Rep:Mod:EBR1401
NH3 Molecule
Calculation Method; RB3LYP
Basis Set; 6-31G(d,p)
Final Energy - E(RB3LYP); -56.55776873 au
RMS Gradient; 0.00000485
Point Group; C3V
Optimized N-H bond length; 1.01798 A
Optimized H-N-H bond angle; 105.741°
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
NH3 Optimized Molecule |
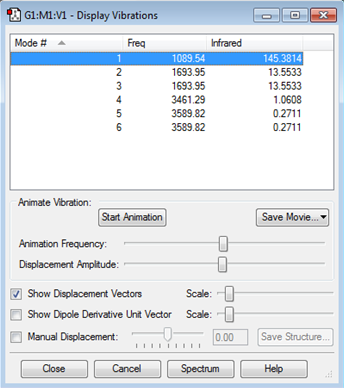
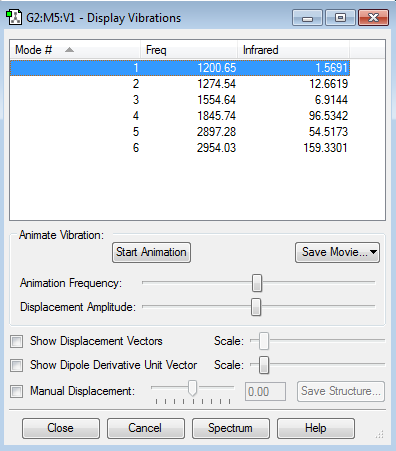
Vibrations
There are 6 vibrational modes observed, as expected from the 3N-6 rule because we have 4 atoms and; 3(4)-6=6. There are 2 pairs of degenerate modes; 2&3 and 5&6 (from the table above). It can also be seen that 1, 2, & 3 are bending vibrations and 4, 5, & 6 are stretching vibrations. The stretching vibration 4 is highly symmetric and bending vibration 1 is known as the "umbrella mode". In an experimental spectrum of gaseous ammonia, 3 bands would be expected to be seen due to the 2 pairs each only showing 1 band between the pair (2), and the highly symmetric mode, 4, not showing a band in the IR spectrum due to this symmetry and then the final mode, 1, showing another band (1).
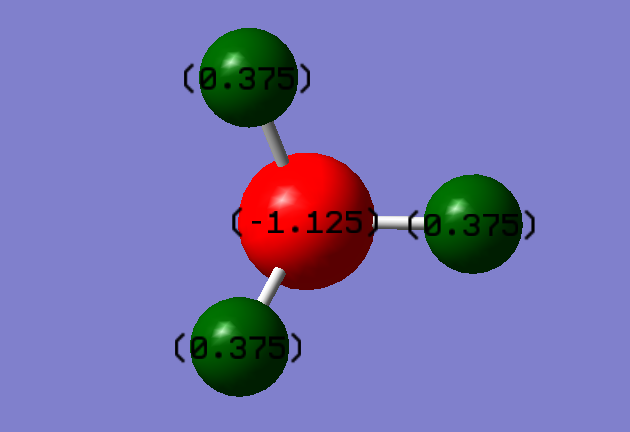
Charges
Charge on N atom; -1.125
Charge on H atoms; 0.375
These charges are as would be expected due to nitrogen being the more electronegative atom of the two.
N2 Molecule
Calculation Method; RB3LYP
Basis Set; 6-31G(d,p)
Final Energy - E(RB3LYP); -109.52412868 au
RMS Gradient; 0.00000060
Point Group; Dinfh
Optimized N-N bond length; 1.10550 A
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
N2 Optimized Molecule |
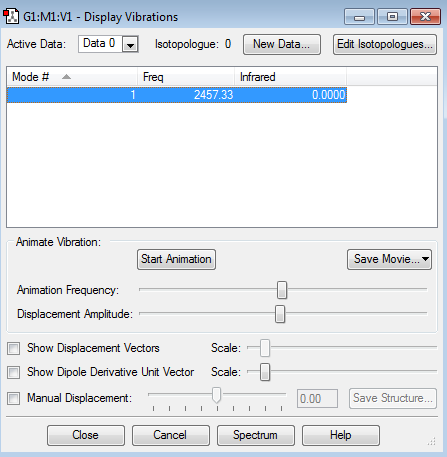
Vibrations
There is only one stretching vibrational mode observed in N2 and, due to the symmetry of the molecule, it is not seen in the IR spectrum. Only one is expected, due to the 3N-5 rule of 2-atom molecules.
