Rep:Mod:FYD9706
NH3
test molecule |
The optimisation is linked to the file: here
bond length and angle
N-H bond length is 1.01798 Angstroms. H-N-H bond angle is 105.741 degrees.
bond charge
The charge on the N-atom is -1.125c and the charge on the H-atom is 0.375c. Because the the electronegativity of nitrogen is larger than hydrogen.
Calculation Summary
| Parameter | Result |
|---|---|
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d.p) |
| Final Energy in Atomic Units | -56.55776873 au |
| RMS Gradient Norm | 0.00000485 au |
| Point Group | C3V |
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-5.986287D-10
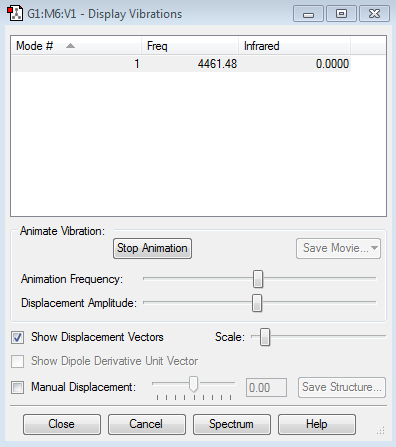
Display Vibrations
How many modes do you expect from the 3N-6 rule?
Six modes.
which modes are degenerate (ie have the same energy)?
Mode 2 and mode 3 are degenerated with frequency of 1693.95cm-1. Mode 5 and mode 6 are degenerated with frequency of 3589.82cm-1.
which modes are "bending" vibrations and which are "bond stretch" vibrations?
Mode 1, 2 and 3 are bending vibrations and mode 4,5 and 6 are bond stretching vibrations.
which mode is highly symmetric?
Mode 4.
one mode is known as the "umbrella" mode, which one is this?
Mode 1.
how many bands would you expect to see in an experimental spectrum of gaseous ammonia?
Because of the degenerated intensity of mode 2 and 3, there will be just two peaks in the spectrum. The intensities of the stretching modes are too small because the changes of dipole moment are small.
H2
test molecule |
The optimisation is linked to the file: here
bond length and charge
H-H bond length is 0.74309 Angstroms.
The charge on hydrogen atom is zero because this molecule consists of two same atoms.
Calculation Summary
| Parameter | Result |
|---|---|
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d.p) |
| Final Energy in Atomic Units | -1.17853936 au |
| RMS Gradient Norm | 0.00000004 au |
| Point Group | D*H |
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-6.835412D-15
Display Vibrations
How many modes do you expect?
One stretching mode and no peak in the spectrum. Because there is no change of dipole moment.
N2
test molecule |
The optimisation is linked to the file: here
bond length and charge
N-N bond length is 1.10550 Angstroms.
The charge on nitrogen atom is zero because this molecule consists of two same atoms.
Calculation Summary
| Parameter | Result |
|---|---|
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d.p) |
| Final Energy in Atomic Units | -109.52412868 au |
| RMS Gradient Norm | 0.17298119 au |
| Point Group | D*H |
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000006 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000006 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000002 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000003 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-1.248809D-11
Display Vibrations
How many modes do you expect?
One stretching mode and no peak in the spectrum. Because there is no change of dipole moment.
Haber-Bosch process
E(NH3)= -56.55776873 au
2*E(NH3)= -113.1155375 au
E(N2)= -109.52416848 au
E(H2)= -1.17853936 au
3*E(H2)= -3.53561808 au
ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]= -0.05575094 au = -146.713 kJ/mol
Since the energy converting hydrogen and nitrogen gas into ammonia gas is negative(exothermic), the ammonia is more stable.
Cl2 (Project Molecule)
test molecule |
The optimisation is linked to the file: here
bond length and charge
Cl-Cl bond length is 2.04155 Angstroms. The charge on nitrogen atom is zero because this molecule consists of two same atoms.
Calculation Summary
| Parameter | Result |
|---|---|
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d.p) |
| Final Energy in Atomic Units | -920.34987886 au |
| RMS Gradient Norm | 0.00001149 au |
| Point Group | D*H |
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000020 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000020 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000056 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000079 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-1.105062D-09
Display Vibrations
How many modes do you expect?
One stretching mode and no peak in the spectrum because there is no change of dipole moment.
Molecular Orbitals
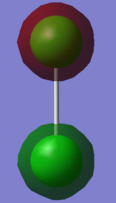
This molecular orbital is an anti-bonding combination of the two 2s atomic orbitals with opposite phases. It is filled by two electrons.

This molecular orbital is an anti-bonding combination of the two 2px atomic orbitals with the opposite phases. It is filled by two electrons.
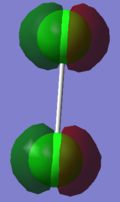
This molecular orbital is a bonding combination of the two 2py atomic orbitals with the same phase. And this is filled by two electrons.

This molecular orbital is the sigma* anti-bonding orbital and is the combination of the two 3s atomic orbitals with opposite phases. And it is filled by two electrons.
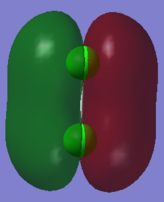
This molecular orbital is the Pi bonding orbital of chlorine molecule. It is the combination of two 3py atomic orbitals with the same phase and is filled by two electrons.