Rep:Mod:InorganicLS
This is my page.
--Ls2510 14:27, 8 October 2012 (BST)
Optimisation
Optimisation of BH3
3-21G Basis Set
.log file for this calculation here
BH3 molecule optimized with 3-21G basis set
H-B bond length = 1.19 A, H-B-H bond angle = 120 degrees, Energy = -26.4622634 au
| BH3 optimized with 3-21G basis set | ' |
| File Name | bh3_opt_LS |
| File Type | .log |
| Calculation Type | FOPT |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 3-21G |
| Charge | 0 |
| Spin | Singlet |
| E(RB3LYP) | -26.46226338 a.u. |
| RMS Gradient Norm | 0.00020672 a.u. |
| Imaginary Freq | |
| Dipole Moment | 0 Debye |
| Point Group | D3H |
| Job Time | 11 Seconds |
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000413 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000271 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.001610 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.001054 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.071764D-06
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.1935 -DE/DX = 0.0004 !
! R2 R(1,3) 1.1935 -DE/DX = 0.0004 !
! R3 R(1,4) 1.1935 -DE/DX = 0.0004 !
! A1 A(2,1,3) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(2,1,4) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(3,1,4) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(2,1,4,3) 180.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
6-31G(d,p) Basis Set
.log file for this calculation here
BH3 molecule optimized with 6-31G(d,p) basis set
H-B bond length = 1.19 A, H-B-H bond angle = 120 degrees, Energy = -26.6153237 au
| BH3 optimization with 6-31G (d,p) basis set | ' |
| File Name | GH3_OPT_631GDP |
| File Type | .log |
| Calculation Type | FOPT |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Charge | 0 |
| Spin | Singlet |
| E(RB3LYP) | -26.61532374 a.u. |
| RMS Gradient Norm | 0.00000236 a.u. |
| Imaginary Freq | |
| Dipole Moment | 0 Debye |
| Point Group | CS |
| Job time | 49 Seconds |
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000005 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000003 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000020 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000012 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.312911D-10
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.1923 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R2 R(1,3) 1.1923 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R3 R(1,4) 1.1923 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A1 A(2,1,3) 120.0002 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(2,1,4) 120.0002 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(3,1,4) 119.9997 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(2,1,4,3) 180.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Optimisation of TlBr3
Link to files on D space: DOI:10042/20567
TlBr3 molecule optimized with LanL3DZ basis set
Br-Tl bond length = 2.65 A, Br-Tl-Br bond angle = 120 degrees
The bond length from a literature source is 2.512 A[1], which is close to the value given by Gaussian (only ~5% difference in value).
| TlBr3 optimisation | ' |
| File Name | TlBr3_opt_LanL2DZ |
| File Type | .log |
| Calculation Type | FOPT |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | LANL2DZ |
| Charge | 0 |
| Spin | Singlet |
| E(RB3LYP) | -91.21750131 a.u. |
| RMS Gradient Norm | 0.00275003 a.u. |
| Imaginary Freq | |
| Dipole Moment | 0 Debye |
| Point Group | D3H |
| Job cpu time | 21.3 seconds |
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000002 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000022 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000014 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-6.084037D-11
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 2.651 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R2 R(1,3) 2.651 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R3 R(1,4) 2.651 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A1 A(2,1,3) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(2,1,4) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(3,1,4) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(2,1,4,3) 180.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Optimisation of BBr3
.log file for this calculation here
BBr3 molecule optimized with mixed 6-31G(d,p) basis set and LanL2DZ pseudo-potential
B-Br bond length = 1.93 A, Br-B-Br bond angles = 120 degrees
| BBr3 optimisation | ' |
| File Name | BBR3_OPT_GEN |
| File Type | .log |
| Calculation Type | FOPT |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | Gen |
| Charge | 0 |
| Spin | Singlet |
| E(RB3LYP) | -64.43645277 a.u. |
| RMS Gradient Norm | 0.00000384 a.u. |
| Imaginary Freq | |
| Dipole Moment | 0.0002 Debye |
| Point Group | CS |
| Job cpu time | 49.0 seconds |
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000008 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000005 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000036 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000024 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-4.098477D-10
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.934 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R2 R(1,3) 1.9339 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R3 R(1,4) 1.934 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A1 A(2,1,3) 120.0022 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(2,1,4) 119.9956 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(3,1,4) 120.0022 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(2,1,4,3) -180.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Comparison of BH3, BBr3 and TlBr3
| Molecule | Bond Distance (Angstroms) |
| BH3 | 1.19 |
| BBr3 | 1.93 |
| TlBr3 | 2.65 |
(All results from using 6-21G(d,p) basis set. When comparing molecules the calculations have to have been carried out with the same method/basis set)
The Br-B bond is longer than H-B, given Br is very electronegative and H is not this can be justified by the Br-B bond being more ionic in character due to bromine withdrawing a large amount of electron density from the boron, i.e. closer to B3+ 3Br- than BBr3
The Br-Tl bonds are much longer again, this could be explained by thallium being very large (81 electrons) and therefore having much more diffuse bonding orbitals than boron, with the electrons less tightly attached to the nucleus so they are easier for bromine to attract and make the bond more ionic (less electrons shared leading to a weaker - hence longer - bond). Also because the atoms Br and Tl are much larger than H and B then the bond will have to be longer simply to accommodate the increased atom size.
