Rep:Mod:AW2415report
Molecule: NH3
Below is shown information about the NH3 molecule. The molecule was initially optimized using the program Gaussview. The data shown is after the optimization and covers bond length, vibrations and charge.
The following table shows information about the calculation method, bond lengths and angles.
| Property | |
|---|---|
| Calculation method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Final Energy | -56.55776873 au |
| RMS gradient | 0.00000485 au |
| Point Group | C3V |
| Optimized N-H bond length | 1.01798 Å |
| Optimized H-N-H angle | 105.74116o |
Item Table
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
Gallery
test molecule |
File:NH3 - 2 (FIRST OPTIMISATION).LOG
Vibrations
Questions
How many modes do you expect from the 3N-6 rule? No. modes=3(4)-6
Which modes are degenerate (ie have the same energy)? 2&3 and 5&6
Which modes are "bending" vibrations and which are "bond stretch" vibrations?
Bends: 1,2,3
Stretch: 4,5,6
Which mode is highly symmetric? 4
One mode is known as the "umbrella" mode, which one is this? 1
How many bands would you expect to see in an experimental spectrum of gaseous ammonia? 4, however you will only see 2 because 2 have such a low intensity that they are likely to get lost in the spectrum.
Charge Analysis
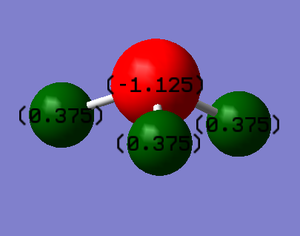
The charge distribution as expected because nitrogen is more electronegative than hydrogen. It therefore attracts electron density towards itself and so is more negative.
Charge on N: -1.125
Charge on H: 0.375
Molecule: H2
The following data is about an H2 molecule. It was obtained by using the program Gaussview after the molecule has been optimized.
| Property | |
|---|---|
| Calculation method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Final Energy | -1.17853936 au |
| RMS gradient | 0.00000017 au |
| Point Group | Dooh |
| Optimised H-H bond length | 1.01798 Å |
Item Table
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES
Gallery

test molecule |
File:AW2415 H2 (FIRST OPTIMISATION).LOG
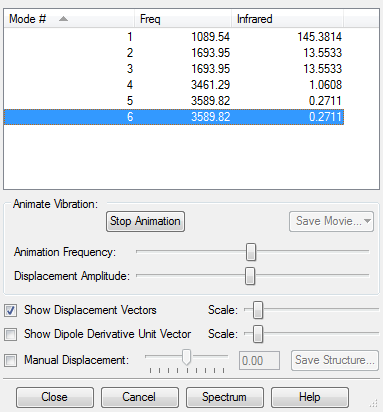
Vibrations
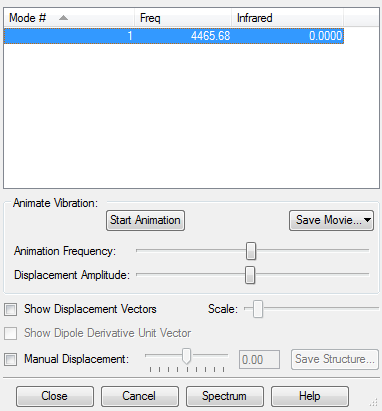 Vibrational anaysis for optimised H2 molecule showing there are no negative frequencies
Vibrational anaysis for optimised H2 molecule showing there are no negative frequencies
Charge Analysis
The two atoms are identical so there is an even charge distribution over the molecule. There is therefore no dipole within the molecule.
Molecule: N2
The following data is about an N2 molecule. It was obtained by using the program Gaussview after the molecule has been optimized.
| Property | |
|---|---|
| Calculation method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Final Energy | -109.524128686 au |
| RMS gradient | 0.00000060 au |
| Point Group | Dooh |
| Optimised N-N bond length | 1.10550 Å |
Item Table
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
Gallery
test molecule |
File:AW2415-N2 (OPTIMISED).LOG
Vibrations
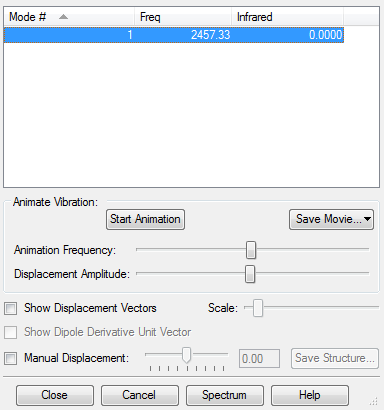 Vibrational anaysis for optimised N2 molecule showing there are no negative frequencies
Vibrational anaysis for optimised N2 molecule showing there are no negative frequencies
Reaction Energies
E(NH3)= -56.55776873 au
2*E(NH3)= -113.1155375 au
E(N2)= -109.524128686 au
E(H2)= -1.17853936 au
3*E(H2)= -3.53561808 au
ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]= -0.055790734 au = -146.8177211 KJmol-1
The enthalpy change for the reaction is negative therefore the products are more stable than the reactants.
Molecular Orbital Gallery
Charge Analysis
The two atoms are identical so there is an even charge distribution over the molecule. There is therefore no dipole within the molecule.
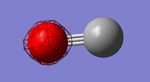
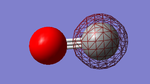
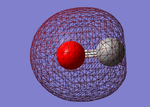
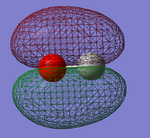
CO
Below is shown information about the carbon monoxide (CO) molecule. The molecule was initially optimized using the program Gaussview. The data shown is after the optimization and cover bond length, vibrations and charge.
| Property | |
|---|---|
| Calculation method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Final Energy | -113.30945314 au |
| RMS gradient | 0.00001828 au |
| Point Group | Dooh |
| Optimised C-O bond length | 1.13793 Å |
Item Table
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000032 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000032 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000012 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000018 0.001200 YES
Gallery
test molecule |
File:AW2415-CO (FIRST OPTIMISATION).LOG
Vibrations

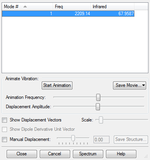
Vibrational analysis for optimized CO molecule shows there are no negative frequencies. The only vibration is a symmetrical stretch, therefore there will only be one peak in the IR spectrum of CO.
Charge Analysis

Carbon and oxygen have different electronegativities and therefore there is an uneven charge distribution over the molecule. Oxygen is the more electronegative of the atoms due to having a higher effective nuclear charge on the valence electrons. Therefore it is the negative ens of the molecule.
Charge on oxygen: -0.506 au
Charge on Carbon: 0.506 au