Rep:Mod:CON8765
Wiki page Computational Chemistry
By Conor Crooks 01364619
NH 3
Questions
What is the molecule? NH3 Ammonia
What is the calculation method? RB3LYP
What is the basis set? 6-31G(d,p)
What is the final energy E(RB3LYP) in atomic units (au)? -56.44397188 a.u.
What is the RMS gradient? 0.00000485 a.u.
What is the point group of your molecule? C3V
Optimised bond length = 1.01798 Å
Optimised bond angle = 105.741
Optimisation
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
Jmol and File Link
NH3 Optimisation 01364619 |
Vibration Frequencies and questions
| Mode # | Frequency | Infrared |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1089.54 | 145.3814 |
| 2 | 1693.95 | 13.5533 |
| 3 | 1693.95 | 13.5533 |
| 4 | 3461.29 | 1.0608 |
| 5 | 3589.82 | 0.2711 |
| 6 | 3589.82 | 0.2711 |
How many modes do you expect from the 3N-6 rule? 6 modes of vibration
Which modes are degenerate (ie have the same energy)? 2 and 3 are degenerate as are 5 and 6
Which modes are "bending" vibrations and which are "bond stretch" vibrations? 1,2,3 are bending, 4,5,6 are stretching.
Which mode is highly symmetric? 4
One mode is known as the "umbrella" mode, which one is this? 1
How many bands would you expect to see in an experimental spectrum of gaseous ammonia?
Several peaks would be visible, however only two stand out clearly. The first peak is at ~1000 cm-1 but would be obscured as this is the fingerprint region of the spectrum, this peak is caused by mode 1. Another peak would appear at ~1700 cm-1 which is caused by modes 2 and 3 which are degenerate. The final peak would be at ~3400 cm-1, it would be smaller than the second peak as only one vibrational mode causes it, mode 4. The final two vibrational modes would not cause a peak due to being obscured by noise from the experiment. [1]
Charges
I would expect Nitrogen to be negative and hydrogen to be positive as nitrogen is more electronegative than hydrogen, therefore attracts more electron density.

Charges on the atoms: N = -1.125 H = 0.375
N 2
Questions
What is the molecule? N2 Diatomic nitrogen
What is the calculation method? RB3LYP
What is the basis set? 6-31G(d,p)
What is the final energy E(RB3LYP) in atomic units (au)? -109.52412868 a.u.
What is the RMS gradient? 0.00000060 a.u.
What is the point group of your molecule? D∞h
Optimised bond length = 1.10550 Å
Optimised bond angle = 180.0
Optimisation
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
Jmol and File Link
N2 Optimisation 01364619 |
Vibration Frequencies
| Mode # | Frequency | Infrared |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2457.33 | 0.0000 |
Charges
No charges as a homo-nuclear diatomic, therefore have the same electronegativity value and as such the electron density is shared equally between them.
H2
Questions
What is the molecule? H2 Diatomic hydrogen
What is the calculation method? RB3LYP
What is the basis set? 6-31G(d,p)
What is the final energy E(RB3LYP) in atomic units (au)? -1.17853936 a.u.
What is the RMS gradient? 0.00000017 a.u.
What is the point group of your molecule? D∞h
Optimised bond length = 0.74279 Å
Optimised bond angle = 180.0
Optimisation
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES
Jmol and File Link
H2 Optimisation 01364619 |
Vibration Frequencies
| Mode # | Frequency | Infrared |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4465.68 | 0.0000 |
Charges
No charges as a homo-nuclear diatomic, therefore have the same electronegativity value and as such the electron density is shared equally between them.
Energy Calculations
Molecule of Choice
O2 Questions
What is the molecule? O2 Diatomic oxygen
What is the calculation method? RB3LYP
What is the basis set? 6-31G(d,p)
What is the final energy E(RB3LYP) in atomic units (au)? -150.25742434 a.u.
What is the RMS gradient? 0.00007502 a.u.