When GaussView does not draw a bond that does not mean there is no bond, the program has an arbitrary distance for deciding if there is a bond or not and this can be exceeded while there is still actually a bond present. The bonds in inorganic molecules tend to be longer than those in organic molecules too, so it is more likely for this to be the case in the molecules being analyzed in this exercise.
In reality, there is no hard and fast definition of a bond and it's not so much a binary option of there being a bond or not, but a spectrum of strong bonds to weak interactions. The definition of a bond is "a mutual attraction between two atoms resulting from a redistribution of their outer electrons"[2] which is a very broad definition so it cannot be decided if there is a bond or not just from whether the atoms are within an arbitrary distance of each other.
Vibrational Analysis
Vibrational Analysis of BH3
.log file for this calculation here
| BH3 frequency | ' |
| File Name | LS_bh3_freq |
| File Type | .log |
| Calculation Type | FREQ |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Charge | 0 |
| Spin | Singlet |
| E(RB3LYP) | -26.61532374 a.u. |
| RMS Gradient Norm | 0.00000237 a.u. |
| Imaginary Freq | 0 |
| Dipole Moment | 0 Debye |
| Point Group | C2V |
| Job cpu time | 27.0 seconds |
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000005 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000002 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000020 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000009 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.329322D-10
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
Low frequencies --- -18.6669 -0.0009 -0.0003 0.0006 12.5167 12.5631 Low frequencies --- 1162.9785 1213.1756 1213.2363
Table of vibrational modes of BH3
IR spectrum of BH3

There are 6 vibrations as shown above, yet only 3 peaks in the IR spectrum. This is because the peaks corresponding to the vibrational modes 2 and 3 are incredibly close in frequency and intensity (difference of 0.06 cm-1) so the peaks are superimposed into one peak on the spectrum. This is also the case with modes 5 and 6, which only have a difference in frequency of 0.03 cm-1. (given that the calculations have a systematic error of ~10% the small differences in values are so small as to be meaningless)
This explains 2 of the missing peaks, and the last missing peak is that which would correspond to vibration 4, which has an intensity of 0 and hence no peak.
Vibrational Analysis of TlBr3
Link to files on D space: DOI:10042/20646
| TlBr3 frequency | ' |
| File Name | LS_TLBR3_FREQ |
| File Type | .log |
| Calculation Type | FREQ |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | LANL2DZ |
| Charge | 0 |
| Spin | Singlet |
| E(RB3LYP) | -91.21812851 a.u. |
| RMS Gradient Norm | 0.00000088 a.u. |
| Imaginary Freq | 0 |
| Dipole Moment | 0 |
| Point Group | D3H |
| Job cpu time | 15.9 seconds |
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000002 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000022 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000011 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-5.660901D-11
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
Low frequencies --- -3.4213 -0.0026 -0.0004 0.0015 3.9367 3.9367 Low frequencies --- 46.4289 46.4292 52.1449
- The lowest "real" normal mode is 46.4289 cm-1
Table of vibrational modes of TlBr3
IR Spectrum of TlBr3

Comparison of Frequencies of BH3 & TlBr3
| Vibrational Mode | BH3 Frequency | TlBr3 Frequency | Symmetry BH3 (point group D3h) | Symmetry TlBr3 (point group D3h) |
| 1 | 1162 | 46 | a''2 | e' |
| 2 | 1213 | 46 | e' | e' |
| 3 | 1213 | 52 | e' | a''2 |
| 4 | 2582 | 156 | a'1 | a'1 |
| 5 | 2715 | 211 | e' | e' |
| 6 | 2715 | 211 | e' | e' |
- The frequencies of TlBr3 are much lower than BH3, given that wavenumber is proportional to energy, then the Tl-Br bonds are weaker than B-H ones (in agreement with the data of bond lengths earlier). Also both Br and Tl are heavier than H and B respectively so it takes more energy to make the atoms move.
