Rep:Mod:DY991021
NH3 molecule
General data
| molecule name | NH3 |
| N-H bond length | 1.01798Å |
| H-N-H bond angle | 105.741º |
| calculation method | RB3LYP |
| basis set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| final energy E in atomic units (au) | -56.44397188 |
| point group | C3V |
Item table
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
Jmol animation
Optimised NH |
Media:DY_NH3_OPTIMISATION_POP.LOG
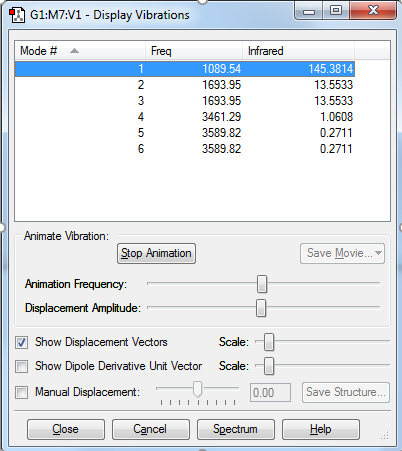
Vibration modes of NH3
The NH3 molecule is expected to have 6 modes according to the 3N-6 rule for non-symmetric particles.
As can be seen from the screen shot, Mode 2 and 3 are degenerate ,as well as Mode 5 and 6.
Mode 1,2,3 are bending vibrations due to the low frequency while Mode 4,5,6 are stretching vibrations.
Mode 4 is highly symmetric. Mode 1 is also called umbrella due to its unique movements. 4 bands would be seen in an experimental spectrum of gaseous ammonia
Particle charge on NH3
| Atom | Charge |
|---|---|
| H | +0.375 |
| N | -1.125 |
Since Nitrogen is more electronegative than Hydrogen, electrons between Nitrogen and Hydrogen tends to move closer to the Nitrogen atom. Therefore, charge on the Nitrogen is more negative, while Hydrogen is more positive.
H2 molecule
General data
| molecule name | H2 |
| H-H bond length | 0.74279Å |
| H-N-H bond angle | 180º |
| calculation method | RB3LYP |
| basis set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| final energy E in atomic units (au) | -1.17853936 |
| point group | D*H |
Item table
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES
Jmole animation
Optimised NH |
Media:DY_H2_OPTIMISATION_POP.LOG
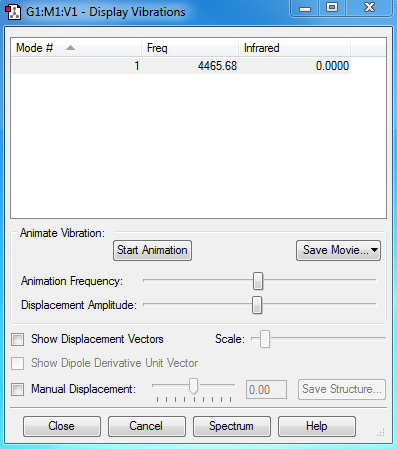
Vibration modes of H2
Particle charge on H2
It is a linear diatomic molecule, the two atoms are of the same element, therefore, they have the same electonegativity and the charge is hence zero.
N2 molecule
General data
| molecule name | N2 |
| H-H bond length | 1.0550Å |
| H-N-H bond angle | 180º |
| calculation method | RB3LYP |
| basis set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| final energy E in atomic units (au) | -109.52412868 |
| point group | D*H |
Item Table
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
Jmole animation
Optimised NH |
Media:DY_N2_OPTIMISATION_POP.LOG
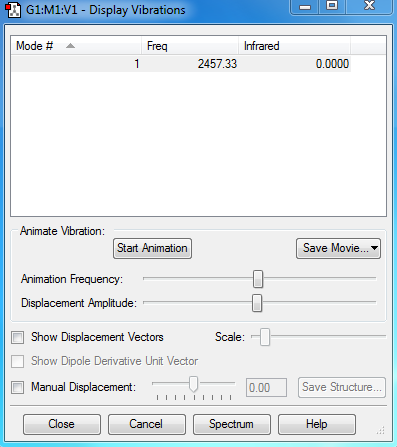
Vibration modes of N2
Particle charge on N2
It is a linear diatomic molecule, the two atoms are of the same element, therefore, they have the same electonegativity and the charge is hence zero.
Reaction energy
Haber process is a reaction that is widely used in the industry in order to converts Hydrogen and Nitrogen into Ammonia.
N2 + 3H2--> 2NH3
| H2 | -1.17853936 |
| N2 | -109.52412868 |
| NH 3 | -56.55776873 |
| ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)] | -0.0557907 |
ΔE=-0.0557907 au=-146.48 KJ/mol
Since the energy of Ammonia is lower, it is more stable.
