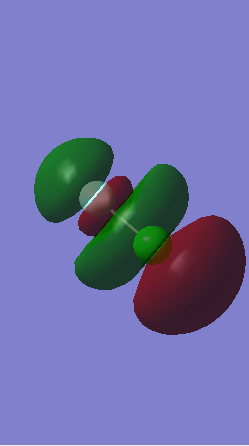Rep:Mod:AV01360062
NH3 Molecule
Optimisation Data
| Molecule | NH3 |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31g(d,p) |
| Final Energy | -56.55776863 au |
| RMS Gradient | 0.00000485 |
| Point Group | C3V |
| Bond Distance | 1.01798 |
| Bond Angle | 105.741 |
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
Diagram
Ammonia |
Media:AV4217-NH3OPTIMISATION.LOG
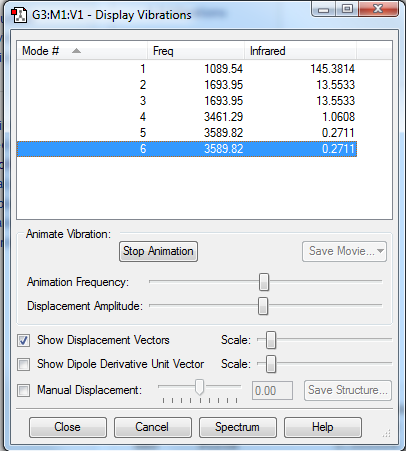
Vibrations
| Questions | Answers |
|---|---|
| modes of vibration | 6 |
| degenerate modes | 2&3 , 5&6 |
| bending vibrations | 4,5,6 |
| bond stretch vibrations | 1,2,3 |
| highly symmetric mode | 4 |
| umbrella mode | 1 |
| experimental bands | 4 |
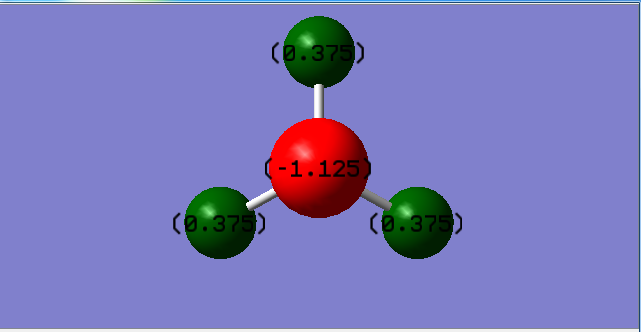
Charges
| Nitrogen | Hydrogen |
|---|---|
| -1.125 | 0.375 |
The nitrogen atom is expected to have a negative charge and the hydrogen atoms are expected to have a positive charge. This is because nitrogen is more electronegative than hydrogen so attracts the electron density towards itself more. Overall the molecule is not charged.
N2 Molecule
Optimisation Data
| Molecule | N2 |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31g(d,p) |
| Final Energy | -109.52412868 |
| RMS Gradient | 0.00000060 |
| Point Group | D*H |
| Bond Distance | 1.10550 |
| Bond Angle | 180.00 |
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
Diagram
nitrogen |
Media:AV4217_N2OPTIMISATION.LOG
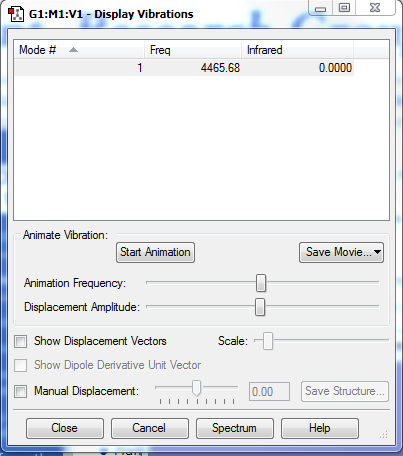
Vibrations
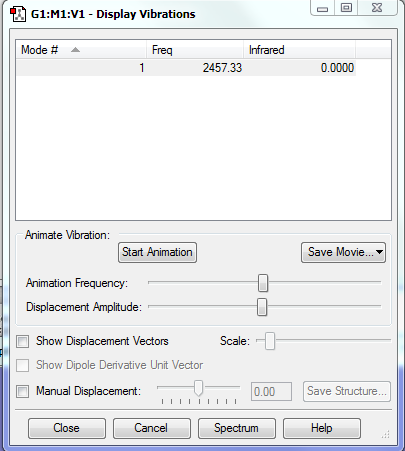
There is only one vibration, which is the asymmetric stretch as the molecule is linear. There is no dipole moment as the atoms are the same, so the molecule is infrared inactive.