- There has been a re-ordering of modes, what was mode 1 in BH3 is 3 in TlBr3, 2 is changed to 1, 3 is changed to 2, 4 5 and 6 are the same in both. This is because mode 1 in BH3 ("umbrella" deformation) involves the most movement of the central atom, and given Tl is so much heavier than B then it requires more energy for this vibrational mode.
- The spectra are similar in that the general "shape" of the graph is the same, at low frequencies the a''2 and the e' are together and at high frequencies the a'1 and other e' modes are together.
- The actual movements in the a'1 and higher energy e' are more pronounced (i.e. the atoms move further), which is why they are higher energy because more energy is needed to make them move.
- The frequency analysis must be carried out on a molecule which has already been optimised, and the same basis set must be used for both calculations because the energy of the molecule from optimisation depends greatly on the quality of the basis set used. A very small difference in energy reported in au is a large difference in kJ/mol.
- The optimisation only confirms that the gradient of the potential energy surface is zero, this could correspond to a maximum or a minimum, so it needs to be confirmed that the molecule generated is truly a minimum. The frequency analysis takes the second derivative of the potential energy surface, so if it is positive we have a minimum and if it is negative we have a maximum.
- Molecules have 3N - 6 vibrations, the low frequencies are simply the "-6", i.e. the motions of the center of mass of the molecule.
Molecular Orbitals
Molecular Orbitals of BH3
Link to files on D space: DOI:10042/20706
MO Diagram of BH3[3]

MO's are shown up to the LUMO, which is a non-bonding orbital. Both the estimate of the MO from LCAO and the MO calculated by Gaussian are displayed. It is apparent from looking at the diagram that the LCAO approximations of MOs are in fact very close to what they "really" are. (Of course the MOs calculated by Gaussian are not exactly correct because a better basis set could be used for example). Therefore qualitative MO theory is accurate and useful, at least for molecules of a similarly small size.
Natural Bond Orbital Analysis
NH3
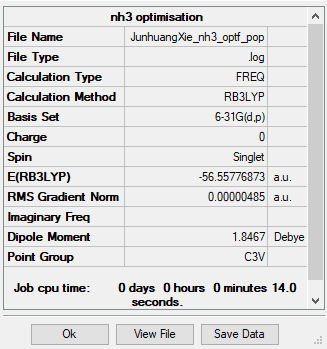
Optimisation of NH3
Because NH3 is such a simple molecule, it can be optimised with the 6-21G(d,p) basis set straight away, there is no need to use the 3-21G basis set first. A stationary point was found as displayed in the item table below.
