Rep:Mod:JG2016
NH3 Molecule
N-H Bond Length = 1.01798 Ångström
Convergence Table and Log
| Item | Value | Threshold | Converged? | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum | Force | 0.000004 | 0.000450 | YES |
| RMS | Force | 0.000004 | 0.000300 | YES |
| Maximum | Displacement | 0.000072 | 0.001800 | YES |
| RMS | Displacement | 0.000035 | 0.001200 | YES |
| Calculation Type | FREQ |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| E(RB3LYP) | -56.55776873 a.u. |
| RMS Gradient Norm | 0.00000485 a.u. |
| Point Group | C3V |
Full Log
Vibrations
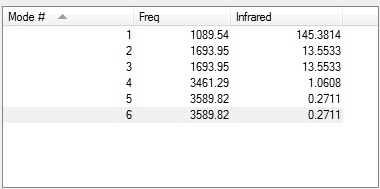
From the 3N-6 Rule, 6 forms of vibrational motion would be expected from a NH3 molecule because it has 4 atoms.
Vibrational modes 2 and 3 are degenerate, aswell as modes 5 and 6 are degenerate.
Vibrational modes 1,2 and 3 are bending vibrations while modes 4,5 and 6 are bond stretch vibrations.
Vibrational mode 4 is highly symmetric.
Vibrational mode 1 is the umbrella mode.
4 bands would be expected in the experimental spectrum of gaseous ammonia.
Charge
The Charge on the nitrogen is -1.125
The Charge on the hydrogen is +0.375
This is expected as nitrogen is more electronegative than hydrogen and so would pull electrons towards it more readily
N2 Molecule
Convergence Table and Log
| Item | Value | Threshold | Converged? | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum | Force | 0.000001 | 0.000450 | YES |
| RMS | Force | 0.000001 | 0.000300 | YES |
| Maximum | Displacement | 0.000000 | 0.001800 | YES |
| RMS | Displacement | 0.000000 | 0.001200 | YES |
| Calculation Type | FREQ |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| E(RB3LYP) | -109.52412868 a.u. |
| RMS Gradient Norm | 0.00000060 a.u. |
| Point Group | D*H |
Full Log
Vibrations
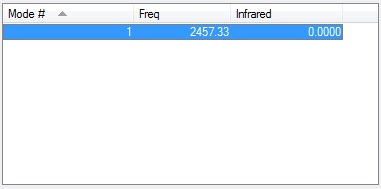
As N2 is a diatomic homonuclear molecule and so the 1 vibration the molecule undergoes will be infrared inactive.
H2 Molecule
Convergence Table and Log
| Item | Value | Threshold | Converged? | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum | Force | 0.000000 | 0.000450 | YES |
| RMS | Force | 0.000000 | 0.000300 | YES |
| Maximum | Displacement | 0.000000 | 0.001800 | YES |
| RMS | Displacement | 0.000001 | 0.001200 | YES |
| Calculation Type | FREQ |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| E(RB3LYP) | -1.17853936 a.u. |
| RMS Gradient Norm | 0.00000017 a.u. |
| Point Group | D*H |
Full Log
Vibrations
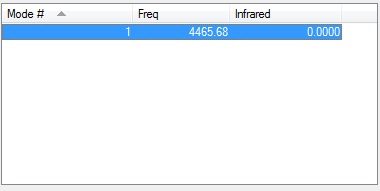
As H2 is a diatomic homonuclear molecule and so the 1 vibration the molecule undergoes will be infrared inactive.
Haber-Bosch Process
| E(NH3) | -56.55776873 a.u. |
| 2*E(NH3) | -113.11553746 a.u. |
| E(N2) | -109.52412868 a.u. |
| E(H2) | -1.17853936 a.u. |
| 3*E(H2) | -3.53561808 a.u. |
| ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)] | -0.05579078 a.u. |
-0.05579078 a.u. = -146.48kJ/mol
This means that the products are more stable than the reactants
H2SiO Molecule
Convergence Table and Log
| Item | Value | Threshold | Converged? | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum | Force | 0.000023 | 0.000450 | YES |
| RMS | Force | 0.000009 | 0.000300 | YES |
| Maximum | Displacement | 0.000023 | 0.001800 | YES |
| RMS | Displacement | 0.000017 | 0.001200 | YES |
| Calculation Type | FREQ |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| E(RB3LYP) | -365.90001403 a.u |
| RMS Gradient Norm | 0.00000941 a.u. |
| Dipole Moment | 3.4340 Debye |
| Point Group | CS |
Full Log
File:JG2016-H2SIO-OPTF-POP.LOG
Vibrations
H2SiO has 4 atoms in each molecule and so from the 3N-6 rule it should have 6 vibrational modes, which it does as shown by the image above.
Molecular Orbitals
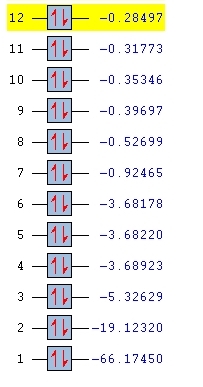
MO 1 is the 1s orbital on the Si
MO 2 is the 1s orbital on the O
MO 3 is the 2s orbital on the Si
MO 4,5,6 are the 3 2p orbitals on the Si
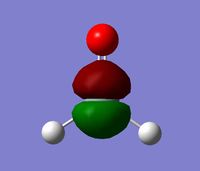
All these orbitals are too small and high energy to contribute to the bonding in the molecule
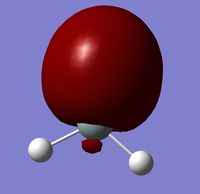
MO 7 is the combination of an sp2 hybrid orbital (formed from the 3s and 2 3p orbitals) on the Si and an sp2 hybrid orbital (formed from the 2s and 2 2p orbitals) on the O. This molecular orbital is the Si-O sigma orbital.
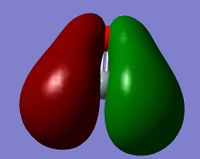
MO 9 is the combination of the 1s orbital on the H and the sp2 hybrid orbital on the Si. It is distorted by the high electronegativity of the O
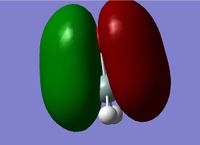
MO 11 is the combination of remaining 3p orbital on the Si and the remaining 2p orbital on the O. This orbital is known as the Si-O pi orbital.
Bond Lengths and angles
Si-O = 1.53172 Ångström
Si-H = 1.48652 Ångström
O-Si-H = 124.15758o
H-Si-H = 111.68594o
Charge
The Charge on the Silicon is +1.472
The Charge on the Hydrogens are -0.236
The Charge on the Oxygen is -1.001