Rep:Mod:Jkt115
NH3
Summary Analysis
Method: RB3LYP
Basis set: 6-31G(d,p)
E(RB3LYP): -56.55776873 au
RMS Gradient: 0.00000485 au
Point Group: C3V
N-H: 1.01798 A
H-N-H: 105.741 degrees
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
Ammonia NH3 |
The optimisation file is linked to here
Frequency Analysis

How many modes do you expect from the 3N-6 rule? (3x4)-6=6
Which modes are degenerate? 2,3 and 5,6
Which modes are "bending" vibrations and which are "bond stretch" vibrations? Bending: 1, 2 and 3 Bond Stretch: 4, 5 and 6
Which modes is highly symmetric? 1 and 4
One mode is known as the "umbrella" mode, which one is this? Mode 1
How many bands would you expect to see in an experimental spectrum of gaseous ammonia? 2 bands because modes 4-6 has an infra-red value that will be too small to be visible.
Charge of N: -1.125
Charge of H: 0.375
I would expect the charge on the nitrogen to be negative and the charge of the hydrogen to be positive. This is because nitrogen is more electronegative than hydrogen, therefore, electron density will be pulled towards the nitrogen nuclei.
N2
Summary Analysis
Method: RB3LYP
Basis set: 6-31G(d,p)
E(RB3LYP): -109.52412868 au
RMS Gradient: 0.00000060 au
Point Group: D∞h
N-N distance: 1.10550 A
N-N angle: 180 degrees
Charge of N: 0 because it is an homonuclear molecule.
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
Nitrogen N2 |
The optimisation file is linked to here
Frequency Analysis

H2
Summary Analysis
Method: RB3LYP
Basis set: 6-31G(d,p)
E(RB3LYP): -1.17853936 au
RMS Gradient: 0.00000017 au
Point Group: D∞h
H-H distance: 0.74279 A
H-H angle: 180 degrees
Charge of H: 0 because it is a homonuclear molecule.
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES
Hydrogen H2 |
The optimisation file is linked to here
Frequency Analysis

Haber-Bosch process
N2 + 3H2 -> 2NH3
E(NH3)= -56.55776873 au
2*E(NH3)= 2*-56.55776873= -113.11553746 au
E(N2)= -109.52412868 au
E(H2)= -1.17853936 au
3*E(H2)= 3*-1.17853936= -3.53561808 au
ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]= -0.0557907 au = -146.48 kJ/mol
The ammonia product is more stable than the gaseous reactants.
H2O
Summary Analysis
Method: RB3LYP
Basis set: 6-31G(d,p)
E(RB3LYP): -76.41973740 au
RMS Gradient: 0.00006276 au
Point Group: C2V
O-H distance: 0.96522 A
H-H angle: 103.745 degrees
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000099 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000081 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000115 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000120 0.001200 YES
Water H2O |
The optimisation file is liked to here
Frequency Analysis

Charge of O: -0.944
Charge of H: 0.472
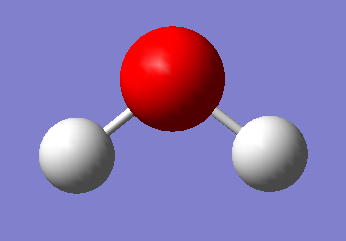





Electrolysis of Water
2H2O -> 2H2 + O2
E(H2O)= -76.41973740 au
2*E(H2O)= 2*-76.41973740= -152.8394748 au
E(H2)= -1.17853936 au
2*E(H2)= 2*-1.17853936= -2.35707872 au
E(O2)= -150.25742434 au
ΔE= [(2*E(H2))+E(O2)]-[2*E(H2O)]= 0.22497174 au = +590.66 kJ/mol