.log file for this calculation here
NH3 molecule optimized with 6-21G(d,p) basis set
H-N bond length = 1.02 A, H-N-H bond angle = 105.7 degrees
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000024 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000012 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000079 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000053 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.629729D-09
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R2 R(1,3) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R3 R(1,4) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A1 A(2,1,3) 105.7413 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(2,1,4) 105.7486 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(3,1,4) 105.7479 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(2,1,4,3) -111.8631 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
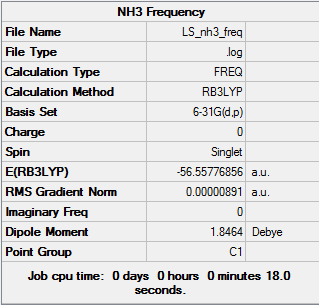
Frequency Analysis of NH3
.log file for this calculation here
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000022 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000009 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000078 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000039 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.621683D-09
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
Low frequencies --- -30.7013 -0.0007 0.0006 0.0013 20.2662 28.2997 Low frequencies --- 1089.5562 1694.1246 1694.1863
MOs of NH3
Link to files on D space: DOI:10042/20743
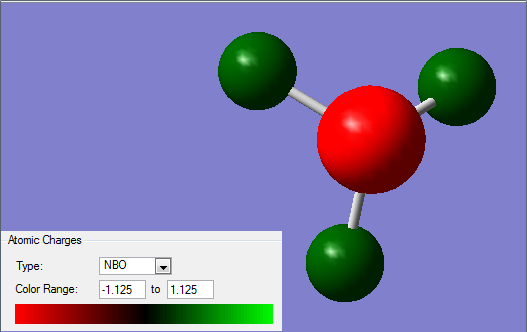
NBO Analysis of NH3
Charge Analysis of NH3
As shown below, the N has a charge of -1.125 and each H has a charge of +0.375
NH3BH3
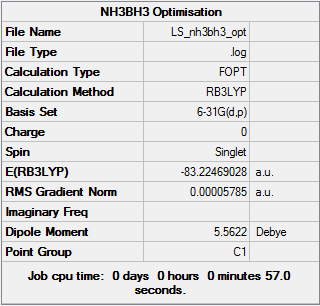
Optimisation of NH3BH3
.log file for this calculation here
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000137 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000038 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.001013 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000223 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.124453D-07
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,7) 1.0185 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R2 R(2,7) 1.0185 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R3 R(3,7) 1.0185 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R4 R(4,8) 1.2097 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R5 R(5,8) 1.2097 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R6 R(6,8) 1.2097 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R7 R(7,8) 1.6686 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! A1 A(1,7,2) 107.8652 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(1,7,3) 107.8652 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(1,7,8) 111.0277 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A4 A(2,7,3) 107.8615 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A5 A(2,7,8) 111.0375 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A6 A(3,7,8) 111.0375 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A7 A(4,8,5) 113.9056 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A8 A(4,8,6) 113.9056 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A9 A(4,8,7) 104.5646 -DE/DX = 0.0001 !
! A10 A(5,8,6) 113.8997 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A11 A(5,8,7) 104.5579 -DE/DX = 0.0001 !
! A12 A(6,8,7) 104.5579 -DE/DX = 0.0001 !
! D1 D(1,7,8,4) 180.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D2 D(1,7,8,5) -59.9968 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D3 D(1,7,8,6) 59.9967 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D4 D(2,7,8,4) -60.0006 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D5 D(2,7,8,5) 60.0026 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D6 D(2,7,8,6) 179.9961 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D7 D(3,7,8,4) 60.0006 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D8 D(3,7,8,5) -179.9962 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D9 D(3,7,8,6) -60.0026 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Frequency Analysis of NH3BH3
.log file for this calculation here

Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000264 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000058 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.001470 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000376 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-2.149184D-07
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
Low frequencies --- -8.8883 -0.0004 0.0008 0.0015 19.3593 19.5893 Low frequencies --- 263.3209 631.2464 638.5710
Energy Comparison
- E(NH3) = -26.61532374 a.u.
- E(BH3) = -56.55776856 a.u.
- E(NH3BH3) = 83.22469028 a.u.
(all optimised using 6-31G(d,p) basis set)
- ΔE=E(NH3BH3)-[E(NH3)+E(BH3)] = -0.05159798 a.u.
- Therefore ΔE = -0.05159798/3.8088×10-4 kJ/mol
- ΔE = -135.47kJ/mol
Therefore the bond association energy between B & N in NH3BH3 is -135.47 kJ/mol. (although the program has an accuracy of +/- 10 kJ/mol so it would be more accurate to report the energy as -140 kJ/mol)
Ionic Liquids: Designer Solvents (Mini Project)
- Unless otherwise stated, all the calculations in this section use the 6-21G(d,p) basis set and are carried out on the HPC. (It can be seen how long the calculations would take if they were performed on a normal computer, so long as to be inconvenient!)
- Also, the "item" tables proving the molecule has been optimised to a gradient of zero no longer include the summary of optimised parameters, because there are so many atoms in the molecule so the tables are incredibly long.
Part 1: Comparison of Selected "onium" Cations
[N(CH3)4]+
Optimisation of [N(CH3)4]+
Jmol of optimised molecule:
Link to files on D space: DOI:10042/20757
![Summary of results for [N(CH3)4]+ optimised with 6-21G(d,p) basis set](/images/8/81/LS_nme4_opt_summary.png)
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000074 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000017 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.001298 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000359 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-5.560629D-08
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
Frequency Analysis of [N(CH3)4]+
The low frequencies below show that the molecule has been optimised to a minimum. The Me-N-Me bond angle is ~109.4 degrees, so the geometry about the central N atom is tetrahedral, which is to be expected.
