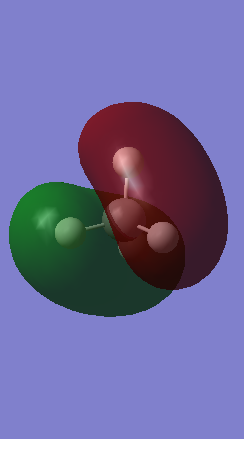Rep:Mod:AM9315
Molecules
All of the following molecules were created through the Gaussview software, all calculations were calculated from data provided in the table and all images were provided by Gaussview.
Ammonia
Summary of data
What is the bond length of the molecule?
1.01798 Angstroms.
What is the bond angle for the molecule?
105.74 degrees
What is the calculation method?
RB3LYP
What is the basis set?
6-31G(d.p)
What is the final energy E(RB3LYP) in atomic units (au)?
-56.55776873
What is the RMS gradient?
0.00000485
What is the point group of your molecule?
C3V
The optimisation file is liked to here
Optimised Ammonia molecule data
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000070 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000033 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-5.785193D-10
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R2 R(1,3) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R3 R(1,4) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A1 A(2,1,3) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(2,1,4) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(3,1,4) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(2,1,4,3) -111.8571 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
test molecule |
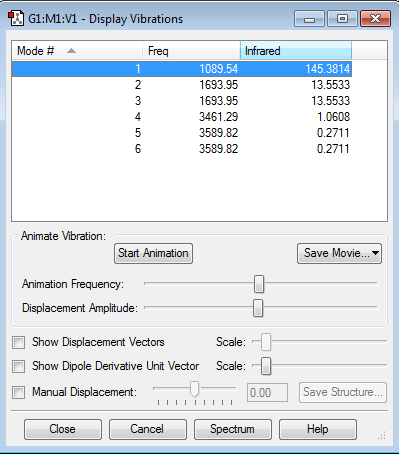
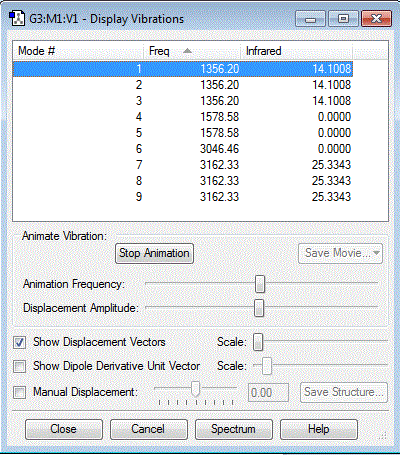
Vibrations of the molecule
How many modes do you expect from the 3N-6 rule?
3x4-6 = 6 modes.
Which modes are degenerate (ie have the same energy)?
2 + 3 are degenerate. 5 + 6 are degenerate.
Which modes are "bending" vibrations and which are "bond stretch" vibrations?
1, 2 + 3 are bending vibrations. 4,5 and 6 are bond stretching vibrations
Which mode is highly symmetric?
Mode 4
One mode is known as the "umbrella" mode, which one is this?
Mode 1
How many bands would you expect to see in an experimental spectrum of gaseous ammonia?
3 as there are 2 different peaks on the spectrum. Mode 1 produces the most significant peak, whereas mode 2 and 3 both are responsible for the 2nd peak. The reason for why not all the stretches can be seen on the spectrum is because there is no change in the dipole through symmetric stretch so the molecule meaning no peak is produced.
Charges of the atoms within the molecule
Charge on the nitrogen atom
Charge on the nitrogen = -1.125 The charge on nitrogen is more negative than hydrogen as nitrogen is more electroegative than hydrogen so will attract the electron density towards itself. As a result, the hydrogen has a lower electron density than nitrogen so the charge on nitrogen will be more negative.
Charge on the hydrogen atom
Charge on the hydrogen = 0.375. The charge on hydrogen is less negative than nitrogen as hydrogen is less electronegative than nitrogen meaning that the electron density around hydrogen is less than that around nitrogen. As a result, hydrogen is more positively charged than nitrogen.
