Rep:Mod:Hz6416
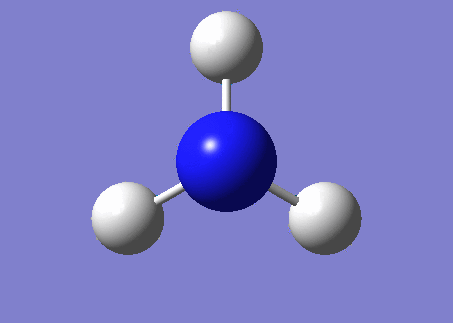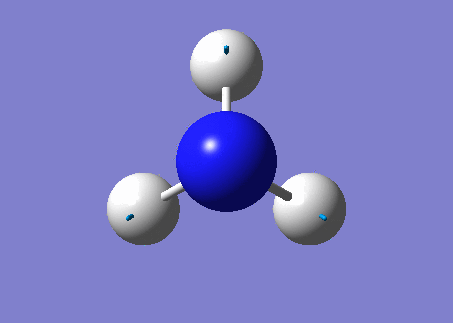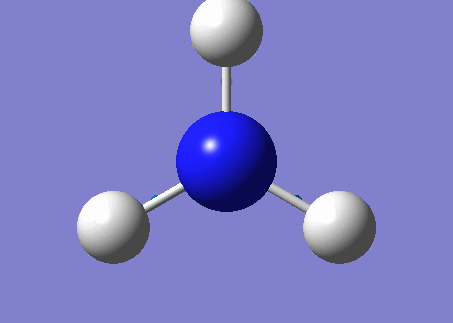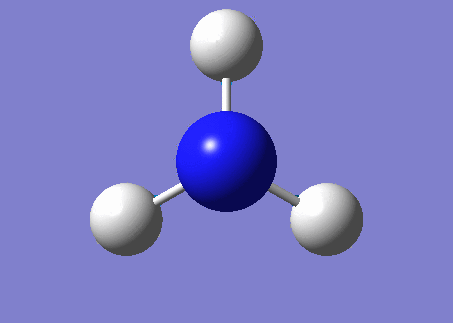
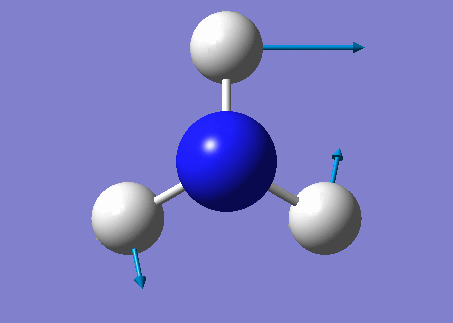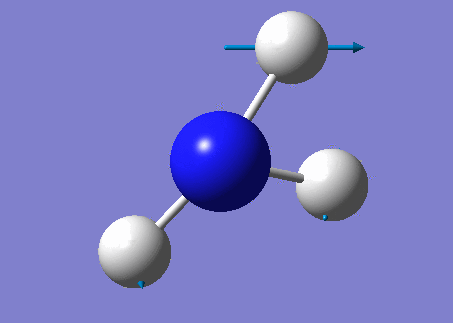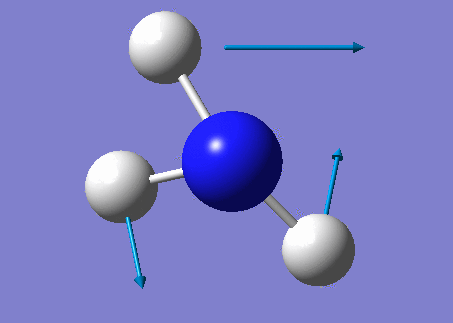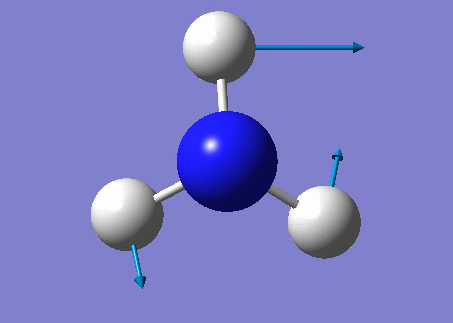
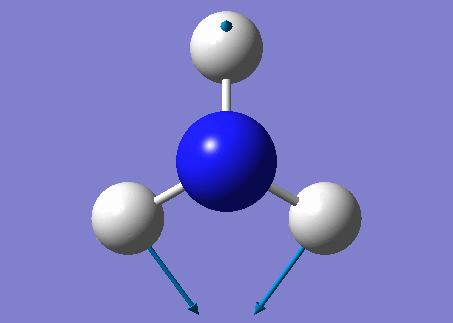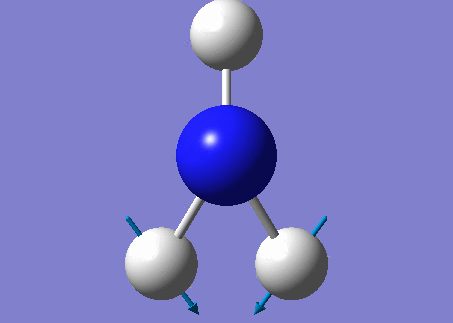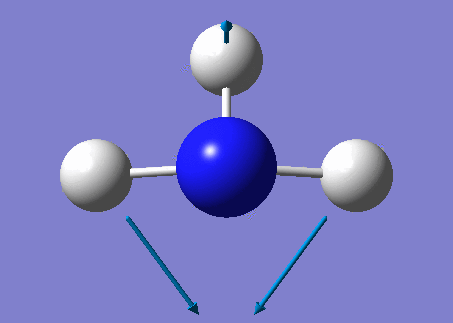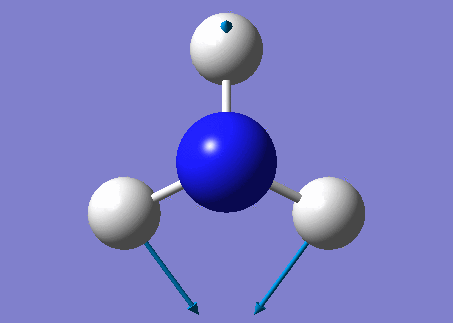
NH3 molecule
Molecule: NH3
Method: RB3LYP
Basis Set: 6-31G(d,p)
E(RB3LYP): -56.55776873 a.u
RMS Gradient Norm: 0.00000485 a.u
Point Group: C3V
Bond distance N-H: 1.01798 A
Bond angle H-N-H: 105.74115°
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
test molecule |
Modes from the 3N-6 rule: 6
Degenerate modes: Modes 2 and 3, Modes 5 and 6
Bending vibrations: Modes 1,2 and 3
Bond stretch vibrations: Mode 4
Highly Symmetric: Modes 1 and 4
Umbrella Mode: Mode 1
Bands in an experimental spectrum of gaseous ammonia: 4
Charge on the N-atom: -1.125
Charge on the H-atom: 0.375
The Energy for the reaction of N2 + 3H2 -> 2NH3
E(NH3)=-56.55776873 a.u
2*E(NH3)= 2*(-56.55776873 a.u)
E(N2)= -109.52359111 a.u
E(H2)= -1.15928020 a.u
3*E(H2)= 3*(-1.17853936 a.u)
ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)] = 2*(-56.55776873 a.u)-[-109.52359111 a.u + 3*(-1.17853936 a.u)]
= -0.05632827 a.u
= -0.05632827*2625.5 kJ/mol
= -147.8898729 kJ/mol
Conclusion: according to the negative result, it is clearly that this reaction is a exothermic reaction.
Therefore, the gaseous reactants is more stable than the ammonia product.