Charges
Charge on N atom; 0.00
As expected, there is no charge on either N atom as they are equivalent and so there is no overall net charge.
H2 Molecule
Calculation Method; RB3LYP
Basis Set; 6-31G(d,p)
Final Energy - E(RB3LYP); -1.17853936 au
RMS Gradient; 0.00000017
Point Group; Dinfh
Optimized H-H bond length; 0.74279 A
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES
H2 Optimized Molecule |
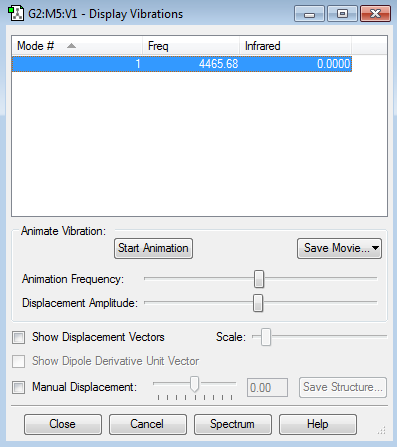
Vibrations
There is only one stretching vibrational mode observed in H2 as expected, from the 3N-5 rule of 2-atom molecules. Again, due to the symmetry of the molecule, the vibration is also not seen in the IR spectrum.
Charges
Charge on H atom; 0.00
As expected, there is no charge on either of the H atoms as they are equivalent to each other and so there is no overall net charge.
The Haber-Bosch Process
Ammonia can be synthesized in a reaction known as the Haber-Bosch process where gaseous hydrogen and nitrogen are reacted together to form ammonia. it is a reversible process with specific conditions to ensure a good yield and rate of reaction of the product, ammonia.
N2 + 3H2 --> 2NH3
E(NH3)= -56.55776873
2*E(NH3)= -113.11553746
E(N2)= -109.52412868
E(H2)= -1.17853936
3*E(H2)= -3.53561808
ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]= -0.0557907 au = -146.48 kJ/mol
This value of -146.48 kJ/mol is much higher than that of literature values around -45.7 kJ/mol [1]
Ammonia, the product, is more stable; as indicated by the negative energy change so the products are obviously of lower energy and most stable.
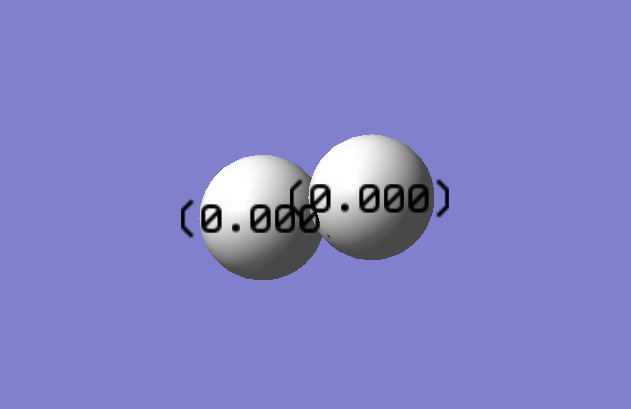
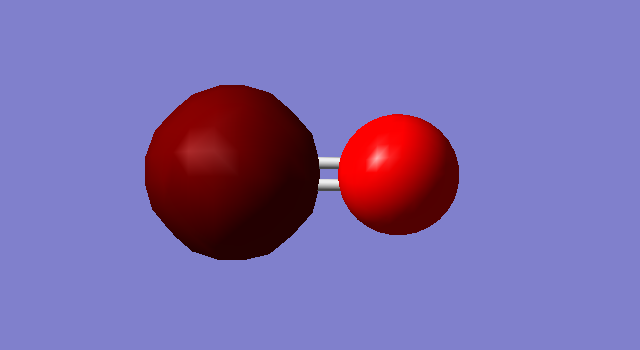
C=O Molecule
Calculation Method; RB3LYP
Basis Set; 6-31G(d,p)
Final Energy - E(RB3LYP); -113.30945314 au
RMS Gradient; 0.00001828
Point Group; Cinfv
Optimized C=O bond length; 1.13793 A
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000032 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000032 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000012 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000018 0.001200 YES
C=O Optimized Molecule |
Vibrations
There is only one vibration seen in the molecule of C=O- a stretch of the double bond.
