Rep:Mod:JC2916
Ammonia
When drawing an ammonia molecule using the Gaussview program, we need to optimized the structure.
Optimisation File
The NH3 optimization file is link to here
Summary table
The setting of the optimization and the obtained useful data such as the lowest energy of the N-H bond and the Point group of the ammonia molecule are contained in the table below.
| Molecule Name | Calculation Method | Basis Set | E(RB3LYP) | Point Group |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NH3 | RB3LYP | 6-31G(d,p) | -56.55776873 a.u. | C3V |
Item table
The item table below shows that the forces and the displacements after the optimization are converged:
| Item | Value | Threshold | Converged? | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum | Force | 0.000004 | 0.000450 | YES |
| RMS | Force | 0.000004 | 0.000300 | YES |
| Maximum | Displacement | 0.000072 | 0.001800 | YES |
| RMS | Displacement | 0.000035 | 0.001200 | YES |
Predicted change in Energy=-5.986297D-10
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R2 R(1,3) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R3 R(1,4) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A1 A(2,1,3) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(2,1,4) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(3,1,4) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(2,1,4,3) -111.8571 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Jmol dynamic image
NH3 Optimisation |
For the optimized NH3 molecule, the H-N-H Bond Angle is 105.741° an the N-H Bond Length is 1.01798Å.
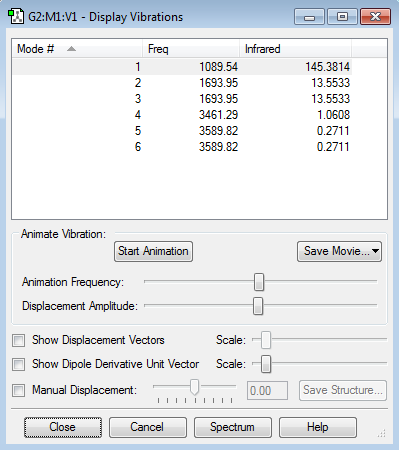
Vibration Data
Ammonia is a non linear molecule that adopts trignol pyramidal structure, so it should have 3N-6 vibration modes, where N is the number of atoms in a molecule, which is 4 in this case. Therefore, ammonia should have 6 vibration modes. Mode 1, 4, and 6 have highly symmetric vibrations, which Mode 1 has the 'umbrella' mode. From animating the vibrations, we can see that mode 1 to 3 are bending vibrations whereas mode 4 to 6 are stretching vibrations.
The vibration table below states the six vibration modes of the ammonia molecule. Mode 2 and 3, 5 and 6 are degenerate, so theoretically 4 bands will appear in the infrared spectrum of gaseous ammonia. However, because the frequencies for mode 4 to 6the relatively small, only 2 bands will be seen in the infrared spectrum.
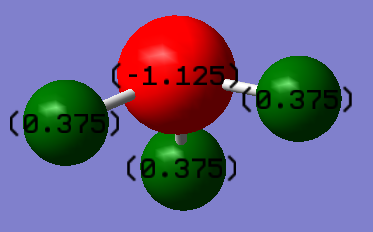
Charge Distribution Image
In the image above, the atom in red color is the nitrogen atom, and the atoms in green color are the hydrogen atoms.
In an ammonia molecule, N atom is more electronegative than the H atom. Therefore, charge on N is a negative value, and charge on H is a positive value.
Because the ammonia molecule is a neutral molecule, the partial charges on N and on H balanced out to give a molecule that carries zero charge in total.
Nitrogen
Optimisation File
The N2 optimization file is link to here
Summary table
The setting of the optimization and the obtained useful data such as the lowest energy of the N-N triple bond and the Point group of the nitrogen molecule are contained in the table below.
| Molecule Name | Calculation Method | Basis Set | E(RB3LYP) | Point Group |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N2 | RB3LYP | 6-31G(d,p) | -109.52412868 a.u. | D∞H |
Item table
The item table below shows that the forces and the displacements after the optimization are converged:
| Item | Value | Threshold | Converged? | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum | Force | 0.000002 | 0.000450 | YES |
| RMS | Force | 0.000002 | 0.000300 | YES |
| Maximum | Displacement | 0.000001 | 0.001800 | YES |
| RMS | Displacement | 0.000001 | 0.001200 | YES |
Predicted change in Energy=-8.701652D-13
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.1055 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Jmol dynamic image
N2 Optimisation |
The N ≡ N bond length is 1.10550Å after optimisation.
