Rep:Mod:HOWDOIDOTHISWHAT
NH3 Molecule
Base data
| Molecule | NH3 |
| N-H bond distance | 1.01798 Å |
| H-N-H bond angle | 105.741° |
| Calculation method | RB3LYP |
| Basis set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Final energy E(RB3LYP) in atomic units | -56.55776873 au |
| RMS gradient | 0.00000485 |
| Point group | C3v |
Item Table
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-5.986262D-10
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
File:Ft1015 NH3 OPTIMISINGPOP.LOG
test molecule |
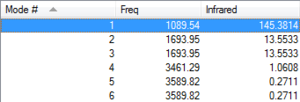
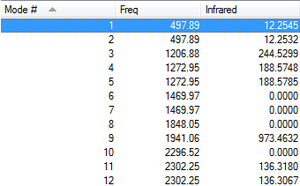
| Expected amount of vibrations using 3N-6 rule | 6 Modes are expected |
| Degenerate modes | Modes 2 & 3 and 5 & 6 are degenerate |
| "Bending" vibrations and "bond stretch" vibrations | Modes 1-3 are bending and 4-6 streching. |
| Highly symmetric mode | Mode 4 is highly symmetric. |
| "Umbrella" mode | Mode 1 is the umbrella mode. |
| Bands in experimental spectrum of gaseous ammonia | 4 Bands are expected |
Colour charge
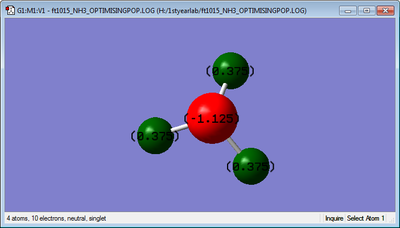
Here we have the charges on the N and H atoms, which are -1.125 and +0.375 respectively. This is because
the Nitrogen is more electronegative than the Hydrogens and so withdraws electrons from them, becoming
more negative and the Hydrogens more positive.
H2 Molecule
Base data
| Molecule | H2 |
| H-H bond distance | 0.74279 Å |
| H-H bond angle | 180.00° |
| Calculation method | RB3LYP |
| Basis set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Final energy E(RB3LYP) in atomic units | -1.17853936 au |
| RMS gradient | 0.00000017 |
| Point group | D∞h |
Item Table
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.164080D-13
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
test molecule |
File:FT1015 H2 OPTIMISINGPOP.LOG
N2 Molecule
Base data
| Molecule | H2 |
| N-N bond distance | 1.10550 Å |
| N-N bond angle | 180.00° |
| Calculation method | RB3LYP |
| Basis set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Final energy E(RB3LYP) in atomic units | -109.52412868 au |
| RMS gradient | 0.00000060 |
| Point group | D∞h |
Item Table
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-3.400973D-13
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
test molecule |
File:FT1015 N2 OPTIMISINGPOP.LOG
Energy of Reaction N2 + 3H2 = 2NH3
| E(NH3) | -56.55776873 au |
| 2*E(NH3) | -113.11553746 au |
| E(N2) | -109.52412868 au |
| E(H2) | -1.17853936 au |
| 3*E(H2) | -3.53561808 au |
| ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)] | -0.0557907 au |
| ΔE | -146.47848285 kJ/mol |
The gaseous product is more stable as energy is given out when the reactants react.
PH5 Molecule
Base data
| Molecule | PH5 |
| P-H bond distance | 1.43316 Å and 1.48687 Å |
| H-P-H bond angle | 90° or 180° |
| Calculation method | RB3LYP |
| Basis set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Final energy E(RB3LYP) in atomic units | -344.25491049 au |
| RMS gradient | 0.00000471 |
| Point group | D3h |
Item Table
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000009 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000055 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000022 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.032823D-09
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
test molecule |
File:FT1015 PH5 OPTIMISINGPOP.LOG
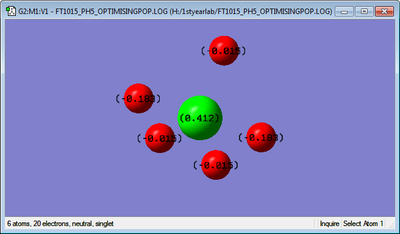
Colour charge
Here we have the charges on the P and H atoms, which are ̟0.412 and -0.015 and -0.183 respectively. This is
because the each Hydrogen is more electronegative than the Phosphorous and the Hydrogens withdraw electrons
from the Phosphorous becoming more negative and the Phosphorous more positive.
