Rep:Mod:CompChemEkart
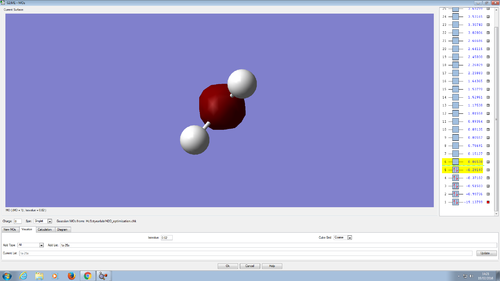
Ammonia
| Paramater | Data |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | NH3 |
| Calculation method | RB3LYP |
| Basis set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Final energy | -56.55776873 a.u. |
| RMS gradient | 0.00000485 a.u. |
| Point group | C3v |
| N-H bond length | 1.01798 Å |
| H-N-H bond angle | 105.741° |
| Item | Value | Threshold | Converged? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum Force | 0.000004 | 0.000450 | YES |
| RMS Force | 0.000004 | 0.000300 | YES |
| Maximum Displacement | 0.000072 | 0.001800 | YES |
| RMS Displacement | 0.000035 | 0.001200 | YES |
Ammonia |
The optimisation file is located here.
The template required to crop the image was acquired from Wikipedia.
6 vibrational modes are to be expected from 3N-6 rule. There are two pairs of vibrational modes that are degenerate, namely 2 and 3, and 5 and 6. 1-3 are bending modes, while 4-6 are stretching modes. Vibrational mode number 4 is highly symmetric. Number 1 is also known as umbrella mode. In the spectrum there would probably be 4 bands, but the ones corresponding to bond stretches would be much less distinct.
Charge distribution is -1.125 for N atom and 0.375 for H atoms. Nitrogen is more electronegative than hydrogen, which means that such charges are to be expected.
Hydrogen
| Paramater | Data |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | H2 |
| Calculation method | RB3LYP |
| Basis set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Final energy | -1.15928020 a.u. |
| RMS gradient | 0.09719500 a.u. |
| Point group | D∞h |
| H-H bond length | 0.74279 Å |
Hydrogen |
| Item | Value | Threshold | Converged? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum Force | 0.000000 | 0.000450 | YES |
| RMS Force | 0.000000 | 0.000300 | YES |
| Maximum Displacement | 0.000000 | 0.001800 | YES |
| RMS Displacement | 0.000001 | 0.001200 | YES |
Nitrogen
| Paramater | Data |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | N2 |
| Calculation method | RB3LYP |
| Basis set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Final energy | -109.52412868 a.u. |
| RMS gradient | 0.00000060 a.u. |
| Point group | D∞h |
| N-N bond length | 1.10550 Å |
Nitrogen |
| Item | Value | Threshold | Converged? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum Force | 0.000001 | 0.000450 | YES |
| RMS Force | 0.000001 | 0.000300 | YES |
| Maximum Displacement | 0.000000 | 0.001800 | YES |
| RMS Displacement | 0.000000 | 0.001200 | YES |
Energetic balance of formation of ammonia
E(NH3)=-56.55776873 a.u.
2*E(NH3)=-113.11553746 a.u.
E(N2)=-109.52412868 a.u.
E(H2)=-1.17853936 a.u
3*E(H2)=-3.53561808 a.u.
ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]=-0.05579070 a.u.
This means that the reaction enthalpy is ΔH=-146.48 kJ/mol. This is implying that ammonia gas is more stable than hydrogen and nitrogen gas on their own.
Water
| Paramater | Data |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | H2O |
| Calculation method | RB3LYP |
| Basis set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Final energy | -76.41973740 a.u. |
| RMS gradient | 0.00006276 a.u. |
| Point group | C2v |
| O-H bond length | 0.96522 Å |
| H-O-H bond angle | 103.745° |
Water |
| Item | Value | Threshold | Converged? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum Force | 0.000099 | 0.000450 | YES |
| RMS Force | 0.000081 | 0.000300 | YES |
| Maximum Displacement | 0.000114 | 0.001800 | YES |
| RMS Displacement | 0.000119 | 0.001200 | YES |
| Reciprocal wavelength (cm-1) | Relative intensity |
|---|---|
| 1665.00 | 70.3477 |
| 3801.05 | 1.6431 |
| 3914.23 | 20.2475 |
Relative charges on hydrogen atoms are 0.472, while on oxygen atom it is -0.944.
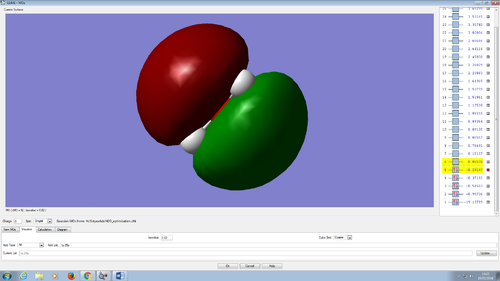
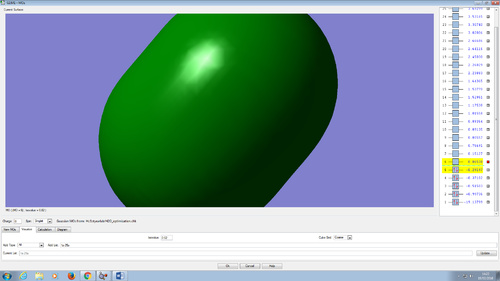
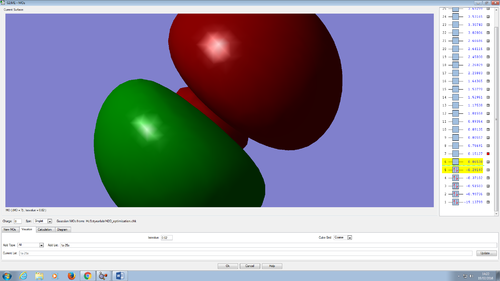
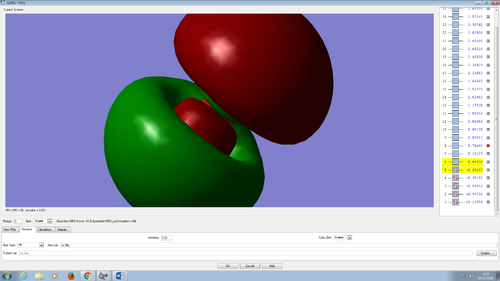
Molecular orbitals in water molecule
All the molecular orbitals are shown from the same perspective and at the same size. They are shown in increasing order of energy
Hydrogen peroxyde
| Paramater | Data |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | H2O2 |
| Calculation method | RB3LYP |
| Basis set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Final energy | -151.54211147 a.u. |
| RMS gradient | 0.00002366 a.u. |
| Point group | C2h |
| O-O bond length | 1.46642 Å |
| O-H bond length | 0.96948 Å |
| H-O-O bond angle | 98.248° |
Hydrogen peroxide |
The data shown is close to the real data, but not quite alright, because the wrong structure has been achieved.
| Item | Value | Threshold | Converged? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum Force | 0.000045 | 0.000450 | YES |
| RMS Force | 0.000023 | 0.000300 | YES |
| Maximum Displacement | 0.000064 | 0.001800 | YES |
| RMS Displacement | 0.000041 | 0.001200 | YES |
Relative charges on hydrogen atoms are 0.483, while on oxygen atoms they are -0.483.