Rep:Mod:Gorrochategui97
Molecule #1: NH3
The optimisation file is liked to here
Basic information
Bond length
1.01798 Å
Bond angle
105.745°
Calculation Method
RB3LYP
Basis set
6-31G(d,p)
Final energy
-56.55664124 a. u.
RMS gradient
0.00836082 a. u.
Point group
C3v
Output
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000006 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000014 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000009 0.001200 YES
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R2 R(1,3) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R3 R(1,4) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A1 A(2,1,3) 105.7446 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(2,1,4) 105.7446 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(3,1,4) 105.7446 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(2,1,4,3) -111.8637 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
test molecule |
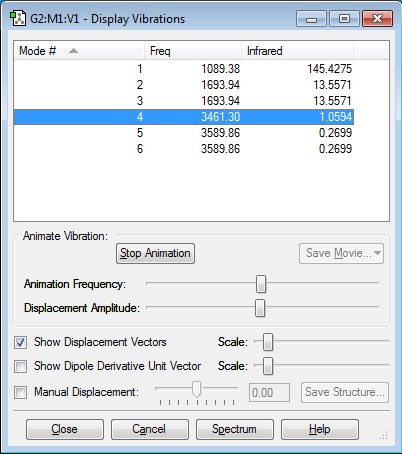
Vibrations
- 6 modes according the 3N-6 rule.
- Modes 2 and 3 (1693.94) and 5 and 6 (3589.86) are degenerate.
- Modes 1, 2 and 3 show bending vibrations, while modes 4, 5 and 6 show stretching vibrations.
- Mode 4 is highly symmetric.
- Mode 1 is known as the umbrella mode.
- 5 bands will appear in the gaseous spectrum, as only mode 4 shows a symmetric stretch.
Charge analysis
Charge of N: -1.125.
Charge of H: 0.375.
N has a negative value due to being more electronegative, so it attracts the electrons of the H atoms.
Molecule #2: N2
The optimisation file is linked to here
Basic information
Bond length
1.10550 Å
Bond angle
180°
Calculation Method
RB3LYP
Basis set
6-31G(d,p)
Final energy
-109.5235911 a. u.
RMS gradient
0.02473091 a. u.
Point group
Dh
Output
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.1055 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
test molecule |
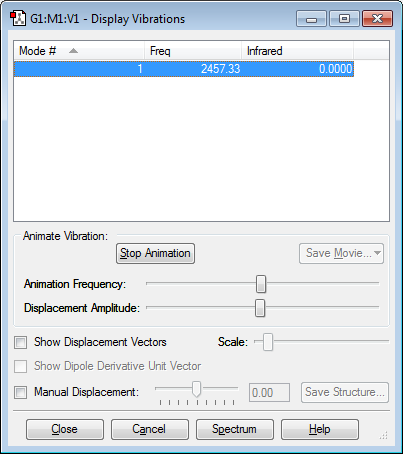
Vibrations
Only one mode of vibration (stretching).
Charge analysis
Apolar bimolecular compound.
Molecule #3: H2
The optimisation file is liked to here
Basic information
Bond length
0.74279 Å
Bond angle
180°
Calculation Method
RB3LYP
Basis set
6-31G(d,p)
Final energy
-1.17853936 a. u.
RMS gradient
0.00000017 a. u.
Point group
Dh
Output
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 0.7428 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
test molecule |
Vibrations
Only one mode of vibration (stretching).
Charge analysis
Apolar bimolecular compound.
Haber-Bosch reaction
N2 + 3H2 ---> 2NH3
Energies
• E(NH3) = -56.55664124 a. u.
• 2E(NH3) = -113.1132825 a. u.
• E(N2) = -109.5235911 a. u.
• E(H2) = -1.17853936 a. u.
• 3E(H2) = -3.53561808 a. u.
• ΔE = 2E(NH3) - [E(N2) + 3E(H2)] = -0.05407332 a. u. = -141.9695017 kJ
Molecule #4: HCl
The optimisation file is liked to here
Basic information
Bond length
1.28599 Å
Bond angle
180°
Calculation Method
RB3LYP
Basis set
6-31G(d,p)
Final energy
-460.80077017 a. u.
RMS gradient
0.00135233 a. u.
Point group
Cv
Output
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000090 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000090 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000139 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000197 0.001200 YES
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.286 -DE/DX = 0.0001 !
test molecule |
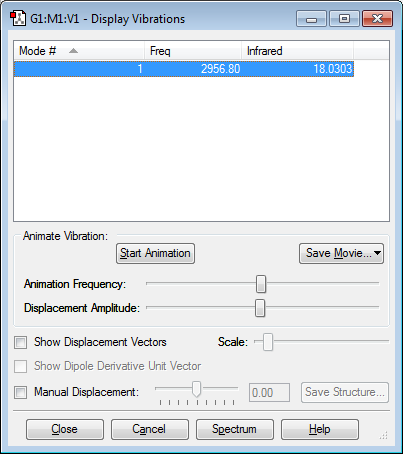
Vibrations
Only one mode of vibration (stretching).
Charge analysis
- Charge of Cl: -0.284.
- Charge of H: 0.284.
- Cl has a negative value due to being more electronegative, so it attracts the electron of the H atom.
Molecular orbitals





Molecule #5: Cl2
The optimisation file is liked to here
Basic information
The optimisation file is liked to here
Bond length
2.04174 Å
Bond angle
180°
Calculation Method
RB3LYP
Basis set
6-31G(d,p)
Final energy
-920.34987886 a. u.
RMS gradient
0.00002511 a. u.
Point group
Dh
Output
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000043 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000043 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000121 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000172 0.001200 YES
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 2.0417 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
test molecule |
Vibrations
Only one mode of vibration (stretching).
Charge analysis
Apolar bimolecular compound.