Reaction energies of the molecule
Summary of data for nitrogen
Summary data
Bond length = 1.10550
What is the calculation method? RB3LYP
What is the basis set? 6-31G(d.p)
What is the final energy E(RB3LYP) in atomic units (au)? -109.52412868
What is the RMS gradient? 0.0000006
What is the point group of your molecule? D*H
The optimisation file is liked to here
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-3.383649D-13
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) ! -------------------------- -------------------------- ! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. ! -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ! R1 R(1,2) 1.1055 -DE/DX = 0.0 ! -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
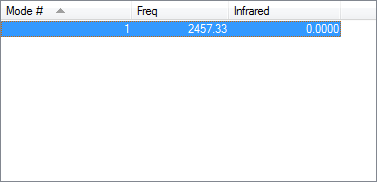
Vibrations
Only 1 vibration as there is a symmetric stretch.
Summary of data for hydrogen
Summary data
Bond length = 0.74279 Angstroms
What is the calculation method? RB3LYP
What is the basis set? 6-31G(d.p)
What is the final energy E(RB3LYP) in atomic units (au)? -1.17853936
What is the RMS gradient? 0.00000017
What is the point group of your molecule? D*H
The optimisation file is liked to here
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-1.164079D-13
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 0.7428 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
Vibrations
Only 1 vibration as there is a symmetric stretch.
Reaction energy
E(NH3) = -56.55776873 2*E(NH3) = -113.1155375 E(N2) = -109.52412868 E(H2) = -1.17853936 3*E(H2) = -3.53561805 ΔE = 2*E(NH3)-[E(N2) + 3*E(H2)]= -113.1155375-[-109.52412868+-3.53561805] = -0.05579077au = -146.5kJ/mol
As the overall reaction is negative, the products formed are more stable than the reactants.
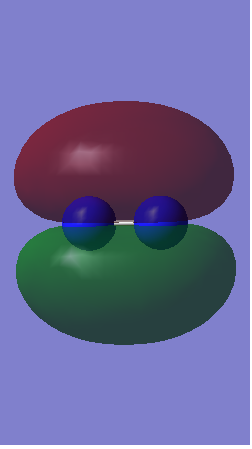
Molecular orbitals for N2
Bonding orbitals
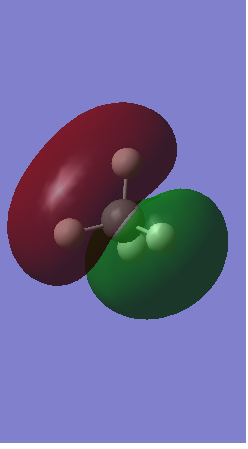
1)The picture below shows 2 bonding 1s orbitals of nitrogen overlapping to form a sigma orbital.
2) The picture below shows the overlap of 2 bonding 2s orbitals of nitrogen to form a single sigma orbital.
3) The picture below shows the overlap of the 2 bonding 2px orbitals of nitrogen to form a pi orbital.
4) The picture below shows the overlap of the 2 bonding 2py orbitals of nitrogen to form a pi orbital.
5) The picture below shows the overlap of the 2 bonding 2pz orbitals of nitrogen to form a pi orbital.
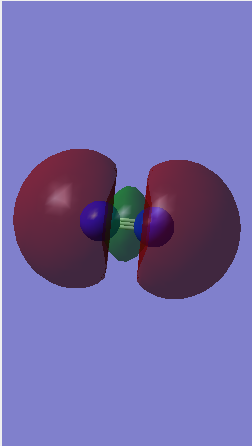
Anti-Bonding Orbitals
1) The picture below shows 2 orbitals, 1 bonding 1s orbital and 1 anti-bonding 1s orbital of nitrogen to form a sigma* orbital.
Energy = -14.44512

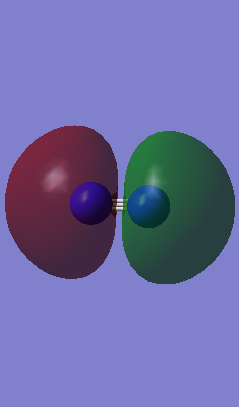
2) The picture below shows 2 orbitals, 1 bonding 2s orbital and 1 anti-bonding 2s orbital of nitrogen to form a sigma* orbital.
Energy = -0.55342
3) The picture below shows 2 orbitals, 1 bonding px orbital and 1 anti-bonding pz orbital. This molecular orbital is unoccupied.
Energy = -0.02412

4) The picture below shows 2 orbitals, 1 bonding py orbital and 1 anti-bonding pz orbital. This molecular orbital is unoccupied.
Energy = -0.02412
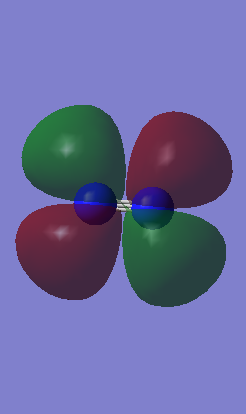
Methane
Summary of data for methane
What is the bond length of the molecule?