Charges
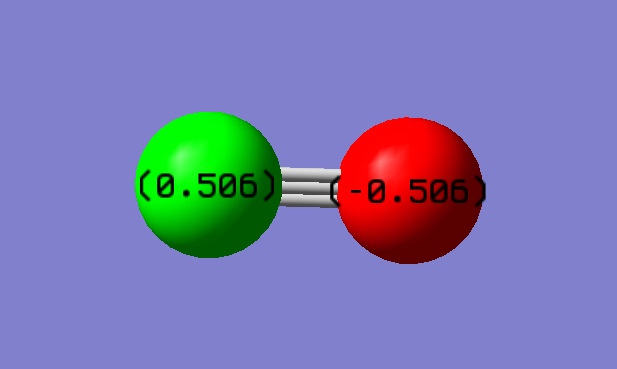
Charge on C atom; 0.506
Charge on O atoms; -0.506
The charges on the two atoms and equal but opposite; as expected on a 2 atom molecule with no net charge. Also, as expected, the oxygen is the atom with the negative charge; it is the more electronegative charge so is the atom most able to attract the electrons in the bond.
Molecular Orbitals
Molecular Orbital 1
Molecular Orbital 2
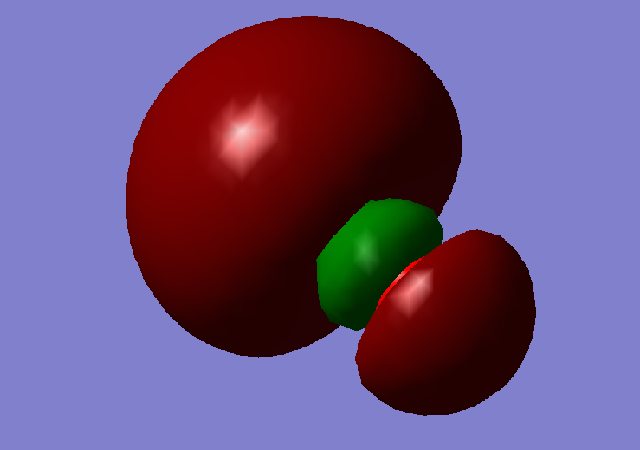
Molecular orbitals 1 and 2 show the bonding and antibonding orbitals of the two 1s AO's. they are very deep in energy at -19.25805 and -10.30433, respectively, this is much deeper than the valence MO's and thus we know that they do not take part in the chemical bonding of the molecule.
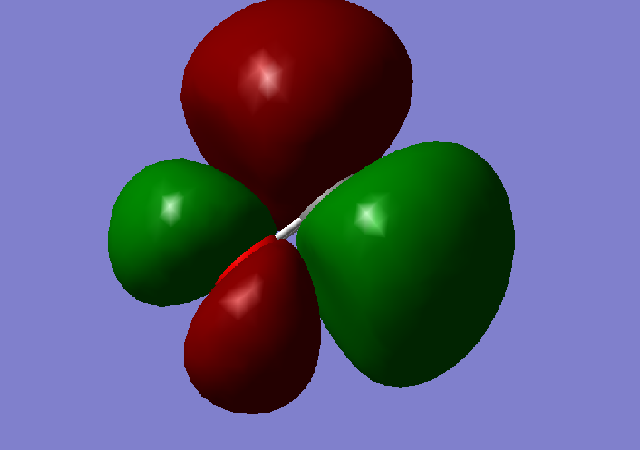
Molecular Orbital 3; This is the highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO), formed from the mixing of 2s and 2p orbitals of the carbon and oxygen. It is a bonding orbital (5σ).
Molecular Orbital 4; This is the lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO), it is the corresponding antibonding orbital (2π) to the MO below (1π).
