Rep:Mod:Chem1235058
NH3 Molecule
Information Output
Molecular formula: NH3
Calculation method: RB3LYP
Basis set: 6-31G(d.p)
E(R3BLYP): -56.55640542 a.u
RMS gradient: 0.00980112 a.u
Point group: C3v
N-H Bond distance: 1.03844 Angstroms
H-N-H Bond angle: 101.721 degrees
Geometry Information
Item Value Threshold Converged?<br>
Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES<br>
RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES<br>
Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES<br>
RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES<br>
Predicted change in Energy=-5.986281D-10<br>
Optimization completed.<br>
-- Stationary point found.<br>
----------------------------<br>
! Optimized Parameters !<br>
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !<br>
-------------------------- --------------------------<br>
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !<br>
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------<br>
! R1 R(1,2) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !<br>
! R2 R(1,3) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !<br>
! R3 R(1,4) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !<br>
! A1 A(2,1,3) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !<br>
! A2 A(2,1,4) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !<br>
! A3 A(3,1,4) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !<br>
! D1 D(2,1,4,3) -111.8571 -DE/DX = 0.0 !<br>
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------<br>
Optimized Ammonia
Calculation method: RB3LYP
Basis Set: 6-31G(d.p)
Final Energy E(RB3LYP): -56.55776873 a.u
Point Group: C3V
Jmol
[NB1516_NH3_OPT.LOG ]
test molecule |
Geometry Information of Optimized Ammonia:
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-5.986281D-10 Optimization completed. -- Stationary point found. ---------------------------- ! Optimized Parameters ! ! (Angstroms and Degrees) ! -------------------------- -------------------------- ! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. ! -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ! R1 R(1,2) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 ! ! R2 R(1,3) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 ! ! R3 R(1,4) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 ! ! A1 A(2,1,3) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 ! ! A2 A(2,1,4) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 ! ! A3 A(3,1,4) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 ! ! D1 D(2,1,4,3) -111.8571 -DE/DX = 0.0 ! --------------------------------------------------------------------------------
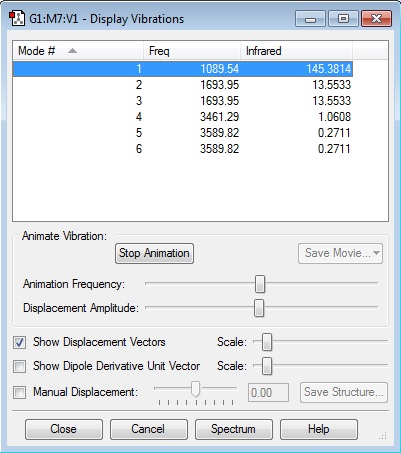
Vibrational Analysis
Link here
Number of vibrational modes: (12-6)= 6
Degeneracy: modes 2 & 3 and 5 & 6 have the same energy
Types of vibrations -those that are stretch: 1,4,5,6 -those that are bend: 2 & 3
The highly symmetric mode is 4 as it does not change the symmetry of the molecule.
The umbrella mode is mode 1.
In the experimental spectrum of ammonia there are 6 different modes but 2 cases of degeneracy- so I would expect to see 4.
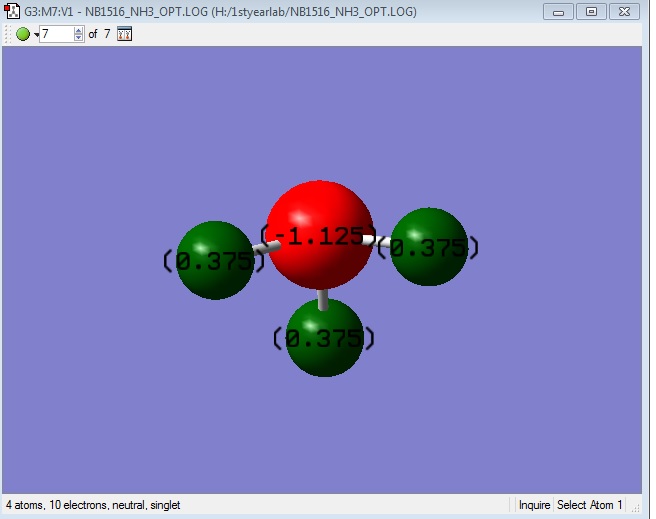
Charge Distribution
Nitrogen Molecule
Formula: N2
After Optimization :
N-N bond distance: 1.10550 Angstroms
N2 is linear and hence N-N triple bond angle is 180 degrees.
Calculation method: RB3LYP
Basis set: 6-31G(d.p)
E(R3BLYP): -109.52412868 a.u
RMS gradient: 6.0 x 10-7 a.u
Point group: D*H
Diatomic nitrogen is a symmetric covalent molecule (with no formal charge) and hence has symmetric electron distribution over the molecule.
Geometry Information
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000200 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000200 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000062 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000088 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.246449D-08
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.1056 -DE/DX = -0.0002 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Vibrational Analysis
Link: here
Jmol
test molecule |
Link: here
Hydrogen Molecule
Formula: H2
After Optimization :
H-H bond distance:0.74279 Angstroms
H2 is linear and hence H-H bond angle is 180 degrees.
Calculation method: RB3LYP
Basis set: 6-31G(d.p)
E(R3BLYP): -1.17853936 a.u
RMS gradient: 4.0 x 10-8 a.u
Point group: D*H
Diatomic hydrogen is a symmetric covalent compound (with no formal charge) and therefore symmetric electron distribution over the molecule.
Geometry Information
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-6.835427D-15
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 0.7428 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Vibrational Analysis
Link: here
Jmol
test molecule |
Link: here
Haber-Bosch Process
The Haber-Bosch process is used to make ammonia from gaseous hydrogen and nitrogen. It is a thermodynamically unfavourable process and hence very high pressure is needed to drive the equilibrium towards the product: ammonia. A low temperature favours formation of ammonia, however the activation energy is very high so heat energy is needed to overcome this energy barrier. To overcpome the activation energy but not drive the equilibrium too far towards the reactants, and iron oxide catalyst is used to lower the energy barrier.
The equation for the reaction is: N2 = 3H2 --> 2NH3
Enthalpy Changes
E(NH3)= -148492.50 kJmol-1
2*E(NH3)= -296985.01 kJmol-1 E(N2)= -287555.26 kJmol-1 E(H2)= -3094.26 kJmol-1 3*E(H2)= -9282.77 kJmol-1 ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]= -296985.01 - (-287555.26 - 9282.77) = -146.98 kJmol-1
The reactants are more stable than the product, since the N-N triple bond is very strong, hence why diatomic nitrogen is at such an exothermic energy value. Also 4 moles of gas go to 2 moles of ammonia as illustrated in the reaction equation, which is unfavorable by the second law of thermodynamics.
Chlorine Molecule
Information Output
Molecular formula: Cl2
Calculation method: RB3LYP
Basis set: 6-31G(d.p)
E(R3BLYP): -920.34987886 a.u
RMS gradient: 0.00002511 a.u
Point group: D*H
Cl-Cl Bond distance: 2.04174 Angstroms
Cl-Cl Bond angle: 180 degrees (linear molecule)
Diatomic chlorine is a symmetric covalent molecule with no formal charge, it has symmetrical electron distribution over the molecule.
Geometry Information
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000043 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000043 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000121 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000172 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-5.277248D-09
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 2.0417 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Vibrational Analysis
Link here