Rep:Mod:APP842
NH3 Molecule
The N-H optimised bond distance is 1.02 Angstroms.
The H-N-H optimised angle distance is 106 degrees.
The molecule studied is NH3, or ammonia.
The Calculation Method is RB3LYP.
The Basis Set is 6-31G(d,p).
The final energy (E(RB3LYP)) is -56.55776873 a.u.
The RMS Gradient Norm is 0.00000485.
The Point Group is C3V.
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
Jmol Image of NH3
NH3 Jmol Image |
The optimisation file is linked to here
NH3 Vibrations
| Wavenumber cm-1 | 1090 | 1694 | 1694 | 3461 | 3590 | 3590 |
| Symmetry | A1 | E | E | A1 | E | E |
| Intensity arbitrary units | 145 | 14 | 14 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Image |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Comments on the NH3 vibrations
Using the 3N-6 rule, because the molecule is not linear, 6 modes of vibration are expected, as found.
The two vibrations at 1694 cm-1 are degenerate as well as the two at 3590 cm-1.
The three vibrations with the lowest wavenumber ( at 1090cm-1,1694cm-1 and 1694cm-1) are bending vibrations and the three highest are "bond-stretch" vibrations (at 3461cm-1,3590cm-1 and 3590cm-1)
The mode at 3461 cm-1 is highly symmetric.
The "umbrella" mode is the one at 1090 cm-1.
Two or three bands would be observed in an IR spectrometer, depending on the precision of the apparatus since one of the modes, at 3461 cm-1, has an intensity of one, which is very low. Also considering that out of the six vibrational modes, there is a pair of degenerate modes, they would have the same band.
Charge analysis of NH3
The charge found when using the NBO charge distribution was of -1.125 for Nitrogen and +0.375 for each Hydrogen
These results are in accordance with expectations since Nitrogen has an electronegativity value of 3 and Hydrogen of 2.1. Therefore, the bond is polarised covalent towards the Nitrogen, which bears more of a negative charge due to its higher electronegativity.
N2 Molecule
The N-N optimised bond distance is 1.11 Angstroms
The molecule is N2, or dinitrogen.
The Calculation Method is RB3LYP.
The Basis Set is 6-31G(d,p).
The final energy (E(RB3LYP)) is -109.52412868 a.u.
The RMS Gradient Norm is 0.00000365.
The Point Group is DinfH.
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000006 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000006 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000002 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000003 0.001200 YES
Jmol Image of N2
Jmol Image of N2 |
The optimisation file is linked to here
N2 Vibrations
| Wavenumber cm-1 | 2457 |
| Symmetry | SGG |
| Intensity arbitrary units | 0 |
| Image | 
|
Charge analysis
The charge found when using the NBO charge distribution was of 0.000 for each of the Nitrogen atoms.
This is in complete agreement with expectations since the bond is purely covalent, both atoms are the same.
Conquest Complex for N2
The unique identifier of the molecule is NAWKED with the following link https://www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/structures/Search?Ccdcid=NAWKED&DatabaseToSearch=Published
The journal reference is referenced here.[1]
The bond length found in the crystalline structure is of 1.107(±0.004) Angstroms while the one calculated on the gaussian optimisation software was of 1.11 Angstroms. Although the value found is within the literature range, there seems to be a slight shortening of the bond length. This is in contradiction with MO theory since the end-on bond between Nitrogen and Cobalt would promote electrons in the LUMO, which is the pi star antibonding orbital, therefore decreasing bond order and increasing bond length. The main reason this is not observed is because both values are not obtained in the same conditions; one measurement is an experimental observation while the other is a computational simulation. There is bound to be differences, which is why a lengthening of the bond is not observed. Firstly, the computational method is inevitably going to be an approximation of the real situation because approximations have to be made to solve the Schrodinger equation. Specifically, the calculation method is RB3LYP and the basis set is 6-31G(d,p), which has its limitations. The ideal case would be an infinite amount of wavefunction calculations. Furthermore, the surroundings in the crystalline structure can also affect the bond length measured experimentally by compresssing the bond. In this case, for example the ether solvent.
H2 Molecule
The H-H optimised bond distance is 0.74 Angstroms
The molecule is H2, molecular hydrogen.
The Calculation Method is RB3LYP.
The Basis Set is 6-31G(d,p).
The final energy (E(RB3LYP)) is -1.17853930 a.u.
The RMS Gradient Norm is 0.00012170.
The Point Group is DinfH.
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000211 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000211 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000278 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000393 0.001200 YES
Jmol Image of H2
Jmol Image of H2 |
The optimisation file is linked to here
H2 Vibrations
| Wavenumber cm-1 | 4461 |
| Symmetry | SGG |
| Intensity arbitrary units | 0 |
| Image | 
|
Charge analysis
The charge found when using the NBO charge distribution was of 0.000 for each of the Hydrogen atoms.
