Rep:Mod:JK2105
Section 2: Introduction to Molecular Dynamics Simulation
Task 1
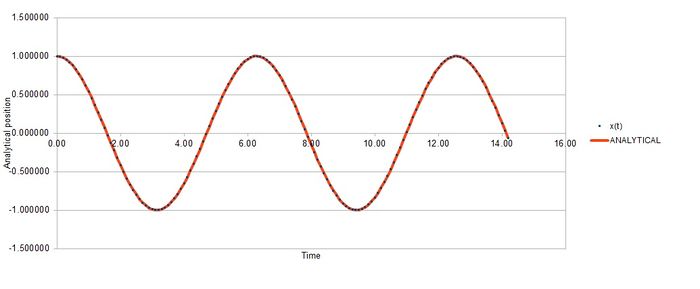
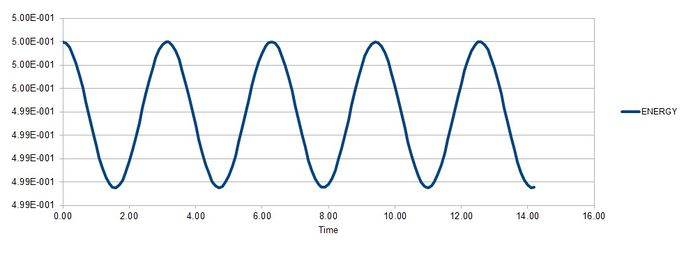
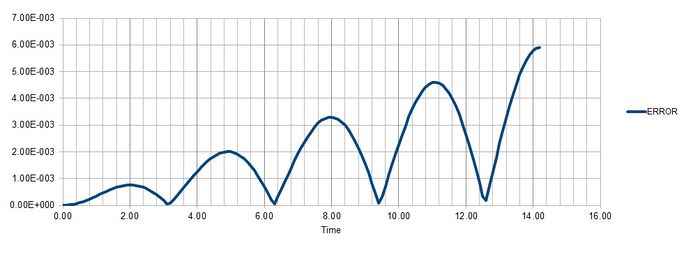
Task 2
Maximum error is found at Time = 2, 4.9, 8, 11.1, 14.2 for timestep 0.1.
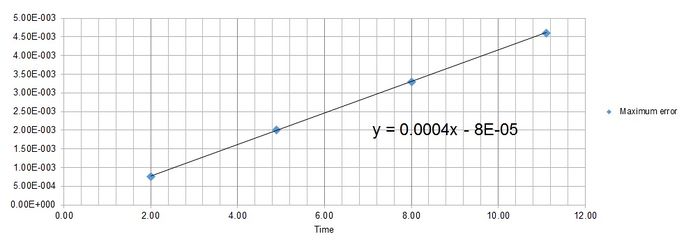
Figure 4 shows the function of the maximum error as where y = error and x = time.
Task 3
The timestep must be less than or equal to 0.2 in order to avoid a change in error greater than 0.005, which is a 1% change. If the energy increases largely, it is an indication that the simulation is incorrect because the total energy of a system experimentally will always want to decrease.
Task 4
Finding the separation, , at which the potential energy is 0:
Assumed that:
If then
Therefore
Next the force was calculated at this separation:
. Substitute to obtain .
Subsequently the equilibrium separation, was calculated:
At equilibrium, .
Assumed that:
And so:
so so
Substitute back into:
To give:
This has shown that is the well depth.
Evaluating the integrals:
Between and :
Between and :
Between and :
Task 5
There is 1 mL of water present, which equals 1 g. First, calculate moles:
Next, multiply by Avogadro's number to calculate the number of molecules present:
The calculation is reversed to find the volume occupied by 10,000 water molecules:
Then to calculate mass:
The simulation clearly models very small volumes.
Task 6
The atom moves to . Taking into account the Periodic Boundary Conditions, this becomes .
Task 7
Calculating the LJ cutoff in real units:
Calculating the well depth, :
Using the Boltzmann Constant:
Calculating the temperature in real units, where :