Link to files on D space: DOI:10042/20759
![Summary of results for [N(CH3)4]+ frequency analysis with 6-21G(d,p) basis set](/images/f/fd/LS_nme4_freq_summary.png)
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000073 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000021 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000749 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000257 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-5.030853D-08
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
Low frequencies --- -13.0303 0.0008 0.0009 0.0012 6.1831 12.0078 Low frequencies --- 179.9148 278.8724 285.7248
MO Calculations of [N(CH3)4]+
Link to files on D space: DOI:10042/20793
NBO Analysis of [N(CH3)4]+
.log file from the NBO analysis here
![Charge analysis of [NMe4]+](/images/a/af/LS_nme4_chargeanalysis.png)
The description commonly used that [NR4]+ (where R = alkyl) has the positive charge on the nitrogen is obviously shown to be incorrect by this analysis, the nitrogen is in fact slightly negatively charged and the positive charge is localised on the hydrogens of the alkyl groups. See the excerpt of the .log file below:
Natural Population
Natural -----------------------------------------------
Atom No Charge Core Valence Rydberg Total
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
C 1 -0.48341 1.99947 4.46945 0.01449 6.48341
H 2 0.26903 0.00000 0.72996 0.00100 0.73097
H 3 0.26905 0.00000 0.72994 0.00100 0.73095
H 4 0.26908 0.00000 0.72991 0.00100 0.73092
C 5 -0.48341 1.99947 4.46945 0.01449 6.48341
H 6 0.26909 0.00000 0.72991 0.00100 0.73091
H 7 0.26905 0.00000 0.72994 0.00100 0.73095
H 8 0.26903 0.00000 0.72996 0.00100 0.73097
C 9 -0.48344 1.99947 4.46949 0.01449 6.48344
H 10 0.26908 0.00000 0.72992 0.00100 0.73092
H 11 0.26907 0.00000 0.72992 0.00100 0.73093
H 12 0.26906 0.00000 0.72993 0.00100 0.73094
C 13 -0.48328 1.99947 4.46932 0.01449 6.48328
H 14 0.26904 0.00000 0.72996 0.00100 0.73096
H 15 0.26904 0.00000 0.72996 0.00100 0.73096
H 16 0.26901 0.00000 0.72999 0.00100 0.73099
N 17 -0.29510 1.99950 5.28970 0.00591 7.29510
=======================================================================
* Total * 1.00000 9.99736 31.92673 0.07591 42.00000
[P(CH3)4]+
Optimisation of [P(CH3)4]+
Jmol of optimised molecule:
Link to files on D space: DOI:10042/20761
![Summary of results for [P(CH3)4]+ optimised with 6-21G(d,p) basis set](/images/6/66/LS_pme4_opt_summary.png)
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000148 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000033 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000959 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000312 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.849677D-07
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
Frequency Analysis of [P(CH3)4]+
Link to files on D space: DOI:[1]
[S(CH3)3]+
Optimisation of [S(CH3)3]+
Jmol of optimised molecule:
Link to files on D space: DOI:10042/20772
![Summary of results for [S(CH3)3]+ optimised with 6-21G(d,p) basis set](/images/6/64/LS_sme3_opt_summary.png)
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000023 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000010 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.001035 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000348 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-2.234092D-08
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
Frequency Analysis of [S(CH3)3]+
The low frequencies shown below prove that the molecule has been optimised to a minimum. The Me-S-Me bond angles are ~ 102.7 degrees, meaning that the methyl groups are pushed closer together than a "perfect" tetrahedral (i.e. angle < 109 degrees) by the lone pair on S. The geometry is trigonal pyramidal.
