Rep:Mod:LK27
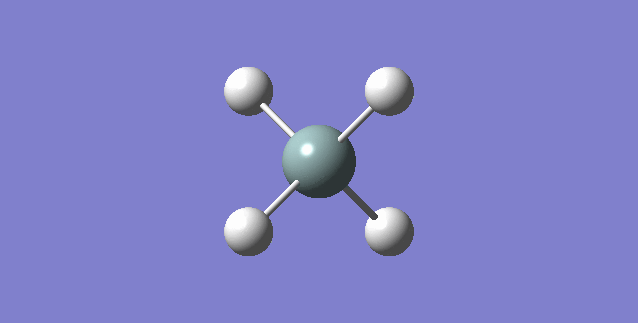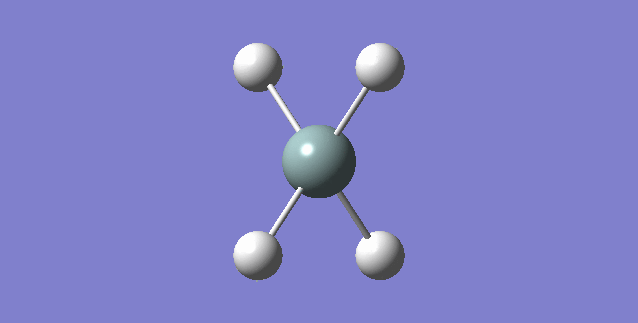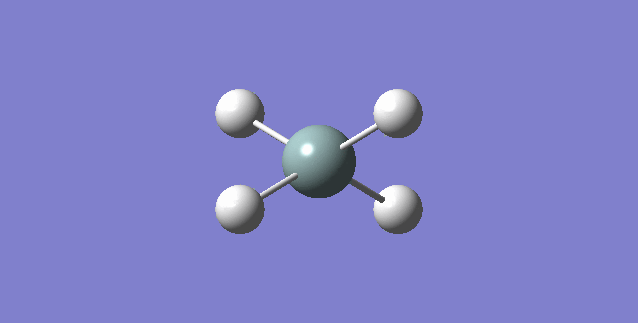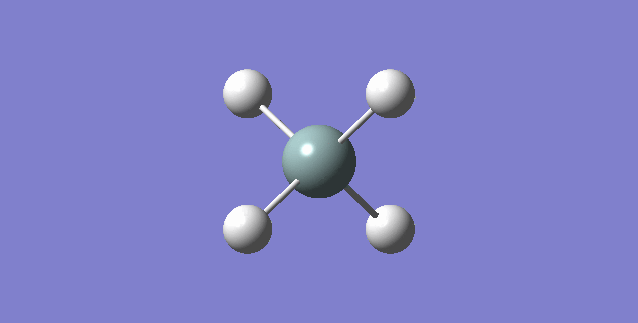
Ammonia
NH3
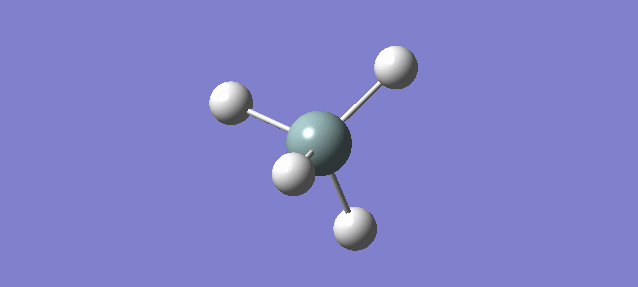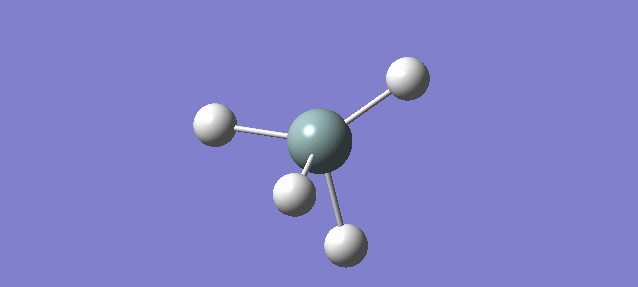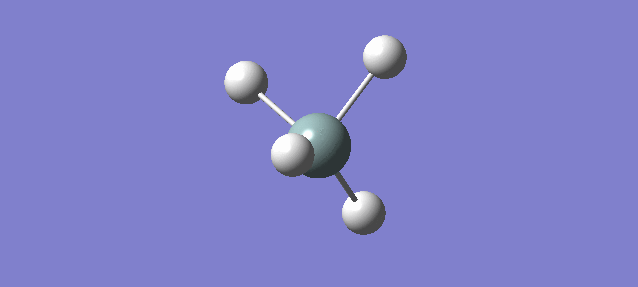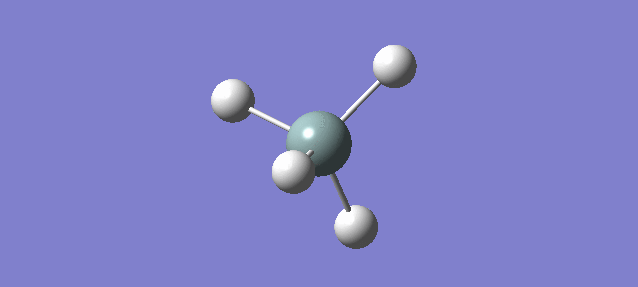
•What is the molecule? NH3 •What is the calculation method? RB3LYP •What is the basis set? 6-31G(d,p) •What is the final energy E(RB3LYP) in atomic units (au)? -56.44397188 au •What is the RMS gradient? 0.05399560 au •What is the point group of your molecule? C3V The N-H bond distance is 1.3 Angstroms and the H-N-H bond angle is 109.471 degrees.