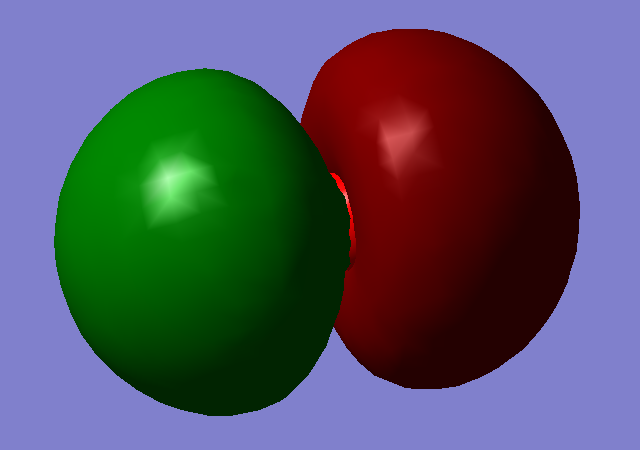
Molecular Orbital 5; This is the bonding orbital formed from the two 2p AO's. It is the first π MO to occur in the molecule of C=O.
Formation of C=O
One way to synthesise C=O is from the reaction of carbon dioxide, CO2, with hydrogen gas to form C=O and water.
CO2 (g) + H2(g) --> CO(g) + H2O(g)
CO2
Calculation Method; RB3LYP
Basis Set; 6-31G(d,p)
Final Energy - E(RB3LYP); -188.58093945 au
RMS Gradient; 0.00001154
Point Group; Dinfh
Optimized C-O bond length; 1.16915 A
Optimized O-C-O bond angle; 180°
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000024 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000017 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000021 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000015 0.001200 YES
CO2 Optimized Molecule |
H2O
Calculation Method; RB3LYP
Basis Set; 6-31G(d,p)
Final Energy - E(RB3LYP); -76.41973740 au
RMS Gradient; 0.00006276
Point Group; C2V
Optimized O-H bond length; 0.96522 A
Optimized H-O-H bond angle; 103.745°
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000099 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000081 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000115 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000120 0.001200 YES
H2O Optimized Molecule |
CO2 (g) + H2(g) --> CO(g) + H2O(g)
E(CO)= -113.30945314
E(H2O)= -76.41973740
E(CO2)= -188.58093945
E(H2)= -1.17853936
ΔE= [E(CO)+E(H20)]-[E(CO2)+E(H2)]= 0.03028827 au = 79.52 kJ/mol
This value of 79.52 kJ/mol is higher than that of the literature value of 41 kJ/mol[2], this may be due to approximations used in Gaussian leading to this error.
H2CO Molecule
Calculation Method; RB3LYP
Basis Set; 6-31G(d,p)
Final Energy - E(RB3LYP); -114.50319933 au
RMS Gradient; 0.00007386
Point Group; CS
Optimized C=O bond length; 1.20676 A
Optimized C-H bond length; 1.11056 A
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000197 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000085 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000232 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000149 0.001200 YES
HC=O Optimized Molecule |
Vibrations
There are 6 non degenerate vibrational modes of H2CO.
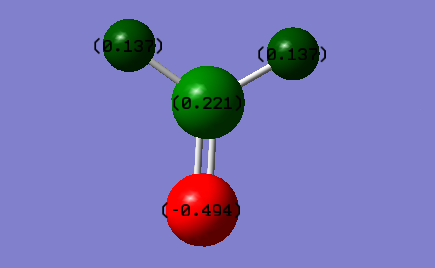
Charges
Charge on C atom; 0.221
Charge on O atom; -0.494
Charge on H atoms; 0.137
These charges are as would be expect because the O atom is the most electonegative however the C=O bond is not as polar as the C=O bond in the C=O molecule above due to the hydrogen's also having a positive electronegativity.
Preparation of Formaldehyde
H2CO can be prepared via the dehydrogenation of methane, CH3OH.
CH3OH --> CH2O + H2
CH3OH
Calculation Method; RB3LYP
Basis Set; 6-31G(d,p)
Final Energy - E(RB3LYP); -115.72396437 au
RMS Gradient; 0.00001494
Point Group; C1
Optimized C-O bond length; 1.41811 A
Optimized C-H bond length; 1.09302 A
Optimized O-H bond length; 0.96520 A
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000038 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000020 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000507 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000240 0.001200 YES
HCOH Optimized Molecule |
CH3OH --> CH2O + H2
E(CH2O)= -114.50319933
E(H2)= -1.17853936
E(CH3OH)= -115.72396437
ΔE= [E(CH2O)+E(H2)]-[E(CH3OH)]= 0.04222568 au = 110.86 kJ/mol
The value of 110.86 kJ/mol is slightly higher than the literature value of 84 kJ/mol [3] but it much closer than other enthalpies calculated above using Gaussian.