N2 molecule
Molecule: N2
Method: RB3LYP
Basis set: 6-31G(d.p)
E(RB3LYP): -109.52359111 a.u
RMS Gradient Norm: 0.02473091 a.u
Point Group: D*H
The Bond Length of N2: 1.10550 A
The Bond Angle of N2: 180°
The frequence of N2: 2457.33
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
H2 molecule
Molecule H2
Method: RB3LYP
Basis Set: 6-31G(d,p)
E(RB3LYP): -1.17853936 a.u
RMS Gradient Norm: 0.00002276 a.u
Point Group: D*H
Bond distance H-H: 0.60000A
Bond angle H-H: 180°
The Frequency of H2: 0, because H2 is a homogeneous molecule.
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.168347 0.000450 NO RMS Force 0.097195 0.000300 NO Maximum Displacement 0.087680 0.001800 NO RMS Displacement 0.050622 0.001200 NO
CH4 Molecule
Molecule: CH4
Method: RB3LYP
Basis Set: 6-31G(d,p)
E(RB3LYP): -40.52401404 a.u
RMS Gradient Norm: 0.00003263 a.u
Point Group: Td
Bond distance C-H: 1.09197 A
Bond angle H-C-H: 109.47122°
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000063 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000034 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000179 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000095 0.001200 YES