H2 Molecule
Optimisation Data
| Molecule | H2 |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31g(d,p) |
| Final Energy | -1.17853936 |
| RMS Gradient | 0.00000017 |
| Point Group | D*H |
| Bond Distance | 0.74279 |
| Bond Angle | 180.00 |
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES
Diagram
Hydrogen |
Media:AV4217-AV4217_H2OPTIMISATION.LOG
Vibrations
The molecule is linear so there is only one vibration (3N-5), which is the assymmetric stretch. It is not infrared active as there is no dipole moment.
Reactivity
Energies
| E(NH3) | -56.55776863 au |
| 2*E(NH3) | -113.1155373 au |
| E(N2) | -109.52412868 au |
| E(H2) | -1.1785393 au |
| 3*E(H2) | -3.5356179 au |
| ΔE | -0.05579072 au |
ΔE=-146.48kJ/mol
The ammonia product is more stable, indicated by the negative energy change.
ClF Molecule
Optimisation Data
| Molecule | ClF |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31g(d,p) |
| Final Energy | -559.94269578 au |
| RMS Gradient | 0.00014211 |
| Point Group | C*V |
| Bond Distance | 1.66434 |
| Bond Angle | 180.00 |
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000246 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000246 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000433 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000613 0.001200 YES
Diagram
ClF |
Media:AV4217_CLFOPTIMISATION.LOG
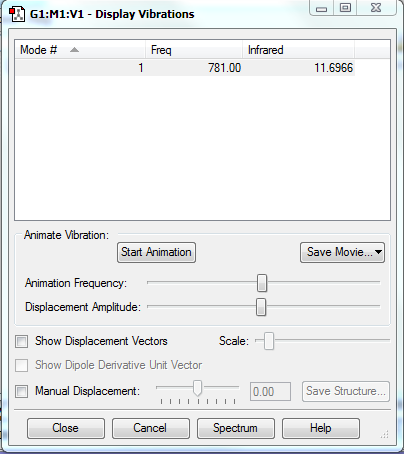
Vibrations
There is only one stretching vibration since it is a linear molecule. It is infrared active as there is a difference in electronegativities, so there is a dipole moment.
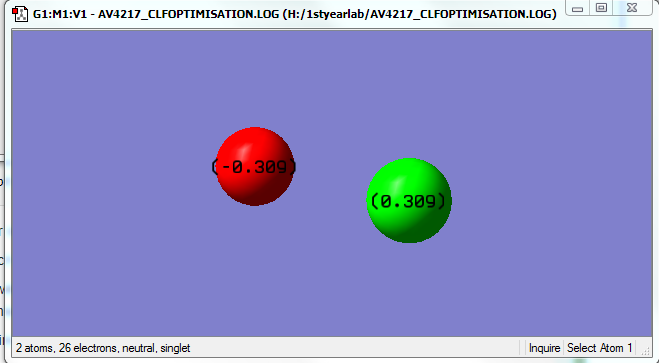
Charges
The charges cancel out overall.
| Chlorine | Fluorine |
|---|---|
| 0.309 | -0.309 |
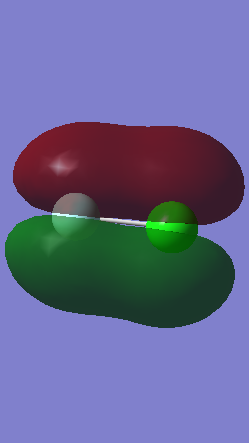
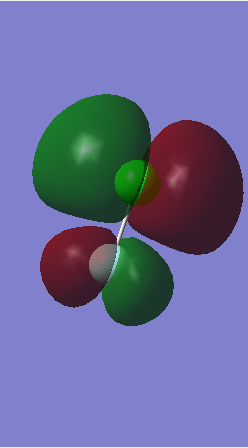
Molecular Orbitals
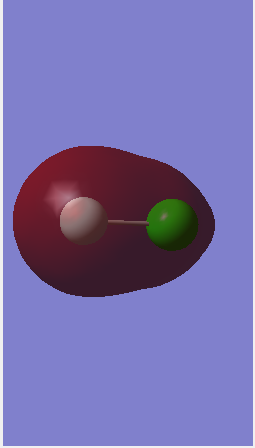
Orbital 7
This is the molecular orbital formed from the in-phase overlap of the 2s orbital from fluorine and the 3s orbital from chlorine. It forms a σ bonding orbital deep in energy as it is the lowest energy and is occupied. Fluorine is more electronegative so there is greater electron density surrounding it.