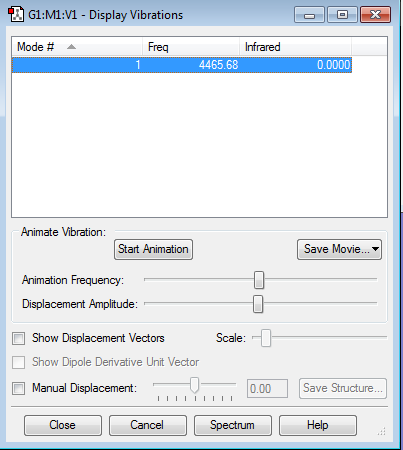
Vibration Data
N2 is a linear structure, so it should have 3N-5 vibration modes that N is 2 in this case. Therefore, nitrogen has 1 vibration mode which is shown in the table below.
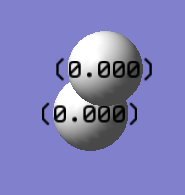
Charge Distribution Image
For a nitrogen molecule, N ≡ N, there is no difference in electronegativity between the two nitrogen atoms, thus the point charges are appeared as 0.000 on both atoms.
Hydrogen
Optimisation File
The H2 optimization file is link to here
Summary table
The setting of the optimization and the obtained useful data such as the lowest energy of the H-H bond and the Point group of the hydrogen molecule are contained in the table below.
| Molecule Name | Calculation Method | Basis Set | E(RB3LYP) | Point Group |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H2 | RB3LYP | 6-31G(d,p) | -1.17853936 a.u. | D∞H |
Item table
The item table below shows that the forces and the displacements after the optimization are converged:
| Item | Value | Threshold | Converged? | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum | Force | 0.000000 | 0.000450 | YES |
| RMS | Force | 0.000000 | 0.000300 | YES |
| Maximum | Displacement | 0.000000 | 0.001800 | YES |
| RMS | Displacement | 0.000001 | 0.001200 | YES |
Predicted change in Energy=-1.164080D-13
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 0.7428 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Jmol dynamic image
H2 Optimisation |
The bond length of hydrogen after optimisation is 0.74279Å.
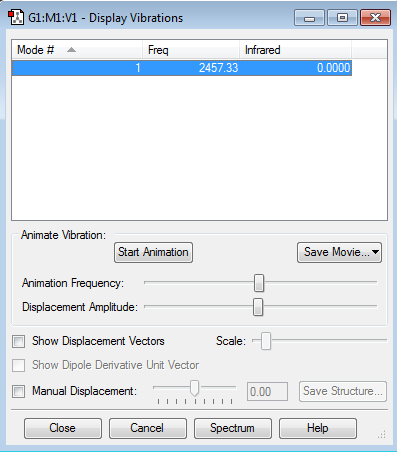
Vibration Data
Hydrogen is a linear molecule, so it should have 3N-5 (N=2) vibration modes in total, and it has 1 vibration mode shown in the table below.
Charge Distribution Image
For a hydrogen molecule, H-H, there is no difference in electronegativity between the two hydrogen atoms, thus the point charges are appeared as 0.000 on both atoms.
Reaction energy for Haber-Bosch process
E(NH3)= -56.55776873 a.u.
2*E(NH3)= -113.11553746 a.u.
E(N2)= -109.52412868 a.u.
E(H2)= -1.17853936 a.u.
3*E(H2)= -3.53561808 a.u.
ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]= -0.0557907 a.u.
ΔE=-146.48 kJ/mol
Because the Haber-Bosch process is an exothermic, the product, ammonia, is more stable than the gaseous reactants, hydrogen and nitrogen.