Hyz ch4 optf pop.gjf
test molecule |
Modes from the 3N-6 rule: 9
Degenerate modes: Modes 1, 2 and 3, Modes 4 and 5, Modes 7, 8 and 9
Bending vibrations: Modes 1,2,3,4 and 5
Bond stretch vibrations: Mode 6
Highly Symmetric: Modes 1 and 4
Bands in an experimental spectrum of gaseous methane: 4
Charge on the C-atom: -0.930
Charge on the H-atom: 0.233
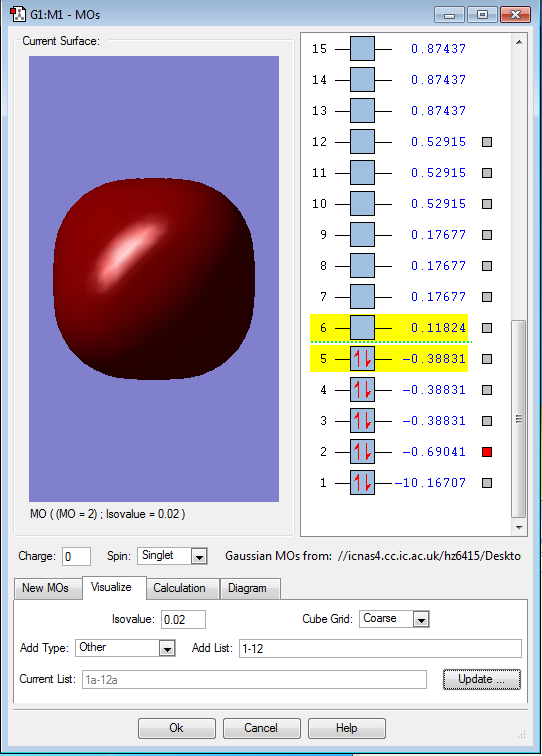
This is the 1s core AOs one the C atom in methane
This is the 2s AOs on the C atom
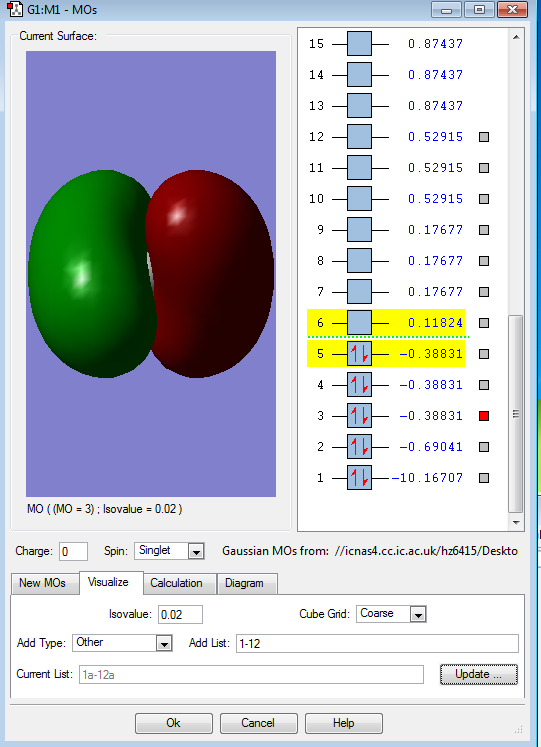
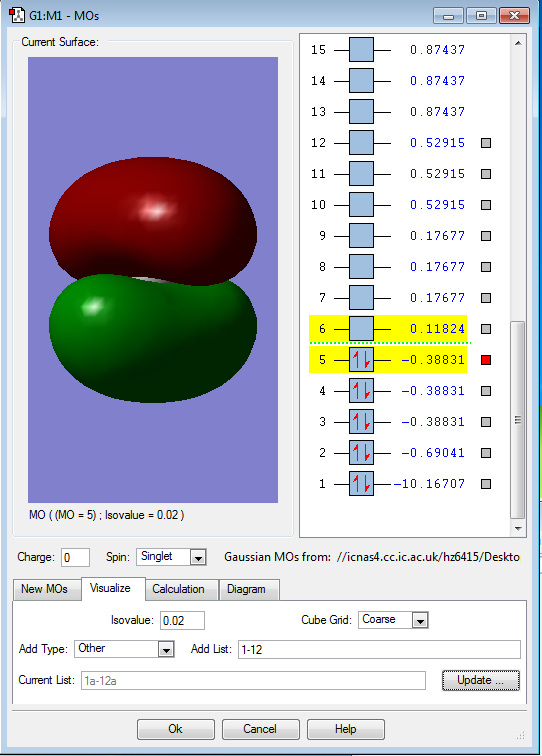
This is the combination(overlap) of the p orbital on the C atom and s orbital on the H atom
This is also the combination(overlap) of the p orbital on the C atom and s orbital on the H atom.
These two picture show that two MOs all have the same energy. This is because they all have the same symmetry but different orientation.
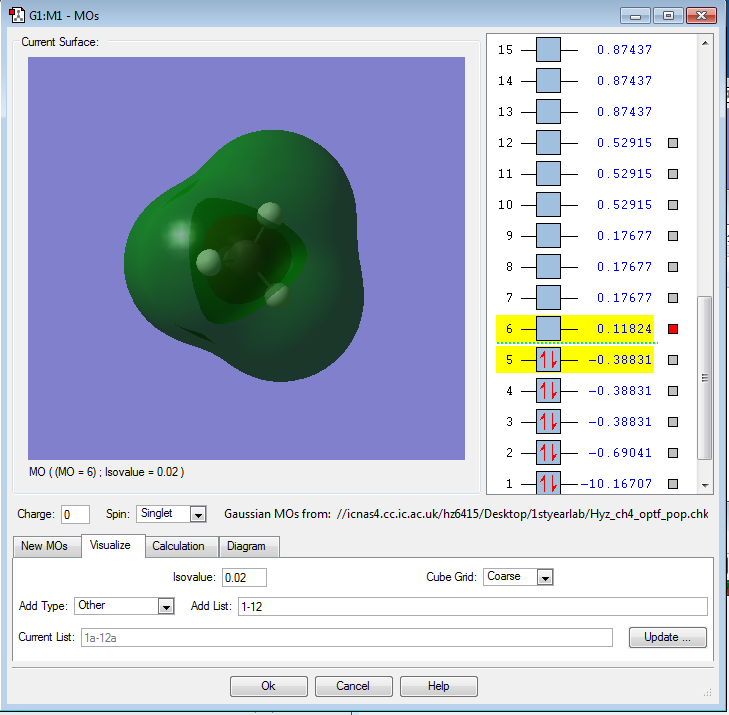
This is the antibonding orbital of the C atom