Molecular Orbital Diagrams
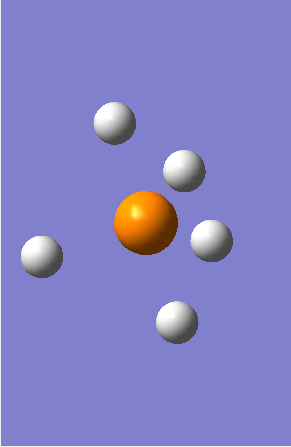 MO1 - Is the 1s non-bonding orbital of Phosphorous with an energy of -77.14583 au
MO1 - Is the 1s non-bonding orbital of Phosphorous with an energy of -77.14583 au
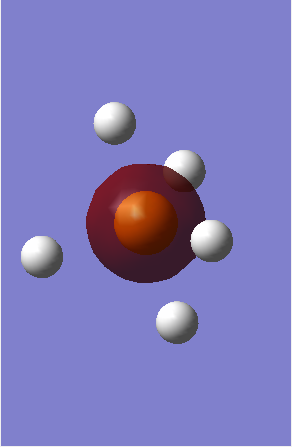 MO2 - Is the 2s non-bonding orbital of Phosphorous with an energy of -6.60693 au
MO2 - Is the 2s non-bonding orbital of Phosphorous with an energy of -6.60693 au
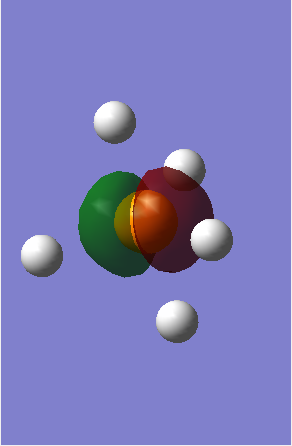 MO3 - Is one of the 2p non-bonding orbitals of Phosphorous with an energy of -4.77017
MO3 - Is one of the 2p non-bonding orbitals of Phosphorous with an energy of -4.77017
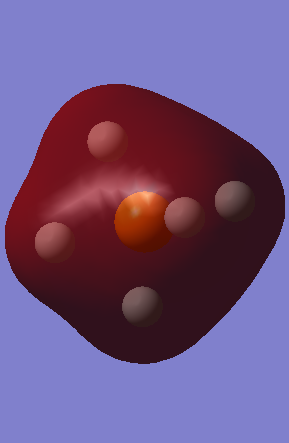 MO6 - Is the complete 1s bonding orbital of all the Hydrogens with the Phosphorous, with an energy of -0.68487 au
MO6 - Is the complete 1s bonding orbital of all the Hydrogens with the Phosphorous, with an energy of -0.68487 au
 MO7 - Is one non-bonding 3p orbital with an energy of -0.42682 interacting with two hydrogens
MO7 - Is one non-bonding 3p orbital with an energy of -0.42682 interacting with two hydrogens
 MO8 - Is another non-bonding 3p orbital, interacting with the three other hydrogens, with an energy of -0.42682
MO8 - Is another non-bonding 3p orbital, interacting with the three other hydrogens, with an energy of -0.42682
 MO10 - With an energy of -0.21463, Mo10 is the HOMO of the PH5 molecule, and contains the 3 anti-bonding 1s orbitals of the trigonal planar Hydrogen atoms, with the two bonding 1s orbitals
MO10 - With an energy of -0.21463, Mo10 is the HOMO of the PH5 molecule, and contains the 3 anti-bonding 1s orbitals of the trigonal planar Hydrogen atoms, with the two bonding 1s orbitals
 MO11 - With an energy of 0.04278, MO11 is the LUMO of the PH5 molecule.
MO11 - With an energy of 0.04278, MO11 is the LUMO of the PH5 molecule.