This is in complete agreement with expectations since the bond is purely covalent, both atoms are the same.
Haber Bosch Process
E(NH3)= -56.55776873 2*E(NH3)= -113.11553746 E(N2)= -109.52412868 E(H2)=-1.17853930 3*E(H2)=-3.53561808 ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]= -0.0557907 a.u. ΔE=-146.5 kJ/mol
Because the difference in energy between the products and reactants is negative, the ammonia product is more stable than the gaseous reactants.
O2 molecule
The O-O optimised bond distance is 1.22 Angstroms
The molecule is O2, molecular oxygen.
The Calculation Method is RB3LYP.
The Basis Set is 6-31G(d,p).
The final energy (E(RB3LYP)) is -150.25742434 a.u.
The RMS Gradient Norm is 0.00007502.
The Point Group is DinfH.
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000130 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000130 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000080 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000113 0.001200 YES
The optimisation file is linked to here
Jmol Image of O2
Jmol Image of Oxygen molecule |
O2 Vibrations
| Wavenumber cm-1 | 1643 |
| Symmetry | SGG |
| Intensity arbitrary units | 0 |
| Image | 
|
There is only one vibrational mode since the molecule is linear and using the formula 3N-5 yields one vibrational mode, as observed. The molecule is symmetrical and with no overall dipole, therefore the intensity of the symmetrical stretch has an intensity of 0.
Charge analysis
The charge found when using the NBO charge distribution was of 0.000 for each of the Oxygen atoms.
This is in complete agreement with expectations since the bond is purely covalent, both atoms are the same.
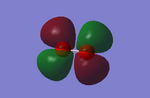
Molecular Orbitals of O2
F2 Molecule (Extra Calculation)
The F-F optimised bond distance is 1.40 Angstroms
The molecule is F2, difluorine.
The Calculation Method is RB3LYP.
The Basis Set is 6-31G(d,p).
The final energy (E(RB3LYP)) is -199.49825218 a.u.
The RMS Gradient Norm is 0.00007365.
The Point Group is DinfH.
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000128 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000128 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000156 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000221 0.001200 YES
The optimisation file is linked to here
Jmol Image of F2
Jmol Image of F2 |
F2 Vibrations
| Wavenumber cm-1 | 1065 |
| Symmetry | SGG |
| Intensity arbitrary units | 0 |
| Image | 
|
Charge analysis
The charge found when using the NBO charge distribution was of 0.000 for each of the Fluorine atoms.
This is in complete agreement with expectations since the bond is purely covalent, both atoms are the same.
References
- ↑ P.A.Rudd, Shengsi Liu, L.Gagliardi, V.G.Young Junior.C.C.Lu, Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2011, 133, 20724, DOI: 10.1021/ja2099744
Marking
Note: All grades and comments are provisional and subject to change until your grades are officially returned via blackboard. Please do not contact anyone about anything to do with the marking of this lab until you have received your grade from blackboard.
Wiki structure and presentation 1/1
Is your wiki page clear and easy to follow, with consistent formatting?
YES
Do you effectively use tables, figures and subheadings to communicate your work?
YES
NH3 1/1
Have you completed the calculation and given a link to the file?
YES
Have you included summary and item tables in your wiki?
YES
Have you included a 3d jmol file or an image of the finished structure?
YES
Have you included the bond lengths and angles asked for?
YES
Have you included the “display vibrations” table?
YES
Have you added a table to your wiki listing the wavenumber and intensity of each vibration?
YES
Did you do the optional extra of adding images of the vibrations?
YES
Have you included answers to the questions about vibrations and charges in the lab script?
YES
N2 and H2 0.5/0.5
Have you completed the calculations and included all relevant information? (summary, item table, structural information, jmol image, vibrations and charges)
YES
Crystal structure comparison 0.5/0.5
Have you included a link to a structure from the CCDC that includes a coordinated N2 or H2 molecule?
YES - However, you were asked to report a monometallic complex instead of a bimetallic one.
Have you compared your optimised bond distance to the crystal structure bond distance?
YES
Haber-Bosch reaction energy calculation 1/1
Have you correctly calculated the energies asked for? ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]
YES
Have you reported your answers to the correct number of decimal places?
YES
Do your energies have the correct +/- sign?
YES
Have you answered the question, Identify which is more stable the gaseous reactants or the ammonia product?
YES
Your choice of small molecule 4/5
Have you completed the calculation and included all relevant information?
YES
Have you added information about MOs and charges on atoms?
YES - you could have used an electronegativity argument to explain the charges. You stated MOs 3 and 4 to be bonding and anti-bonding. As no overlap of the AOs is observed these MOs are non-bonding.
Independence 1/1
If you have finished everything else and have spare time in the lab you could: Check one of your results against the literature, or Do an extra calculation on another small molecule, or
YES - Well done! Do some deeper analysis on your results so far