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-5.785197D-10
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R2 R(1,3) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R3 R(1,4) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A1 A(2,1,3) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(2,1,4) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(3,1,4) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(2,1,4,3) -111.8571 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
The Maximum Force on any atom does not exceed 0.00045 au, the average (RMS) force does not exceed 0.0003 au and so the system is in equilibrium (no forces acting on it), and the displacements are converged. Therefore the molecule is optimised.
test molecule |
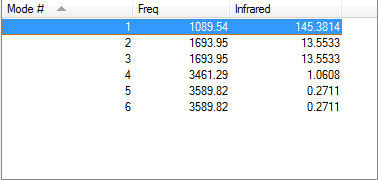
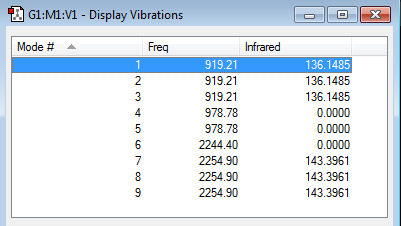
•how many modes do you expect from the 3N-6 rule? (3*4)-6= 6 modes which is what was generated. •which modes are degenerate (ie have the same energy)? The 2nd and 3rd are degenerate, and the 5th and the 6th are degenerate. •which modes are "bending" vibrations and which are "bond stretch" vibrations? 1,2 and 3 are the bending vibrations. 4,5 and 6 are the stretching vibrations. The bending modes have lower frequencies than the stretching modes. •which mode is highly symmetric? The 4th mode. •one mode is known as the "umbrella" mode, which one is this? The 1st mode. •how many bands would you expect to see in an experimental spectrum of gaseous ammonia? 4 bands as there are four different modes (degenerate modes contribute to the same band).
The charge on N is -1.125 and on H is 0.375. Nitrogen is more electronegative than hydrogen so it would be expected that nitrogen would be more negative.
N2
•What is the molecule? N2 •What is the calculation method? RB3LYP •What is the basis set? 6-31G(d,p) •What is the final energy E(RB3LYP) in atomic units (au)? -109.52412868 au •What is the RMS gradient? 0.0000006 au •What is the point group of your molecule? D*H The N-N bond distance is 1.10550 Angstrom.
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-3.383654D-13
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.1055 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
The molecule is optimised.
test molecule |
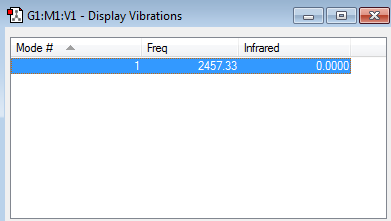
There is only one frequency, 2457.33 wavenumbers, and it is postive. Therefore there are no negative ones.
H2
What is the molecule? H2 What is the calculation method? RB3LYP What is the basis set? 6-31G(d,p) What is the final energy E(RB3LYP) in atomic units (au)? -1.17853936 au What is the RMS gradient? 0.00000017 au What is the point group of your molecule? D*H The H-H bond distance is 0.74279 Angstrom.
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES
----------------------------
Predicted change in Energy=-1.167770D-13
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 0.7428 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
The molecule is optimised.
test molecule |
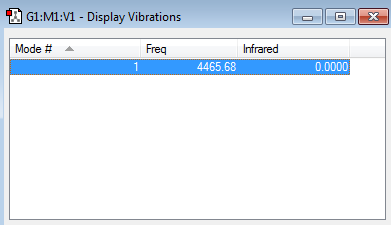
Only one frequency is observed, 4465.68 wavenumbers, and it is positive and so there are no negative ones.
