Rep:Mod:KK4717
Summary of Nh3, H2 and N2 molecules
| Molecule | NH3 | H2 | N2 | H2S | BH3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP | RB3LYP | RB3LYP | RB3LYP | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) | 6-31G(d,p) | 6-31G(d,p) | 6-31G(d,p) | 6-31G(d,p) |
| E(RB3LYP) (a.u.) | -56.55776873 | -1.17853936 | -109.52412868 | -399.39162414 | -26.61532364 |
| RMS Gradient (a.u.) | 0.00000485 | 0.00000017 | 0.00000060 | 0.00012068 | 0.00000211 |
| Point Group | C3V | D*H | D*H | C2V | D3H |
| Bond lenght (pm) | 101.798 | 74.279 | 110.550 | 134.737 | 119.232 |
| Bond angle (°) | 105.741 | 180 | 180 | 92.681 | 120 |
NH3
NH3 |
| Mode | Frequency | Infrared |
|---|---|---|
| Bend 1 | 1089.54 | 145.3814 |
| Bend 2 | 1693.95 | 13.5545 |
| Bend 3 | 1693.95 | 13.5545 |
| Stretch 1 | 3461.29 | 1.0608 |
| Stretch 2 | 3589.82 | 0.2711 |
| Stretch 3 | 3589.82 | 0.2711 |
•Expected nodes in NH3 molecule from 3N-6 rule is 6.
•Stretch 2&3 and Bend 2&3 are degenerate.
•Bend 1 is called the "umbrella" mode and Stretch 1 is highly symmetric.
•In the experimental spectrum of NH3(g) only 2 bands are seen: 1) "Umbrella" Bend; 2) degenerate Bend 2&3. Stretches give too low peaks to be recognised from the noise.
NH3 Charges
It is expected that H in ammonia have a positive and N has a negative charge because N atom has a much larger electronegativity.
| Molecule | NH3 | Electronegativity |
|---|---|---|
| H Charge | 0.375 | 2.1 |
| N Charge | -1.125 | 3.0 |
| Overall Charge | 0 |
H2
H2 |
H2 dipole moment is zero and because its vibrational mode doesn't induce a dipole, it's not seen on IR spectra.
| Mode | Frequency | Infrared |
|---|---|---|
| Stretch 1 | 4465.68 | 0.0000 |
N2
N2 |
N2 dipole moment is zero and because its vibrational mode doesn't induce a dipole, it's not seen on IR spectra.
| Mode | Frequency | Infrared |
|---|---|---|
| Stretch 1 | 2457.33 | 0.0000 |
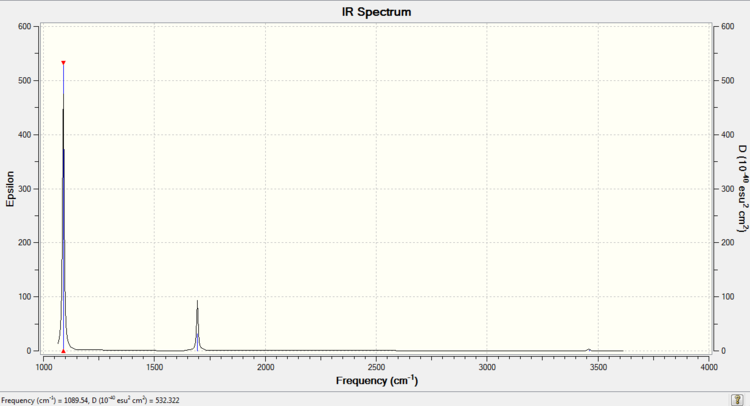
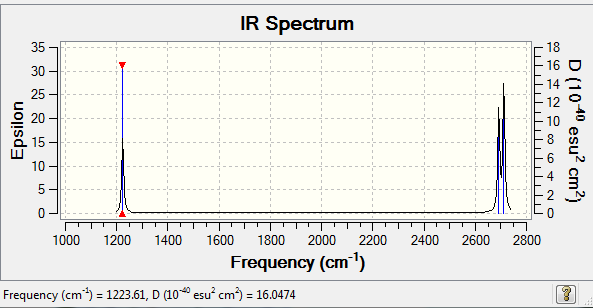
H2S
H2S |
| Mode | Frequency | Infrared |
|---|---|---|
| Bend 1 | 1223.61 | 4.9220 |
| Stretch 1 | 2691.87 | 6.7347 |
| Stretch 2 | 2711.64 | 8.6219 |
•Expected nodes in H2S molecule from 3N-6 rule is 3.
•No modes are degenerate.