1.09197 Angstroms.
What is the bond angle for the molecule?
109.471 degrees
What is the calculation method?
RB3LYP
What is the basis set?
6-31G(d.p)
What is the final energy E(RB3LYP) in atomic units (au)?
-1.1873936
What is the RMS gradient?
0.0000003263
What is the point group of your molecule?
TD
The optimisation file is liked to here
Optimised CH4 molecule Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000063 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000034 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000179 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000095 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-2.112867D-08
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.092 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! R2 R(1,3) 1.092 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! R3 R(1,4) 1.092 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! R4 R(1,5) 1.092 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! A1 A(2,1,3) 109.4712 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(2,1,4) 109.4712 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(2,1,5) 109.4712 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A4 A(3,1,4) 109.4712 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A5 A(3,1,5) 109.4712 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A6 A(4,1,5) 109.4712 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(2,1,4,3) -120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D2 D(2,1,5,3) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D3 D(2,1,5,4) -120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D4 D(3,1,5,4) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
-----------------------------------------------------------
test molecule |
Vibrations of the molecule
How many modes do you expect from the 3N-6 rule?
9 modes.
Which modes are degenerate (i.e. have the same energy)?
1,2 and 3 are degenerate. 4 and 5 are degenerate. 7,8 and 9 are degenerate.
Which modes are "bending" vibrations and which are "bond stretch" vibrations?
Vibrations 1,2,3,4 and 5 are all bending vibrations. 6,7,8 and 9 are all bond stretch vibrations.
Which mode is highly symmetric?
Mode 6 is highly symmetric.
====How many bands would you expect to see in an experimental spectrum of gaseous methane? 2 which are modes 1 and 9 and can both be seen as significant peaks on the spectrum. The reason for why not all the stretches can be seen on the spectrum is because there is no change in the dipole through symmetric stretch so the molecule meaning no peak is produced.
Charges of the atoms within the molecule
Charge on the carbon atom
Charge on the carbon = -0.930. One would expect the carbon charge to be more negative than that for hydrogen as carbon is more electronegative than hydrogen meaning it will attract the electron density towards itself, as a result, the electron density might slightly outweigh the proton density meaning that the atom has an oveall negative charge.
Charge on the hydrogen atom
Charge on the hydrogen atoms = 0.233. One would expect that the hydrogen charge will be more positive as it is less electronegative than carbon meaning that the hydrogen has less electron density surrounding the nucleus than the carbon. This results in the hydrogen having a more positive charge than the carbon atom.
Reaction energies of the molecule
E(CH4) = -40.52401404 E(CO2) = -188.58093945 E(H2) = -1.17853936 4*E(H2) = -4.71415744 E((H2O) = -76.41973740 2*E((H2O) = -152.8394748 ∆E = E(CH4) + 2*E((H2O) - (E(CO2) + 4*E(H2)) = -0.06839195au = -179.6kJmol
As the overall reaction is exothermic, it suggests that the products formed are more stable than the reactants.
Molecular orbitals for CH4
Bonding orbitals
1) The picture below represents the 1s orbital of carbon overlapping with the 1s orbitals of the 4 hydrogen atoms to form a sigma orbital.
2) The picture below represents the 2s orbital of carbon overlapping with the 1s orbitals of the 4 hydrogen atoms to form a sigma orbital.
3) The picture below represents the 2px orbital of carbon overlapping with the 1s orbitals of the 4 hydrogen atoms to form a pi orbital.
4) The picture below represents the 2py orbital of carbon overlapping with the 1s orbitals of the 4 hydrogen atoms to form a pi orbital.
5) The picture below represents the 2pz orbital of carbon overlapping with the 1s orbitals of the 4 hydrogen atoms to form a pi orbial.
Actual data for reaction energy for Sabatier reaction i.e. Formation of methane
Reaction energy calculated through Gaussview
-179.6kJ/mol
Reaction energy from Wiki page (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sabatier_reaction)
-165kJ/mol
Difference in energy
-14.6kJ/mol
Percentage difference
(-14.6/-165)*100 = 8.85%
Explanation
The reason why the energy change for the Gaussview reaction is more negative than that for the actual reaction could be due to errors in the Gaussview software meaning that the reaction calculated would be more exothermic.