Reactivity: Determining energy for the reaction N2 + 3H2 -> 2NH3
E(NH3)=-56.55776873 au
2*E(NH3)=-113.11553700 au
E(N2)=-109.52412868 au
E(H2)=-1.17853936 au
3*E(H2)=-3.53561808 au
ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]=-0.05579024 au =-0.05579024*2625.5 =-146.48 kJ/mol
Since this is an exothermic reaction, energy is being released and so the ammonia product is lower in energy compared to the gaseous reactants. Thus the product is more stable than the reactants. A literature value for the enthalpy of formation of ammonia is -45.90 kJ/mol. This differs dueto the assumptions made in calculating the theoretical value compared to the experimental.[1]
Silane
SiH4
What is the molecule? SiH4
What is the calculation method? RB3LYP
What is the basis set? 6-31G(d,p)
What is the final energy E(RB3LYP) in atomic units (au)? -291.88802549 au
What is the RMS gradient? 0.00023228 au
What is the point group of your molecule? Td
The Si-H bond distance is 1.48485 Angstrom and the H-Si-H bond angle is 109.471 degrees.
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-2.412805D-14
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.4849 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R2 R(1,3) 1.4849 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R3 R(1,4) 1.4849 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R4 R(1,5) 1.4849 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A1 A(2,1,3) 109.4712 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(2,1,4) 109.4712 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(2,1,5) 109.4712 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A4 A(3,1,4) 109.4712 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A5 A(3,1,5) 109.4712 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A6 A(4,1,5) 109.4712 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(2,1,4,3) -120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D2 D(2,1,5,3) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D3 D(2,1,5,4) -120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D4 D(3,1,5,4) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
The molecule is optimised.
test molecule |
how many modes do you expect from the 3N-6 rule? (3*5)-6 = 9
which modes are degenerate (ie have the same energy)? 1,2,3 are degenerate, 4 and 5 are degenerate and 7,8,9 are degenerate.
which modes are "bending" vibrations and which are "bond stretch" vibrations? 1,2,3,4,5 are bends and 6,7,8,9 are stretches.
which mode is highly symmetric? 4,5,6 as there is no change in dipole moment and so they have zero IR absorbance.
how many bands would you expect to see in an experimental spectrum of gaseous silane? Two bands
An example of a bend contributing to the first peak in the IR spectra:
An example of a bend with zero absorbance in IR:
An example of a stretch contributing to the second peak in the IR spectra:
The charge on Si is +0.629 and hydrogen is -0.157. Hydrogen is more electronegative than silicon and so as expected, hydrogen is negatively charged and silicon is positively charged.
Molecular Orbitals
Silicon has 14 electrons and bonds to four hydrogen's which have one electron. Silicon contributes four and each hydrogen contributes one electron to the molecular orbitals. Four sigma bonds are produced as a result with filled 3p orbitals.

The first orbital is the core 1s orbital of silicon which is not involved in bonding as it is much lower in energy than the rest of the orbitals with an energy of -66.12596 au.
This shows silicon's non-bonding core 2s atomic orbital with a fairly low energy of -5.28056 au. 
 This is one of silicon's three degenerate non-bonding core 2p atomic orbitalss (2px, 2py, 2pz).
This is one of silicon's three degenerate non-bonding core 2p atomic orbitalss (2px, 2py, 2pz).
This is silicon's non-bonding valence 3s AO. It is higher in energy than the previous orbitals. 
 This is one of the three degenerate valence 3p bonding molecular orbitals. It is comprised of two silicon electrons and four hydrogen electrons. These are the highest energy molecular orbitals at -0.35184 au. It is also the HOMO.
This is one of the three degenerate valence 3p bonding molecular orbitals. It is comprised of two silicon electrons and four hydrogen electrons. These are the highest energy molecular orbitals at -0.35184 au. It is also the HOMO.
A drawback of using GaussView is that is doesn't consider hybridisation. SiH4 actually forms four identical bonds which is possible due to sp3 hybridisation between hydrogen's singly occupied 1s orbital and silicon's valence electrons (the promotion of a 3s electron to the 3p orbital so there are now four unpaired electrons). This would show four sp3 AOs with s and p character in the ratio 1:3 respectively, that would form four MOs with hydrogen's 1s.
 This is the unoccupied sigma* antibonding orbital. It is much higher in energy with a positive value of 0.05053 au.It is also the LUMO.
This is the unoccupied sigma* antibonding orbital. It is much higher in energy with a positive value of 0.05053 au.It is also the LUMO.
Reactivity: Determining energy for the reaction SiH4(g) + 2O2(g) -> SiO2(s) + 2H2O(g)
O2
test molecule |
SiO2
test molecule |
H2O
test molecule |
E(SiH4)=-291.88802760 au 2*E(O2)=2*-150.25742434 au = -300.51484870 E(SiO2)=-439.92811459 au 2*E(H2O)=2*-76.41973740 au = -152.83947480 ΔE=[E(SiO2)+2*E(H2O)]-[E(SiH4)+2*E(O2)]= -0.36471309 au =-0.36471309*2625.5 =-957.55 kJ/mol
This is an exothermic value as expected for a combustion reaction. This implies that the products are more stable than the reactants as the products are of a lower energy due to the release of energy. There may be discrepancies with this calculated value. For example, SiO2 forms crystalline structures and here it has been assumed as a simple molecular structure as it is not possible to create such a complicated structure in Gaussian.