Link to files on D space: DOI:10042/20774
![Summary of results for [S(CH3)3]+ frequency analysis with 6-21G(d,p) basis set](/images/8/86/LS_sme3_freq_summary.png)
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000049 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000019 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.001590 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000520 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-3.086772D-08
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
Low frequencies --- -24.9923 -14.4720 -12.1032 -0.0032 -0.0027 -0.0023 Low frequencies --- 158.9980 192.6129 202.1628
MO Calculations of [S(CH3)3]+
Link to files on D space: DOI:10042/20805
NBO Analysis of [S(CH3)3]+
.log file from the NBO analysis here
![Charge analysis of [SMe3]+](/images/f/f1/LS_sme3_chargeanalysis.png)
Part 2: Influence of Functional Groups
[N(CH3)3(CH2OH)]+
Optimisation of [N(CH3)3(CH2OH)]+
Jmol of optimised molecule:
Link to files on D space: DOI:10042/20806
![Summary of results for [N(CH3)3(CH2OH)]+ optimised with 6-21G(d,p) basis set](/images/4/47/LS_nme3ch3oh_opt_summary.png)
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000074 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000020 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.001619 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000425 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-8.892484D-08
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
Frequency Analysis of [N(CH3)3(CH2OH)]+
Link to files on D space: DOI:10042/20810
![Summary of results for [N(CH3)3(CH2OH)]+ frequency analysis with 6-21G(d,p) basis set](/images/1/1e/LS_nme3ch2oh_freq_summary.png)
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000066 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000020 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000869 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000330 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-8.288691D-08
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
Low frequencies --- -4.0940 -0.0002 0.0008 0.0009 12.5644 18.9824 Low frequencies --- 130.9693 217.1689 258.6409
MO Calculations of [N(CH3)3(CH2OH)]+
Link to files on D space: DOI:10042/20814
NBO Analysis of [N(CH3)3(CH2OH)]+
.log file from the NBO analysis here
![Charge analysis of [N(CH3)3(CH2OH)]+](/images/1/16/LS_nme3ch2oh_chargeanalysis.png)
[N(CH3)3(CH2CN)]+
Optimisation of [N(CH3)3(CH2CN)]+
Jmol of optimised molecule:
Link to files on D space: DOI:10042/20831
![Summary of results for [N(CH3)3(CH2CN)]+ optimised with 6-21G(d,p) basis set](/images/a/a2/LS_nme3ch2cn_opt_summary.png)
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000005 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000002 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000398 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000076 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.565289D-09
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
Frequency Analysis of [N(CH3)3(CH2CN)]+
Link to files on D space: DOI:10042/20839
![Summary of results for [N(CH3)3(CH2cn)]+ frequency analysis with 6-21G(d,p) basis set](/images/5/5d/LS_nme3ch2cn_freq_summary.png)
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000016 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000003 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000391 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000100 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.261257D-09
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
Low frequencies --- -0.0008 -0.0005 -0.0001 11.4792 16.4024 17.6028 Low frequencies --- 91.6640 155.1565 217.4529
MO Calculations of [N(CH3)3(CH2CN)]+
Link to files on D space: DOI:10042/20841
NBO Analysis of [N(CH3)3(CH2CN)]+
.log file from the NBO analysis here
![Charge analysis of [N(CH3)3(CH2CN)]+](/images/f/f1/LS_nme3ch2cn_chargeanalysis.png)
Comparison of the 2 Molecules
From the NBO analysis of the molecules above, it can be seen that when a hydrogen is replaced with a -OH (electron donating group) then the relative charge on N rises from -0.295 in [N(CH3)4]+ to -0.322, which is more negative i.e. electron density is pushed onto nitrogen.
When the hydrogen is replaced with a -CN group instead (electron withdrawing), then the relative charge on N of -0.295 in [N(CH3)4]+ is decreased to -0.289. i.e. the -CN group has drawn electron density off the central nitrogen making it less negatively charged.
| Molecule | HOMO | LUMO |
| [N(CH3)4]+ |  |

|
| [N(CH3)3(CH2OH)]+ |  |

|
| [N(CH3)3(CH2CN)]+ |  |

|
- Comparisons of the HOMO and LUMO MOs of [N(CH3)4]+, [N(CH3)3(CH2OH)]+ and [N(CH3)3(CH2CN)]+ are shown in the table above.
References
- ↑ http://actachemscand.dk/pdf/acta_vol_36a_p0125-0135.pdf
- ↑ Collins English Dictionary - Complete & Unabridged 10th Edition 2009 © William Collins Sons & Co. Ltd. 1979, 1986 © HarperCollins Publishers 1998, 2000, 2003, 2005, 2006, 2007, 2009
- ↑ http://www.huntresearchgroup.org.uk/teaching/teaching_comp_lab_year3/Tut_MO_diagram_BH3.pdf