:Mod:LWH0802
Project title
In this wiki page different molecules were analysed on their energies and other properties by using Gaussview
NH3 Molecule
Key Information
- Molecule: NH3
- Calculation Method: RB3LYP
- Basis Set: 6-31G(d.p)
- Final Energy: -56.55776873 au
- RMS gradient: 0.00000485
- Point Group: C3V
- Bond length N-H: 1.01789 Å
- Bond angle H-N-H: 105.741°
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-5.986281D-10
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R2 R(1,3) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R3 R(1,4) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A1 A(2,1,3) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(2,1,4) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(3,1,4) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(2,1,4,3) -111.8571 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
Image of NH3
Ammonia |
The optimized file is linked to here
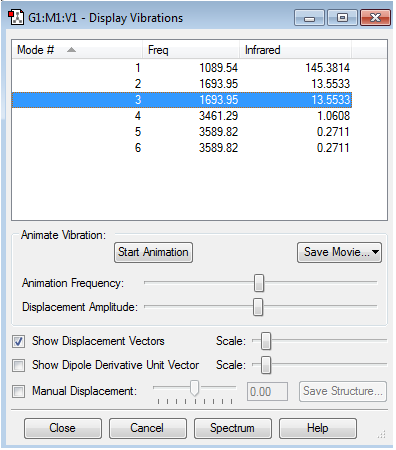
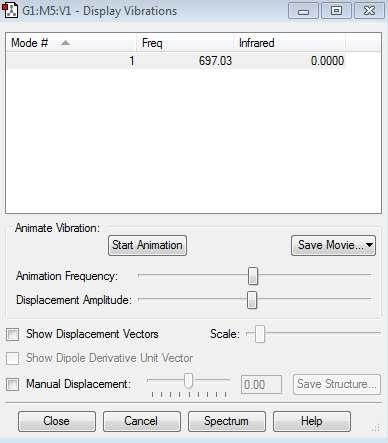
Vibrations
Information about vibrations
- Expected modes from the 3N-6 rule are 6 which corresponds to the obtained information
- The modes 2 and 3 are degenrate and the modes 5 and 6 are degenerate
- Modes 1, 2 and 3 are bending vibrations while modes 4, 5 and 6 are stretching vibrations
- Mode 4 is highly symmetric
- Mode 1 is known as the umbrella mode as it resembles the opening and closing of an umbrella
- You would expect to see 2 bands as the change in dipole moment is very small for the other 2 bands so they won't be seen in the spectra.
Charge Analysis
The charge of the N atom in the molecules is -1.125 and the charge of each H atom in the molecule is 0.375. These charges correspond in sign with what you would expect as N is more electronegative than H thus be partially more negative. The numbers make sense as well, because the overall charge added up is equal to 0.
N2 Molecule
Key Information
- Molecule: N2
- Calculation Method: RB3LYP
- Basis Set: 6-31G(d.p)
- Final Energy: -109.52412868 au
- RMS gradient: 0.00000060
- Point Group: D∞h
- Bond length N-N: 1.10550 Å
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-3.400956D-13
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.1055 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Image of N2
N-N |
The optimized file is linked to here
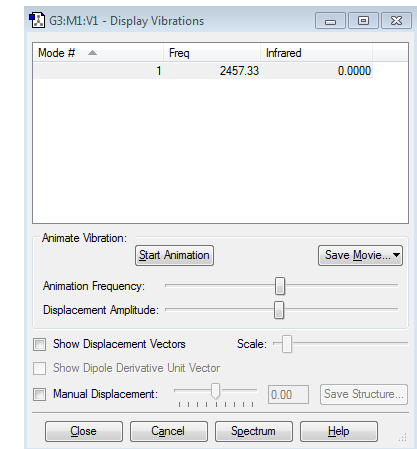
Vibrations
Information about vibrations
- Expected modes from the 3N-5 rule are 1 which corresponds to the obtained information
- Only one mode
- Mode 1 is a stretching mode
- Mode 1 is symmetric
- You would expect to see no band, because there is no change in dipole moment
Charge Analysis
Because both nuclei are the same there is no charge distribution, as there is no change in electronegativity.
H2 Molecule
Key Information
- Molecule: H2
- Calculation Method: RB3LYP
- Basis Set: 6-31G(d.p)
- Final Energy: -1.178539360 au
- RMS gradient: 0.00000017
- Point Group: D∞h
- Bond length H-H: 0.74279 Å
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.164080D-13
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 0.7428 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Image of H2
H-H |
The optimized file is linked to here
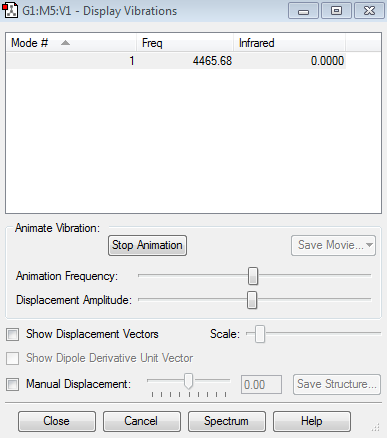
Vibrations
Information about vibrations
- Expected modes from the 3N-5 rule are 1 which corresponds to the obtained information
- Only one mode
- Mode 1 is a stretching mode
- Mode 1 is symmetric
- You would expect to see no band, because there is no change in dipole moment
Charge Analysis
Because both nuclei are the same there is no charge distribution, as there is no change in electronegativity.