Cyanide - The small molecule
Optimisation File
The CN- optimization file is link to here
Summary Table
The setting of the optimization and the obtained useful data such as the lowest energy of the C-H triple bond and the Point group of the cyanide molecule are contained in the table below.
| Molecule Name | Calculation Method | Basis Set | E(RB3LYP) | Point Group |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cyanide | RB3LYP | 6-31G(d,p) | -92.82453153 a.u. | C∞V |
Item table
The item table below shows that the forces and the displacements are converged:
| Item | Value | Threshold | Converged? | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum | Force | 0.000012 | 0.000450 | YES |
| RMS | Force | 0.000012 | 0.000300 | YES |
| Maximum | Displacement | 0.000005 | 0.001800 | YES |
| RMS | Displacement | 0.000008 | 0.001200 | YES |
Predicted change in Energy=-6.650391D-11
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.1841 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Jmol dynamic image
Cyanide, C≡N-, is an anion that contains 2 atoms, 14 electrons and -1 charge.
Cyanide Optimisation |
After optimisation, the C≡N bond length is 1.18409Å.
Vibration Data
Cyanide has a linear structure, so it should have 3N-5 vibration modes. N is the number of atoms in a cyanide molecule, which is 2. Therefore, cyanide anion will only have one vibration mode.
Charge Distribution Image
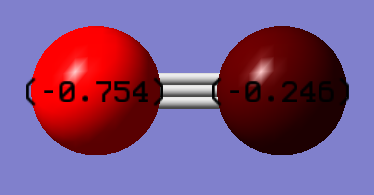
Image below shows the charge distribution for the cyanide anion. The atom on the left is the nitrogen atom that carries -0.754 charge, and the atom on the right is the carbon atom that carries -0.246 charge.
Since nitrogen atom is more electronegative than the carbon atom, charge on nitrogen is more negative than that of carbon. Adding the partial charges on each atoms together, cyanide carries -1 charge in total.
Molecular Orbitals
In all the images below, carbon atom is grey colored, and nitrogen atom is blue colored. Because cyanide anion is a heteronuclear diatomic molecule, it does not have a center of inversion. Therefore, gerade and ungerade cannot be assigned to these molecular orbitals.
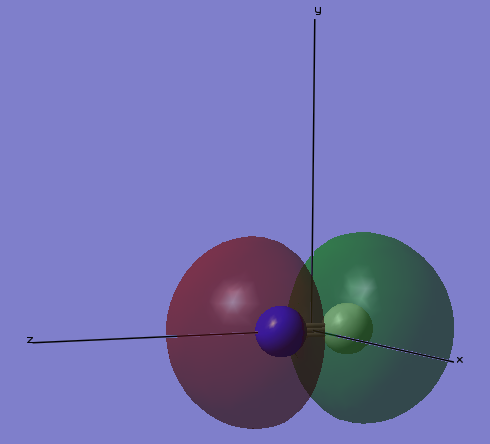
MO3
The image below gives the shape of the orbital that is the third lowest in molecular orbitals of cyanide anion. This is the σ-bonding orbital of the 2s orbitals on C and N. This 2s-bonding orbital is occupied, however, because the 2s-anti bonding orbital is also occupied, this bond is not shown in the overall cyanide structure. Because N is more electronegative than C, N contributes more to the bonding orbital. Because the 2s orbital of C atom is hybridized with the 2pz orbital giving a sp hybridized orbital, there is a hole on the surface of this molecular orbital.
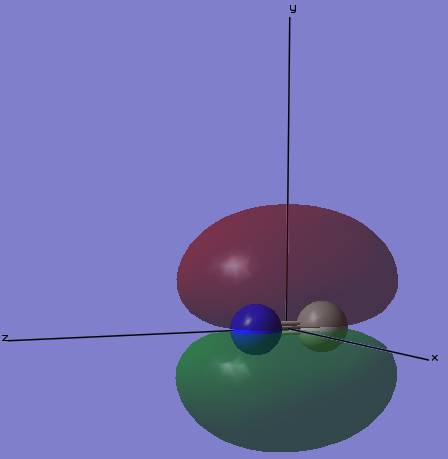
MO4
The image below gives the shape of the orbital that is the 4th lowest in molecular orbitals of cyanide anion. This is the σ-anti bonding orbital of the 2s orbitals on C and N, which is occupied with 2 electrons. Because C is more electropositive than N, C contributes more to the anti bonding orbital. Because the 2s orbital on C is hybridized, there is no nodal plane between the C and N atom.