What is the point group of your molecule? D∞h
Optimised bond length = 1.21602 Å
Optimised bond angle = 180.0
Optimisation
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000130 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000130 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000080 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000112 0.001200 YES
Jmol and File Link
O2 Optimisation 01364619 |
Vibration Frequencies
| Mode # | Frequency | Infrared |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1642.74 | 0.0000 |
Charges
No charges as a homo-nuclear diatomic, therefore have the same electronegativity value and as such the electron density is shared equally between them.
Molecular orbitals of O2
-
Orbital 1
-
Orbital 2
-
Orbital 3
-
Orbital 4
-
Orbital 5
Orbital 1
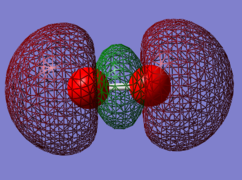
This is a bonding orbital which is made up from a combination of 2*1s AOs. It is low in energy with a value of -19.30736 Ha. This MO does not contribute to the bonding of the molecule. Occupied with 2 electrons.
Orbital 2
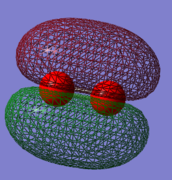
This is a bonding orbital which is made up from a combination of 2 2pz AOs. It is relatively high in energy with a value of -0.53151 Ha. This MO contributes to the bonding of the molecule. Occupied with 2 electrons.
Orbital 3
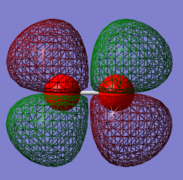
This is a bonding orbital which is made up from a combination of 2 2px or 2 2py AOs. It is relatively high in energy with a value of -0.51526 Ha. This MO contributes to the bonding of the molecule. Occupied with 2 electrons.
Orbital 4
This is a anti-bonding orbital which is made up from a combination of 2 2px or 2 2py AOs. It is relatively high in energy with a value of -0.25018 Ha. This MO contributes to the bonding of the molecule by containing anti-bonding electrons. Occupied with 2 electrons.
This would actually be a SOMO but due to the way Gauss view visualizes MOs, it is shown as a HOMO. In reality the two orbitals are degenerate and following Hund's rule of maximum multiplicity, this would mean the orbitals fill singly first, therefore making them SOMOs rather than HOMOs.
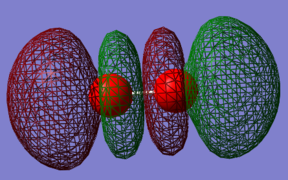
Orbital 5
This is a anti-bonding orbital which is made up from a combination of 2pz AOs. It is high in energy with a value of 0.21200 Ha. This MO does not contribute to the bonding of the molecule. Unoccupied orbital.
Second Molecule of Choice
O2 Questions
What is the molecule? CF4 Tetrafluoromethane
What is the calculation method? RB3LYP
What is the basis set? 6-31G(d,p)
What is the final energy E(RB3LYP) in atomic units (au)? -437.47627267
What is the RMS gradient? 0.00004049 a.u.
What is the point group of your molecule? TD
Optimised bond length = 1.32939 Å
Optimised bond angle = 109.471
Optimisation
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000078 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000042 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000133 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000071 0.001200 YES
Jmol and File Link
CF4 Optimisation 01364619 |
Vibration Frequencies
| Mode # | Frequency | Infrared |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 424.00 | 0.0000 |
| 2 | 424.00 | 0.0000 |
| 3 | 616.80 | 4.5048 |
| 4 | 616.80 | 4.5048 |
| 5 | 616.80 | 4.5048 |
| 6 | 906.23 | 0.0000 |
| 7 | 1305.80 | 387.1737 |
| 8 | 1305.80 | 387.1737 |
| 9 | 1305.80 | 387.1737 |
Charges
I would expect fluorine to be negative and carbon to be positive as fluorine is more electronegative than carbon, therefore attracts more electron density.
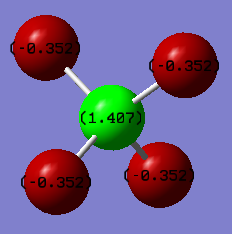
Charges on the atoms: F = -0.352 C = 1.407