Haber-Bosch Process
The reaction
N2 + 3H2 -> 2NH3
Energies
- E(NH3)=-56.55776873 au
- 2*E(NH3)=-113.1155375
- E(N2)=-109.52412868 au
- E(H2)=-1.178539360 au
- 3*E(H2)=-3.53561808
- ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]=-0.05573074
- ΔE in kJ/mol = -146.4785879 kJ/mol
- The change in energy is negative therefore it is lower energy, which means the ammonia product is more stable
SiH4 Molecule
Key Information
- Molecule: SiH4
- Calculation Method: RB3LYP
- Basis Set: 6-31G(d.p)
- Final Energy: -291.88802760 au
- RMS gradient: 0.00000002
- Point Group: TD
- Bond length N-H: 1.48485 Å
- Bond angle H-Si-H: 109.471°
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-2.453930D-14
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.4849 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R2 R(1,3) 1.4849 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R3 R(1,4) 1.4849 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R4 R(1,5) 1.4849 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A1 A(2,1,3) 109.4712 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(2,1,4) 109.4712 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(2,1,5) 109.4712 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A4 A(3,1,4) 109.4712 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A5 A(3,1,5) 109.4712 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A6 A(4,1,5) 109.4712 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(2,1,4,3) -120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D2 D(2,1,5,3) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D3 D(2,1,5,4) -120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D4 D(3,1,5,4) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Image of SiH4
SiH4 |
The optimized file is linked to here
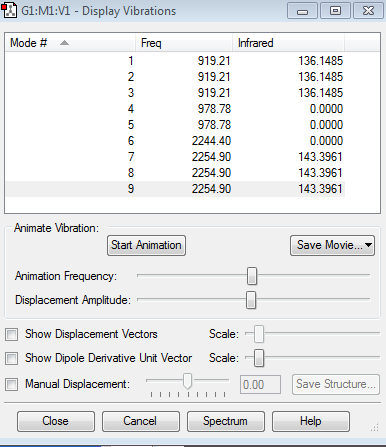
Vibrations
Information about vibrations
- Expected modes from the 3N-6 rule are 9 which corresponds to the obtained information
- The modes 1, 2 and 3 are degenrate, the modes 4 and 5 are degenerate and the modes 7, 8 and 9 are degenerate
- Modes 1 to 5 are bending vibrations while modes 6 to 9 are stretching vibrations
- Mode 6 is highly symmetric
- You would expect to see 2 bands as the change in dipole moment for the other 2 bands is 0 so they won't be seen in the spectra.
Charge Analysis
The charge of the Si atom in the molecules is 0.620 and the charge of each H atom in the molecule is 0.157. These charges correspond in sign with what you would expect as H is more electronegative than Si thus be partially more negative. The numbers make sense as well, because the overall charge added up is equal to 0.
Molecular Orbitals
In this picture one can see the 2p orbital of the Si atom. Because it doesn't overlap with any of the Hydrogen 1s orbitals there is no orbital density near the H atoms, so it is just a plane p orbital. There is no overlap as the 2s is too low in energy to interact with the 1s orbitals of the H atoms. The 2p orbitals are a degenerate set and are all in low energies thus are all occupied.
In this orbital one can see that all atoms are included, here there is overlap as the 3s is high enough in energy to interact with the 1s orbitals of the H atoms. It is a σ-bonding orbital and all H s orbitals are overlapping with the Si 3s orbital an there are no nodes between the bonds. So energies are lower in this orbital than for either 1s orbital of H or 3s orbital of Si. This orbital is occupied.
This is the antibonding orbital corresponding to the 3s-1s overlap. As seen in the picture there is a spherical node between the H atoms and the Si atom. So the energy is higher than the corresponding Atomic orbitals. This orbital is unoccupied.
This is 1 of 3 degenerate bonding orbitals of the overlap between one of the 3p orbitals and the 1s orbitals of the H atoms. As seen in the picture the orbitals are between the H atoms and the Si atom and there is a node going through the middle of it. These bonding orbitals are all the HOMOs as they are in a slightly higher energy than the 3s-1s overlap orbital. The energy of these MOs is still lower in energy than the corresponding AOs.
This is 1 of the 3 degenerate anti-bonding orbital of the overlap between one of the 3p orbitals and the 1s orbitals of the H atoms. As seen in the picture the nodes are between the H atoms and the Si atom, this shows that there are antibonding. They are also the LUMOs as there energy is higher than the bonding 3p-1s molecular orbitals but still lower in energy than the antibonding 3ps-1s molecular orbital.
S2 Molecule (extra)
Key Information
- Molecule: N2
- Calculation Method: RB3LYP
- Basis Set: 6-31G(d.p)
- Final Energy: -796.32599779 au
- RMS gradient: 0.00000372
- Point Group: D∞h
- Bond length N-N:1.92943 Å
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000006 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000006 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000011 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000016 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-7.077701D-11
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.9294 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Image of S2
S-S |
The optimized file is linked to here
Vibrations
Information about vibrations
- Expected modes from the 3N-5 rule are 1 which corresponds to the obtained information
- Only one mode
- Mode 1 is a stretching mode
- Mode 1 is symmetric
- You would expect to see no band, because there is no change in dipole moment
Charge Analysis
Because both nuclei are the same there is no charge distribution, as there is no change in electronegativity.