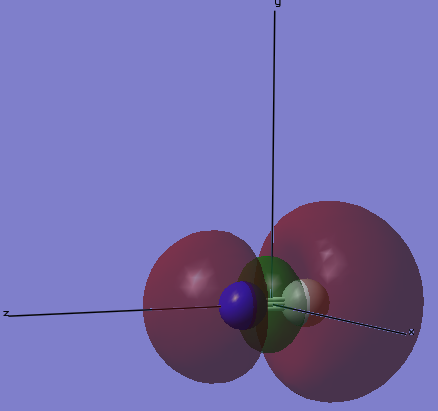
MO5
The image below gives the shape of the orbital that is the 5th lowest in molecular orbitals of cyanide anion. This is the π bonding orbital of the 2py orbitals on C and N. This π bonding orbital is occupied with 2 electrons, and it appears as one of the two degenerate pi bonds between the cyanide ion. Because N is more electronegative than C, N contributes more to the bonding orbital.
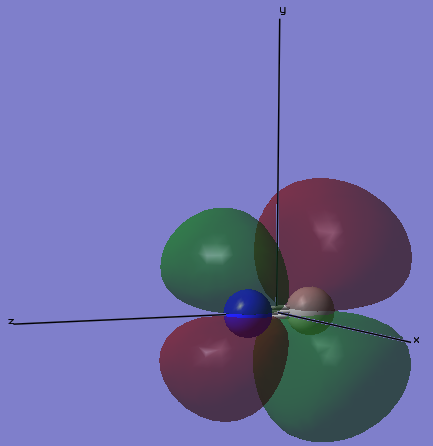
MO7
The image below gives the shape of the orbital that is the 7th lowest in molecular orbitals of cyanide anion. This is the σ-bonding orbital of the 2pz orbitals on C and N. This is the highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) of the cyanide ion. This σ-bonding orbital is occupied with 2 electrons, so it appears as the C-N sigma bond in the cyanide molecule.Since carbon is sp hybridized, so the 2pz orbital of C has 50% s character, so it has a smaller loop colored in green and a larger loop colored in red than 2pz orbital of N.
MO8
The image below gives the shape of the orbital that is the 8th lowest in molecular orbitals of cyanide anion. This is the π-anti bonding orbital of the 2py orbitals on C and N. This is the lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO) of the cyanide ion. This π-anti bonding orbital is not occupied with electrons. Because C is more electropositive than N, C contributes more to the anti bonding orbital.
Ethene - The extra molecule
Optimisation File
The ethene optimization file is link to here
Summary Table
The setting of the optimization and the obtained useful data such as the Point group of the ethene molecule are contained in the table below.
| Molecule Name | Calculation Method | Basis Set | E(RB3LYP) | Point Group |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ethene | RB3LYP | 6-31G(d,p) | -78.59380796 a.u. | C2H |
Item table
The item table below shows that the forces and the displacements after the optimization are converged:
| Item | Value | Threshold | Converged? | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum | Force | 0.000107 | 0.000450 | YES |
| RMS | Force | 0.000040 | 0.000300 | YES |
| Maximum | Displacement | 0.000168 | 0.001800 | YES |
| RMS | Displacement | 0.000092 | 0.001200 | YES |
Predicted change in Energy=-2.636302D-08
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.0867 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! R2 R(1,3) 1.0867 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! R3 R(1,4) 1.3301 -DE/DX = 0.0001 !