•Stretch 1 is highly symmetric.
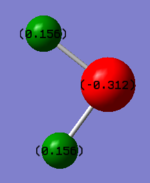
H2S Charges
It is expected that Hydrogen atoms in Hydrogen Sulfide have a positive and Sulphur has a negative charge because S atom has a larger electronegativity than H atoms. Charge on S atom in H2S is smaller however compared to N in NH3 because of the difference in electronegativities (S=2.5 ;N=3) and number of H atoms.
| Molecule | H2S | Electronegativity |
|---|---|---|
| H Charge | 0.156 | 2.1 |
| S Charge | -0.312 | 2.5 |
| Overall Charge | 0 |
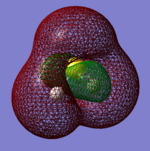
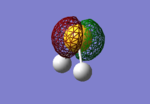
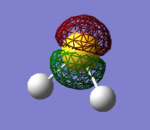
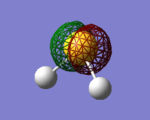
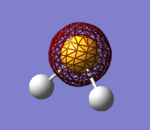
H2S Molecular Orbitals
The first 5 orbitals on S are too small and low in energy to interact with 1s orbitals on Hydrogen atoms.
Bonding orbitals are 6-8 which bond with either H2 bonding (σ) or antibonding (σ*) molecular orbital.
The highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) is 9th MO which is also non-bonding due to no orbital overlap between Sulphur's AO and H2 MO. The lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO) is 10th MO, which is also the first antibonding MO.
Due to fully occupied bonding MOs and not occupied antibonding MOs, H2S is energetically very stable.
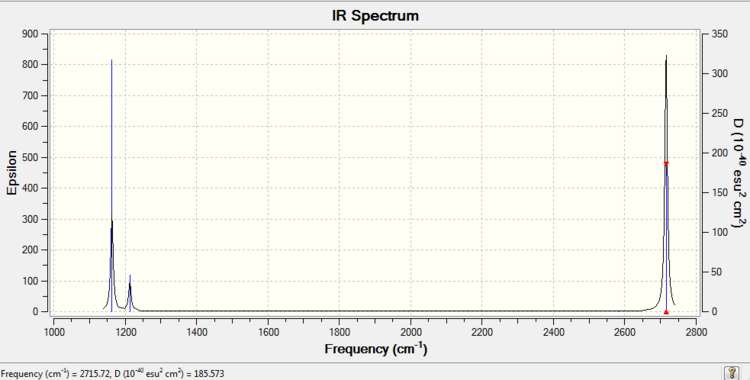
BH3
BH3 |
| Mode | Frequency | Infrared |
|---|---|---|
| Bend 1 | 1162.97 | 92.5682 |
| Bend 2 | 1213.14 | 14.0550 |
| Bend 3 | 1213.14 | 14.0544 |
| Stretch 1 | 2582.58 | 0.0000 |
| Stretch 2 | 2715.72 | 126.3320 |
| Stretch 3 | 2715.72 | 126.3260 |
•Expected nodes in BH3 molecule from 3N-6 rule is 6.
•Stretch 2&3 and Bend 2&3 are degenerate.
•Bend 1 is called the "umbrella" mode.
•Stretch 1 is symmetric, therefore induces no dipole and is not seen on IR spectrum.
•In the experimental spectrum of NH3(g) only 3 bands are seen: 1) "Umbrella" Bend; 2) degenerate Bend 2&3; 3) degenerate Stretch 2&3. Degenerate modes both give one peak and Stretch 1 induces no dipole.
BH3 Charges
It is expected that B atom in BH3 has a positive and H atoms have a negative charge.
| Molecule | BH3 | Electronegativity |
|---|---|---|
| H Charge | -0.099 | 2.1 |
| B Charge | 0.297 | 2.0 |
| Overall Charge | 0 |
Haber-Bosch Reaction energy
| Energy | Value |
|---|---|
| E(NH3) | -56.55776873 a.u. |
| 2*E(NH3) | -113.11553746 a.u. |
| E(N2) | -109.52412868 a.u. |
| E(H2) | -1.17853936 a.u. |
| 3*E(H2) | -3.53561808 a.u. |
| ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)] | -0.0557907 a.u. = -146.48 kJ/mol |
Reaction between H2 and N2 is exothermic, 146.48 kJ/mol of energy is released in the making of NH3.
Item tables
NH3
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
H2
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES
N2
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
H2S
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000175 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000145 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000472 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000386 0.001200 YES
BH3
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000003 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000017 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000011 0.001200 YES