Methane CH4 Molecule
General data
| molecule name | CH4 |
| C-H bond length | 1.09197Å |
| H-C-H bond angle | 109.47122º |
| calculation method | RB3LYP |
| basis set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| final energy E in atomic units (au) | -40.52401404 |
| point group | TD |
Item Table
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000063 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000034 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000179 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000095 0.001200 YES
Jmol animation
Optimised NH |
Media:DY_CH4_OPTIMISATION_POP.LOG
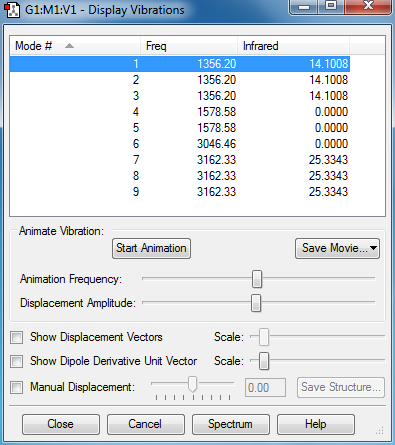
Vibration modes of CH4
Methane Molecule is expected to have 9 modes according to the 3N-6 rule.
As can be seen from the screen-shot above, Mode 1,2 and 3 are degenerate bending vibrations. Mode 4,5 and 6 are also degenerate, however, mode 4 and 5 are symmetric bending vibrations while mode 6 is a symmetric stretching vibration. Mode 7, 8 and 9 are degenerate as well but these are stretching vibrations.
Particle Charge on CH4
| Atom | Charge |
|---|---|
| C | -0.930 |
| H | +0.233 |
Methane is a polar molecule. Carbon atom is slightly more electronegative than Hydrogen, therefore, electrons tend to be closer to the central carbon centre. Hence, Carbon has a negative charge of -0.930 while Hydrogen atoms have a positive charge of +0.233.
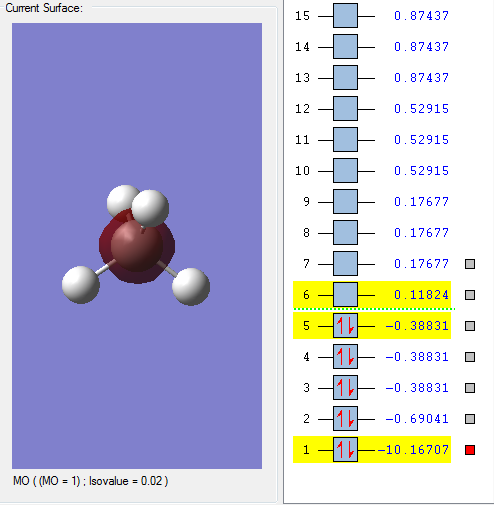
Molecular orbitals
This is the 1s orbital of the Carbon atom. It is an occupied orbital but not combined orbital since electrons in the hydrogen atom doesn't contribute anything. The orbital is deep in energy since the energy, as shown, is negative.
This MO is generated by combining the 2s orbital of the Carbon atom and the 1s orbital of the hydrogen atom. It is an occupied orbital which is deep in energy. This is due to the relatively high negative energy as shown on the screen-shot. The MO is also formed as a bonding orbital since the s-orbitals from the carbon atom and the hydrogen atom doesn't cancel each other out.
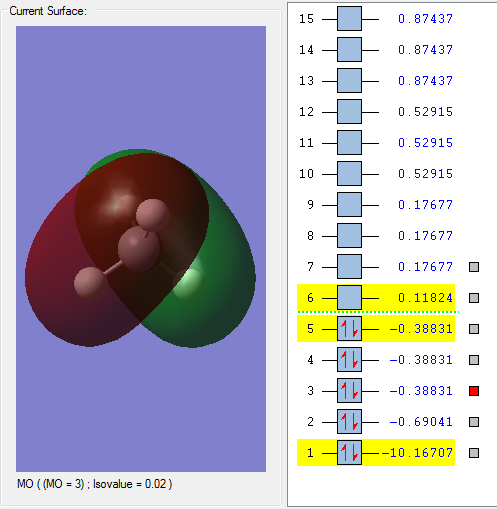
These 3 MOs are degenerate as can be seen from the screen-shot. They are generated by combing the 2p orbital of the carbon atom with the 1s orbital of the hydrogen atom. 3 MO can be formed since p-orbital has 3 different arrangements. These three MOs are in the HOMO because they have the highest energy within all the occupied orbitals as shown on the picture. All the 3 orbitals are bonding orbitals and they tighten the chemical bond of the Molecule.