Rep:Mod:AFD18
Ammonia, NH3
Calculation method | B3YLP
Basis set | 6-31G(d,p)
Final energy E(RB3LYP) in (au) | -56.55776873
RMS gradient (au)? 0.00000485
Point group of your molecule? C3V
Optimised Bond length (Å) = 1.01798
Optimised Angle (°) = 105.741
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
NH3 Optimised Molecule |
The optimisation file is given here.
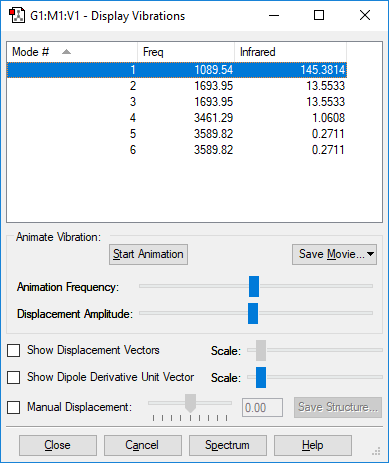
Bond Vibrations
| Bond Mode Number | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| wavenumber cm-1 |
1089 | 1694 | 1694 | 3461 | 3590 | 3590 |
| symmetry | A1 | E | E | A1 | E | E |
| intensity arbitrary units |
145 | 14 | 14 | 1 | 0.3 | 0.3 |
I expected 6 modes of vibration from the 3N-6 property of virbations.
Both pairs of wavenumbers at 1693 cm-1 (Modes 2 and 3) and 3589 cm-1 (Modes 5 and 6) have the same energy.
Modes 1, 2 and 3 are bending vibrations.
Modes 4, 5 and 6 are stretching vibrations.
Mode 4 is a highly symmetrical stretch vibration.
Mode 1 is the "umbrella" stretch.
I would expect to see two bands in the spectrum of gaseous ammonia, one of those for Mode 1 and the other for the degenerate vibrations of Mode 2 and 3.
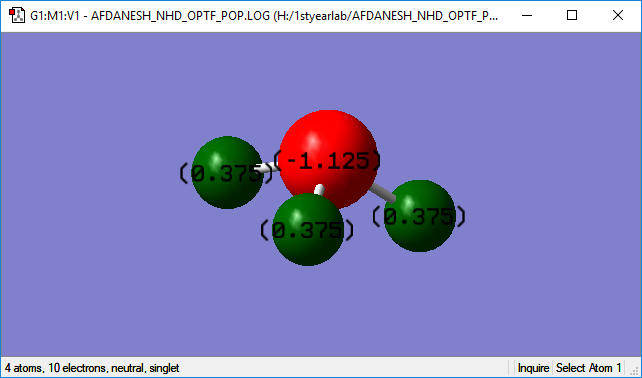
NH3 charges
I expected the Nitrogen atom's charge to be negative and the Hydrogen atom's charge to be positive since the Nitrogen atom is more electronegative hence it will pull more of the electron density in each of its bonds closer to its own atom.
| Atom Type | Nitrogen | Hydrogen |
| Charge | -1.125 | +0.375 |
Nitrogen, N2
Calculation method | B3YLP
Basis set | 6-31G(d,p)
Final energy E(RB3LYP) in (au) | = -109.523591113
RMS gradient (au)? = 0.0247
Point group of your molecule? D*H
Optimised Bond length (Å) = 1.09200
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
N2 Optimised Molecule |
The optimisation file is given here.
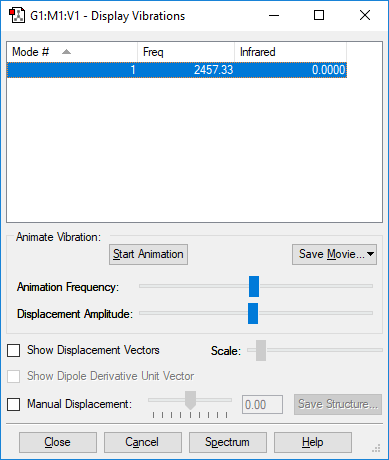
Bond Vibrations
| Bond Mode Number | 1 |
| wavenumber cm-1 |
2457 |
| symmetry | SGG |
| intensity arbitrary units |
0 |
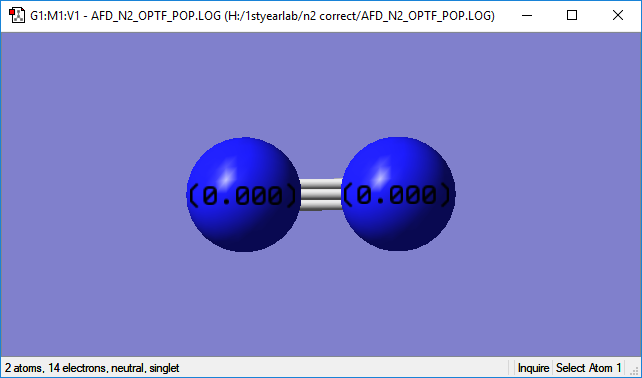
N2 charges
| Atom Type | Nitrogen | Nitrogen |
| Atom Position | Left | Right |
| Charge | 0.000 | 0.000 |
Hydrogen, H2
Calculation method | B3YLP
Basis set | 6-31G(d,p)
Final energy E(RB3LYP) in (au) | = -1.15928019702
RMS gradient (au)? = 0.0971
Point group of your molecule? D*H
Optimised Bond length (Å) = 0.0600
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES
H2 Optimised Molecule |
The optimisation file is given here.