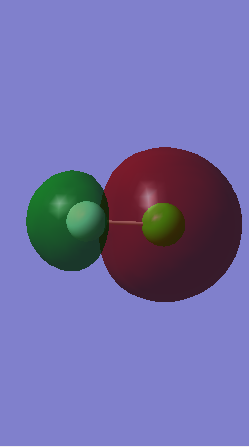
Orbital 8
This occupied molecular orbital is formed from the out of phase overlap of the 3s orbital (Cl) and the 2s orbital (F). It forms a σ* antibonding orbital, deep in energy.
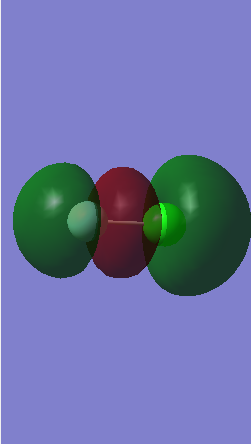
Orbital 9
This molecular orbital is formed from the overlap of 2p (F) and 3p (Cl) atomic orbitals. An occupied σ bonding orbital is formed. The antibonding orbital formed form the out of phase overlap of these two atomic orbitals is unoccupied so this moleculao orbital forms a sigma bond between the atoms.
Orbital 10
This a σ bonding orbital formed by the overlap of the 2p (F) and 3p (Cl) orbitals and is occupied.
Orbital 13
This is a σ* antibonding orbital formed from the out of phase overlap of 2p (F) and 3p (Cl) orbital. It is the HOMO of the molecule.
Orbital 14
This is a σ* antibonding orbital that is unoccupied and is the LUMO of the molecule. It is formed by the out of phase over lap of the 2p (F) and 3p (Cl) orbitals.
H2O Molecule
Optimisation Data
| Molecule | H2O |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31g(d,p) |
| Final Energy | -76.41973740 au |
| RMS Gradient | 0.00006276 |
| Point Group | C2V |
| Bond Distance | 0.96522 |
| Bond Angle | 103.745 |
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000099 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000081 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000115 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000120 0.001200 YES
Diagram
Water |
Media:AV4217_H2OOPTIMISATION.LOG
Vibrations
| Mode | Frequency | Infrared | Vibration |
| 1 | 1665.00 | 70.347 | Bending |
| 2 | 3801.05 | 1.6431 | Symmetrical Stretch |
| 3 | 3914.23 | 20.2475 | Asymmetrical stretch |
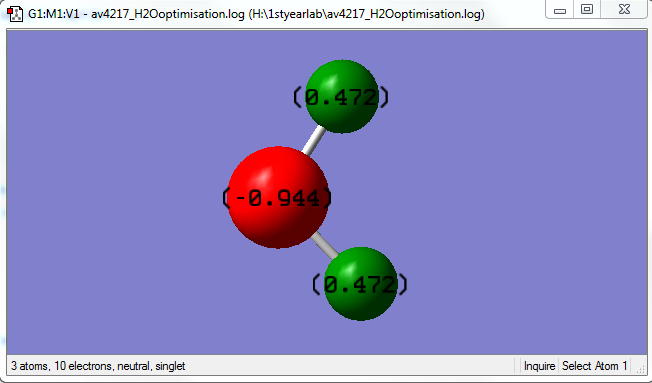
Charges
Overall the molecule is not charged.
| Hydrogen | Oxygen |
|---|---|
| 0.472 | -0.944 |
Molecular Orbitals
Orbital 1
This is a non-bonding orbital formed from the 1s orbital of oxygen and is very deep in energy.
Orbital 2
This is a sigma bonding orbital formed from the in-phase overlap of the 1s orbital from hydrogen and the 2s orbital from oxygen. It is deep in energy.