Rep:Mod:CAS1997
NH3 Molecule
N-H bond distance = 1.01798angstroms
H-N-H bond angle = 105.741
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-5.986267D-10
Optimization completed.
NH3
| File Type | .log |
| Calculation Type | FREQ |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Charge | 0 |
| Spin | Singlet |
| E(RB3LYP) | -56.55776873 a.u. |
| RMS Gradient Norm | 0.00000485 a.u. |
| Imaginary Freq | 0 |
| Dipole Moment | 1.8466 Debye |
| Point Group | C3V |
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R2 R(1,3) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R3 R(1,4) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A1 A(2,1,3) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(2,1,4) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(3,1,4) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(2,1,4,3) -111.8571 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
test molecule |
The optimisation file is liked to here
Questions:
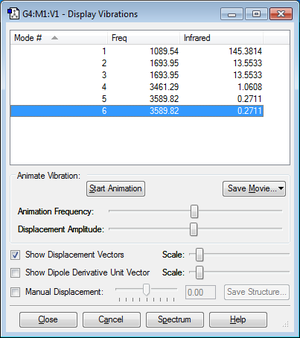
Modes for 3N-6: 2
Degenerate: 2&3, 5&6
Bending vibrations:1,2,3
Bond stretch vibrations:4,5,6,
Highly symmetric:4
Umbrella:6
How many bands expected to be seen: 4 due to 2 pairs of degenerate energies
N charge of -1.25, H charge of 0.375, due to electronegativity of N being greater than
H. this causes N to draw more electrons to its self and away from the H atoms making it more polar negative and causing polar positive formation of H atoms.
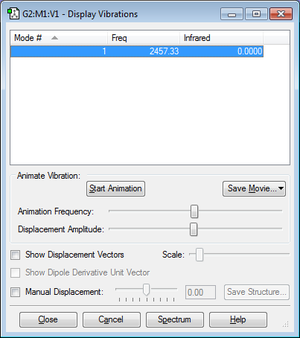
H2
| summary | H2 optimisation |
| File Name | H2 optimisation |
| File Type | .log |
| Calculation Type | FREQ |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Charge | 0 |
| Spin | Singlet |
| E(RB3LYP) | -1.17853936 a.u. |
| RMS Gradient Norm | 0.00000017 a.u. |
| Imaginary Freq | 0 |
| Dipole Moment | 0.0000 Debye |
| Point Group | D*H |
Convergence of structure
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.164080D-13
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
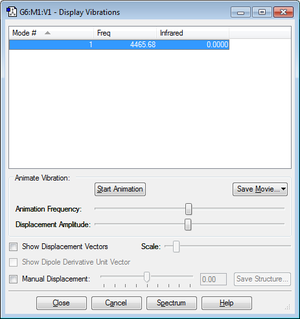
N2
N2 optimisation
| File Name | N2 optimisation |
| File Type | .log |
| Calculation Type | FREQ |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Charge | 0 |
| Spin | Singlet |
| E(RB3LYP) | |
| RMS Gradient Norm | 0.00000060 a.u. |
| Imaginary Freq | 0 |
| Dipole Moment | 0.0000 Debye |
| Point Group | D*H |
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-3.401114D-13
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
Haber process reaction energy
In atomic units:
E(NH3)= -56.55776873 2*E(NH3)= -113.1155375 E(N2)=-109.52412868 E(H2)=-1.17853936 3*E(H2)= -3.53561808 ΔE=2*E(NH)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]= -0.05579074
In kj/mol ΔE=2*E(NH)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]= -146.4785879
The product is more stable due to reaction being energetically negative so favouring RHS products formation
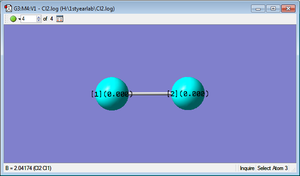
Project molecule, Cl2
test molecule |
| Cl2 molecule summary | |
| File Name | Cl2 |
| File Type | .log |
| Calculation Type | FREQ |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Charge | 0 |
| Spin | Singlet |
| E(RB3LYP) | -920.34987886 a.u. |
| RMS Gradient Norm | 0.00002511 a.u. |
| Imaginary Freq | 0 |
| Dipole Moment | 0.0000 Debye |
| Point Group | D*H |
Charges on Cl2 molecule displayed below
Convergence of molecule
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000043 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000043 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000121 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000172 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-5.277261D-09 Optimization completed.
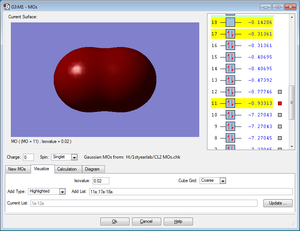
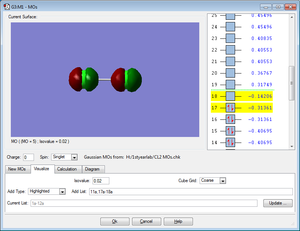
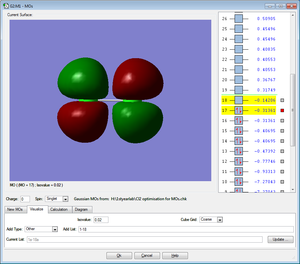
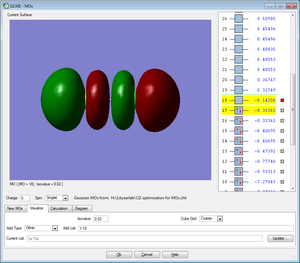
Five MOs for the Cl2 molecule are shown below
All MOs shown below are occupied by electrons.
Charge is distributed evenly due to Cl2 being no polar. Any uneven charge distribution would be created by an instantaneous dipole.
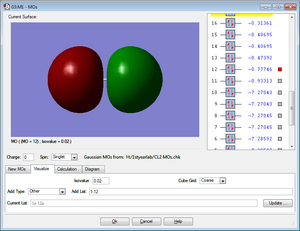
HOMO
The MO shows the highest bonding molecular orbital for the Cl2 molecule. It is an occupied anti-bonding MO created from 3p orbitals of x orientation.
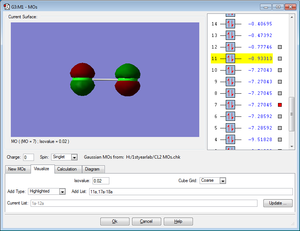
LUMO
The MO shows the lowest unoccupied molecular orbital for the Cl2 molecule. It is an anti-bonding MO formed from 3p orbitals of z orientation. It is unoccupied with electrons.
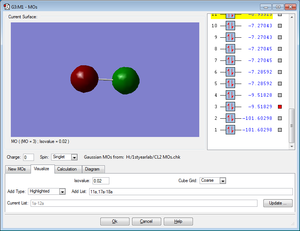
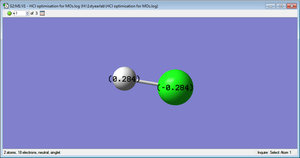
Comparison Molecule; HCl
Above the charge distribution of a HCl molecule is shown. There is a charge difference between the 2 atoms due to Cl being a more electronegative than H, so therefore Cl draws electrons towards itself. This creates a polar molecule with Cl experiencing a slight negative charge and H experiencing a Slight positive charge. This differs from the Cl2 molecule that is non-polar due to charge being equally distributed.