Bond Vibrations
| Bond Mode Number | 1 |
| wavenumber cm-1 |
4465 |
| symmetry | SGG |
| intensity arbitrary units |
0 |
H2 charges
| Atom Type | Hydrogen | Hydrogen |
| Atom Position | Left | Right |
| Charge | 0.000 | 0.000 |
Nitrogen Bond, N2 Analysis
The molecule used to analyse the Nitrogen Triple bond was called DIDNAF.
The link is given below - https://bit.ly/2VpJrP9
A Jmol applet is shown below:
DIDNAF Molecule |
The bond length for DIDNAF is larger than the computated bond length from N2. This is because the Nitrogen atom in the TM complex is bonded to the metal atom, hence the bond has smaller energy and causes the bond length to be longer.
Haber-Bosch Process
The following values are calculated to work out the energy of the reaction
N2 + 3H2 -> 2NH3
All values are given in atomic units (a.u) before conversion to kJ/mol
- E(NH3)= -56.55776873
- 2*E(NH3)= -113.11553746
- E(N2)= -109.523591113
- E(H2)= -1.15928019702
- 3*E(H2)= -3.47784059106
- ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]=
in kJ/mol (multply by 2625.5) = -299.58466 kJ/mol
The ammonia product is more stable than the gaseous reactants.
Nitrogen trifluoride, NF3
Calculation method | B3YLP
Basis set | 6-31G(d,p)
Final energy E(RB3LYP) in (au) | -354.03254421
RMS gradient (au)? = 0.07304523
Point group of your molecule? = c3v
Optimised Bond length (Å) = 1.28000
Optimised Angle (°) = 109.471
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000164 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000108 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000613 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000296 0.001200 YES
NF3 Optimised Molecule |
The optimisation file is given here.
Bond Vibrations
| Bond Mode Number | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| wavenumber cm-1 |
482 | 482 | 644 | 930 | 930 | 1062 |
| symmetry | E | E | A1 | E | E | A1 |
| intensity arbitrary units |
1 | 1 | 3 | 208 | 208 | 40 |
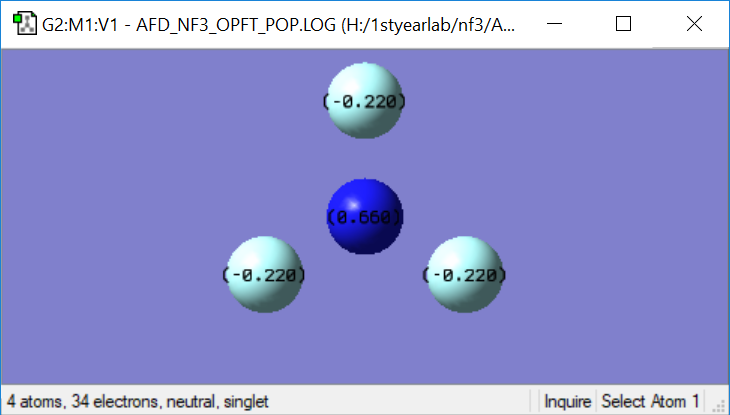
NF3 charges
| Atom Type | Nitrogen | Flourine |
| Charge | +0.660 | -0.220 |
Marking
Note: All grades and comments are provisional and subject to change until your grades are officially returned via blackboard. Please do not contact anyone about anything to do with the marking of this lab until you have received your grade from blackboard.
Wiki structure and presentation 1/1
Is your wiki page clear and easy to follow, with consistent formatting?
YES
Do you effectively use tables, figures and subheadings to communicate your work?
YES
NH3 1/1
Have you completed the calculation and given a link to the file?
YES
Have you included summary and item tables in your wiki?
YES
Have you included a 3d jmol file or an image of the finished structure?
YES
Have you included the bond lengths and angles asked for?
YES
Have you included the “display vibrations” table?
YES
Have you added a table to your wiki listing the wavenumber and intensity of each vibration?
YES
Did you do the optional extra of adding images of the vibrations?
YES
Have you included answers to the questions about vibrations and charges in the lab script?
YES - good explanations, well done.
N2 and H2 0.5/0.5
Have you completed the calculations and included all relevant information? (summary, item table, structural information, jmol image, vibrations and charges)
YES
Crystal structure comparison 0.5/0.5
Have you included a link to a structure from the CCDC that includes a coordinated N2 or H2 molecule?
YES
Have you compared your optimised bond distance to the crystal structure bond distance?
YES
Haber-Bosch reaction energy calculation 0.5/1
Have you correctly calculated the energies asked for? ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]
YES
Have you reported your answers to the correct number of decimal places?
no - you should have reported the energy to 1 d.p maximum.
Do your energies have the correct +/- sign?
YES
Have you answered the question, Identify which is more stable the gaseous reactants or the ammonia product?
YES
Your choice of small molecule 2/5
Have you completed the calculation and included all relevant information?
YES
Have you added information about MOs and charges on atoms?
It looks like you ran out of time, and only managed to report the charges.
Independence 0/1
If you have finished everything else and have spare time in the lab you could: Check one of your results against the literature, or Do an extra calculation on another small molecule, or Do some deeper analysis on your results so far