Rep:Mod:AMZ1470
NH3 Molecule
Key Information
N-H bond length = 1.01798 A
H-N-H bond angle = 105.74115 degrees
Calculation Method: RB3LYP
Basis Set: 6-31G(d,p)
Final Energy: -56.55776873 au
RMS Gradient: 0.00000485 au
Point Group: C3V
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-5.986259D-10
test molecule |
Link to optimized file: File:Sk4915 NH3 optf pop.log
Vibration
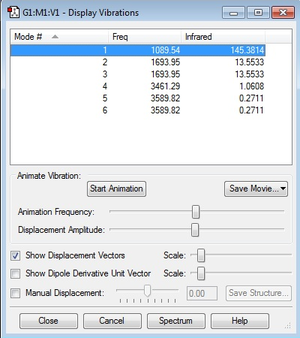
How many modes do you expect from the 3N-6 rule?
6
Which modes are degenerate (i.e have the same energy)?
Modes 2 & 3 are degenerate. Modes 5 & 6 also are degenerate.
Which modes are "bending" vibrations and which are "bond stretch" vibrations?
Modes 1, 2 & 3 are bending vibrations and modes 4, 5 & 6 are bond stretch vibrations.
Which mode is highly symmetric?
Mode 4.
One mode is known as the "umbrella" mode, which one is this?
Mode 1.
How many bands would you expect to see in an experimental spectrum of gaseous ammonia?
Two bands.
Charge Distribution
Charge on the N-atom: -1.125
Charge on the H-atoms: 0.375
These charges match expectations as Nitrogen is the most electronegative atom in this molecule and so more strongly attracts the bonding electrons, pulling the electrons further away from the Hydrogen atoms. Therefore, there is a slight negative charge on the Nitrogen and slight positive charges on the Hydrogen atoms.
H2 Molecule
Key Information
H-H bond length = 0.74279 A
Calculation Method: RB3LYP
Basis Set: 6-31G(d,p)
Final Energy: -1.17853936 au
RMS Gradient: 0.00000017 au
Point Group: D*H
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.164080D-13
test molecule |
Link to optimized file: File:SK4915 H2.LOG
Vibration
Vibrational modes in an H2 molecule.
Charge Distribution
Charge on the H-atoms: 0.00 C
Both atoms in this molecule are identical so there is no dipole.
N2 Molecule
Key Information
N-N bond length = 1.09200 A
Calculation Method: RB3LYP
Basis Set: 6-31G(d,p)
Final Energy: -109.52359111 au
RMS Gradient: 0.02473091 au
Point Group: D*H
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-3.400935D-13
test molecule |
Link to optimized file: File:SK4915 N2.LOG
Vibration
Vibrational modes in an N2 molecule.
Charge Distribution
Charge on the N-atom: 0.00 C
Both atoms in this molecule are identical so there is no dipole.
Energy Calculations
Reaction:
N2 + 3H2 -> 2NH3
E(NH3) = -56.55776873 au
2*E(NH3) = -113.1155375 au
E(N2) = -109.52359111 au
E(H2) = -1.17853936 au
3*E(H2) = -3.53561808 au
ΔE = 2*E(NH3) - [E(N2) + E(H2)] = -0.05632827 au
= -147.890 kJmol-1
The Ammonia product is more stable than the gaseous reactants.
CH4 Molecule
Key Information
C-H bond length = 1.07000 A
H-C-H bond angle = 109.47122 degrees
Calculation Method: RB3LYP
Basis Set: 6-31G(d,p)
Final Energy: -40.52401404 au
RMS Gradient: 0.00003263 au
Point Group: TD
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000063 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000034 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000179 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000095 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-2.256038D-08
test molecule |
Link to optimized file: File:SK4915 CH4.LOG
Vibration
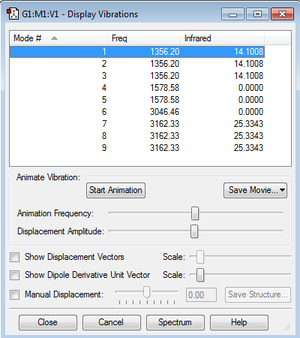
How many modes do you expect from the 3N-6 rule?
9
Which modes are degenerate (i.e have the same energy)?
Modes 1, 2 & 3, modes 4 & 5 and modes 7, 8 & 9 are degenerate.
Which modes are "bending" vibrations and which are "bond stretch" vibrations?
Modes 1, 2, 3, 4 & 5 are bending vibrations and modes 6, 7, 8 & 9 are bond stretch vibrations.
Which mode is highly symmetric?
Mode 6.
Charge Distribution
Charge on the C-atom: -0.930
Charge on the H-atoms: 0.233
These charges match expectations as Carbon is the most electronegative atom in this molecule and so more strongly attracts the bonding electrons, pulling the electrons further away from the Hydrogen atoms. Therefore, there is a slight negative charge on the Carbon and slight positive charges on the Hydrogen atoms.
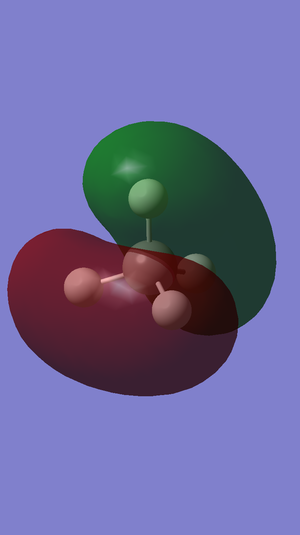
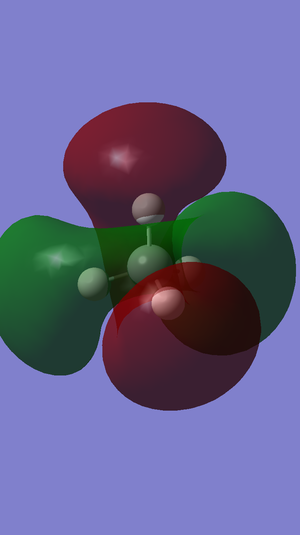
Molecular Orbitals
The highest occupied molecular orbital in methane is the 2p orbital and the HOMO-LUMO gap in methane is 0.50655 au.