Rep:Mod:CY01180359
NH3 molecule
Basic Information
The molecule: NH3
Calculation Method: RB3LYP
Basis Set: 6-31G(d,p)
E(RB3LYP): -56.55776873 a.u.
RMS Gradient Norm: 0.00000485 a.u.
Point Group: C3V optimised
N-H bond distance: 1.01798 A literature value: 1.012 A [1]
optimised
H-N-H bond angle: 105.741° literature value: 106.7° [1]
Dipole Moment: 1.8466 D literature value: 1.73 D [2]
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-5.986285D-10
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R2 R(1,3) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R3 R(1,4) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A1 A(2,1,3) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(2,1,4) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(3,1,4) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(2,1,4,3) -111.8571 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
test molecule |
The optimisation file is liked to here
Vibrational and charge analysis
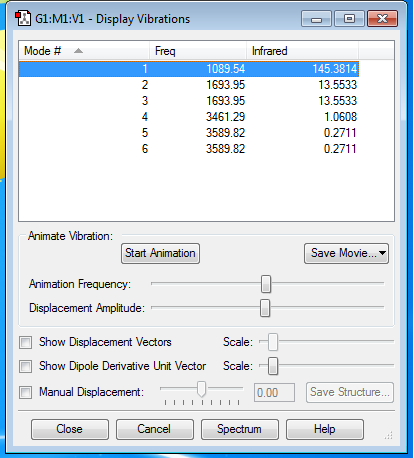
how many modes do you expect from the 3N-6 rule?: 6
which modes are degenerate (ie have the same energy)?: 2&3 and 5&6
which modes are "bending" vibrations and which are "bond stretch" vibrations?: Bending: 2, 3; Stretch: 1, 4, 5 and 6
which mode is highly symmetric?: 1, 3, 4 and 6
one mode is known as the "umbrella" mode, which one is this?: 1
how many bands would you expect to see in an experimental spectrum of gaseous ammonia?: 4
Charge on N: -1.125
Charge on H: 0.375
I expect N to carry a negative charge and Hs to carry positive charges because N is more electronegative than H
N2 Molecule
The molecule: N2
Calculation Method: RB3LYP
Basis Set: 6-31G(d,p)
E(RB3LYP): -109.52412868 a.u.
RMS Gradient Norm: 0.00000060 a.u.
Point Group: D∞h optimised
N-N bond distance: 1.10550 A literature value: 1.10 A [3] optimised
N-N bond angle: 180°
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-3.401023D-13
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.1055 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
test molecule |
The optimisation file is liked to here
Vibration: Freq 2457.33cm-1 Infrared 0.0000
H2 Molecule
The molecule: H2
Calculation Method: RB3LYP
Basis Set: 6-31G(d,p)
E(RB3LYP): -1.17853936 a.u.
RMS Gradient Norm: 0.00000017 a.u.
Point Group: D∞h optimised
H-H bond distance: 0.74279 A literature value: 0.74 A optimised
H-H bond angle: 180°
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.164080D-13
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 0.7428 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
test molecule |
The optimisation file is liked to here
Vibration: Freq 4465.68cm-1 Infrared 0.0000
Haber reaction Energy
For the reaction: N2 + 3H2 -> 2NH3
E(NH3)=-56.55776873 a.u.
2*E(NH3)=-113.11553746 a.u.
E(N2)=-109.52412868 a.u.
E(H2)=-1.17853936 a.u.
3*E(H2)=-3.53561808 a.u.
ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]=-0.0557807 a.u. =-146.45 kJ/mol. Literature value: -91.8 kJ/mol [4]
Therefore NH3 gas is more energetically stable
CO molecule
The molecule: CO
Calculation Method: RB3LYP
Basis Set: 6-31G(d,p)
E(RB3LYP): -113.30945314 a.u.
RMS Gradient Norm: 0.00001828 a.u.
Dipole Moment: 0.0599 Debye
Point Group: C∞V optimised
C-O bond distance: 1.13793 A literature value: 1.128 A [5] optimised
C-O bond angle: 180°
Vibrational Freq: 2209.14 cm-1, Infrared: 67.9587 Literature value for Freq: 2139 cm-1 [6]
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000032 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000032 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000012 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000018 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-3.956716D-10
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.1379 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
test molecule |
The optimisation file is liked to here
- 3 sigma orbital, mainly contributed from the 2s orbitals from both C and O. The energy of it is -1.15791 a.u., a deep-energy occupied bonding orbital. It will definitely contributes a lot to the overall bonding of the molecule.
- 4 sigma orbital, mainly contributed from the 2s orbitals from both C and O, and also the 2pz orbitals from the two atoms. The energy of it is -0.57004 a.u., an occupied antibonding orbital whose energy is near the HOMO_LUMO region. It destabilises the diatomic molecule by a small extent.
- 1 pi orbital, mainly contributed from the 2px orbitals from both C and O. The energy of it is -0.46743 a.u., an occupied bonding orbital whose energy is near the HOMO_LUMO region. It will contributes a lot to the overall bonding of the molecule as it extends to the whole molecule. There is another degenerate 1 pi orbital formed from the 2py orbitals from the two atoms.
- 5 sigma orbital, mainly contributed from the 2pz orbitals from both C and O, and also the 2s orbitals from the two atoms. The energy of it is -0.37145 a.u., an occupied bonding HOMO orbital. It stablises the diatomic molecule by a small extent. It is also involved in lots of reactions as a frontier orbital.
- 2 pi orbital, mainly contributed from the 2px orbitals from both C and O, in which C contributes a larger part. The energy of it is -0.02177 a.u., an unoccupied antibonding LUMO orbital. It will destabilises the overall molecule as an antibonding molecule, and it is also involved in lots of reactions as a frontier orbital. There is another degenerate 2 pi antibonding orbital formed from the 2py orbitals from the two atoms.
Charge on O: -0.506
Charge on C: 0.506
I expect O to carry a negative charge and C to carry a positive charge because O is more electronegative than C
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 94th ed. Page 9-26. Retrieved 18 June 2013.
- ↑ Calculation of the Dielectric Constant of Water to 1000°C and Very High Pressures, E. U. Franck; S. Rosenzweig; M. Christoforakos, February 1990.
- ↑ Huheey, pps. A-21 to A-34; T.L. Cottrell, "The Strengths of Chemical Bonds," 2nd ed., Butterworths, London, 1958; B. deB. Darwent, "National Standard Reference Data Series," National Bureau of Standards, No. 31, Washington, DC, 1970; S.W. Benson, J. Chem. Educ., 42, 502 (1965).
- ↑ Mechanistic aspects of dinitrogen cleavage and hydrogenation to produce ammonia in catalysis and organometallic chemistry: relevance of metal hydride bonds and dihydrogen, Hong-Peng Jia and Elsje Alessandra Quadrelli, 9th October 2013
- ↑ Gilliam, O. R.; Johnson, C. M.; Gordy, W. (1950). "Microwave Spectroscopy in the Region from Two to Three Millimeters". Physical Review. 78 (2): 140–144
- ↑ Giuliano, B. M., Escribano, R. M., Martín-Doménech, R., Dartois, E. & Muñoz Caro, G. M. Interstellar ice analogs: band strengths of H 2 O, CO 2 , CH 3 OH, and NH 3 in the far-infrared region. Astron. Astrophys. 565, A108 (2014).