! R4 R(4,5) 1.0867 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! R5 R(4,6) 1.0867 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! A1 A(2,1,3) 116.3631 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(2,1,4) 121.8168 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(3,1,4) 121.8201 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A4 A(1,4,5) 121.8168 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A5 A(1,4,6) 121.8201 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A6 A(5,4,6) 116.3631 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(2,1,4,5) 180.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D2 D(2,1,4,6) 0.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D3 D(3,1,4,5) 0.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D4 D(3,1,4,6) 180.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Jmol dynamic image
Ethene Optimisation |
The bond length of C=C after optimisation is 1.33008Å; The bond length of C-H after optimisation is 1.08673Å.
And the H-C-H bond angle is 116.363°; H-C-C bond angle is 121.820°.
Vibration Data
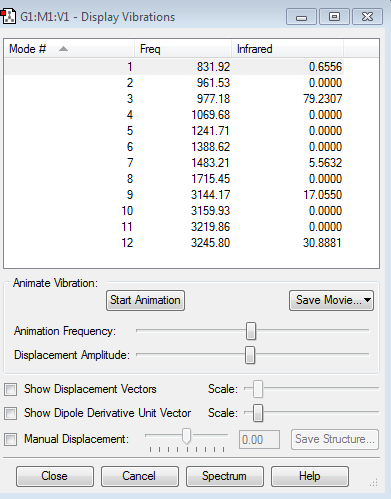
Ethene is a non linear molecule, so it should have 3N-6 vibration modes. N is the number of atoms, which is six in this case. So ethene has 12 vibration modes, which are shown in the table below.
Form the animation, we can tell that vibration modes 1-8 are bending modes, and vibration 9-12 are stretching mode.
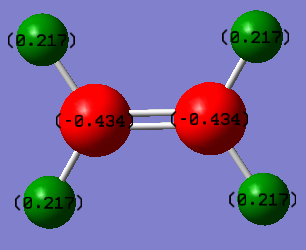
Charge Distribution Image
Ethene is a neutral compound. Because carbon is more electronegative than hydrogen atom, so charges on carbon are negative and charges on hydrogen are positive. Adding the partial charges on each atom together, ethene carries 0 charge in total.
Molecular Orbitals
Ethene has a center of inversion, so gerade(g) and ungerade(u) of the molecular orbitals can be assigned.
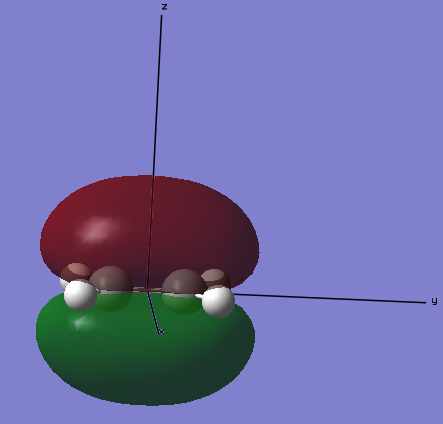
HOMO
The highest occupied molecular orbital for ethene is the molecular that is the 8th lowest energy orbital. This is the πu-bonding orbital of the 2pz orbitals on the two carbon atoms.
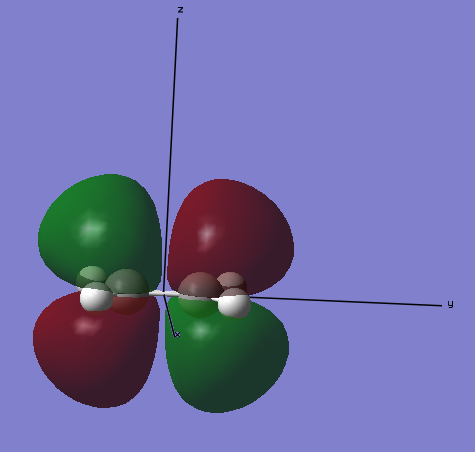
LUMO
The lowest unoccupied molecular orbital for ethene is the molecular that is the 9th lowest energy orbital. This is the πg-anti bonding orbital of the 2pz orbitals on the two carbon atoms.