Rep:Mod:ABC1234
NH3 Optimization
N-H Bond length= 1.01798 H-N-H Bond angle=105.7410
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
Calculation Method = RB3LYP
Basis set = 6.31G(d,p)
Final Energy = -56.55776873 a.u
Point Group = C3v
File:SENITHAT NH3 OPTF POP.LOG
test molecule |
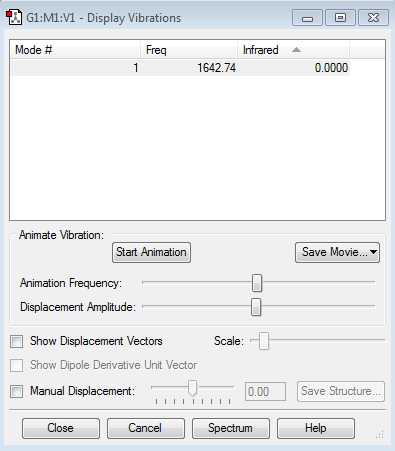
Display Vibrations
how many modes do you expect from the 3N-6 rule?
N = number of atoms, therefore 6 modes are calculated from the 3N-6 rule.
which modes are degenerate (ie have the same energy)? 2nd and 3rd, 5th and 6th
which modes are "bending" vibrations and which are "bond stretch" vibrations? 4,5 and 6 are stretching vibrations and 1,2 and 3 are bending vibrations
which mode is highly symmetric?
4th
one mode is known as the "umbrella" mode, which one is this?
1st
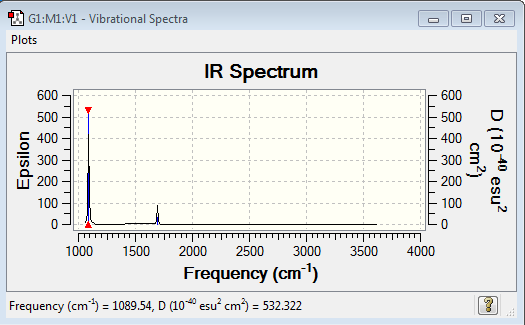
how many bands would you expect to see in an experimental spectrum of gaseous ammonia?
Two modes
Experimental IR spectrum
In the ammonia molecule since nitrogen is more electronegative than hydrogen, Nitrogen pulls the electron cloud generating a slight negative charge on itself and a slight positive charge on hydrogen.
Charge on Nitrogen = -1.125 Charge on hydrogen = 0.375
N2 Optimization
Bond length = 1.09200 A
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
Calculation Method = RB3LYP
Basis set = 6.31G(d,p)
Final energy = -109.52359111 a.u
Point group = D∞h
test molecule |
Display vibrations
SINCE MOLECULE IS LINEAR, THE 3n-5 RULE IS USED,
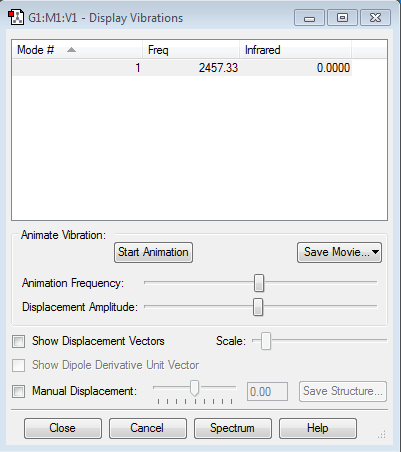
how many modes do you expect from the 3N-5 rule?
N = number of atoms, therefore 1 mode is calculated from the 3N-5 rule.
For nitrogen, since molecule is linear and since there is no dipole movement, there is only one vibrational mode is produced.
H2 Optimization
Bond length = 0.74279 A
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES
Calculation Method = RB3LYP
Basis set = 6.31G(d,p)
Final energy = -1.17853936 a.u
Point group = D∞h
test molecule |
Display vibrations
For Hydrogen, since molecule is linear and since there is no dipole movement, there is only one vibrational mode produced.
Haber process reaction Energies
E(NH3)= -56.55776873 a.u
2*E(NH3)= -113.1155375 a.u
E(N2)= -109.52359111 a.u
E(H2)= -1.17853936 a.u
3*E(H2)= -3.53561808 a.u
ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]= -0.05632831 a.u = -148.23 kJ/mol
O2 Optimisation (molecule of my choice)
Bond length = 1.21602 A
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000130 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000130 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000080 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000113 0.001200 YES
Calculation Method = RB3LYP
Basis set = 6.31G(d,p)
Final energy = -150.25742434 a.u
Point group = Dh∞
test molecule |
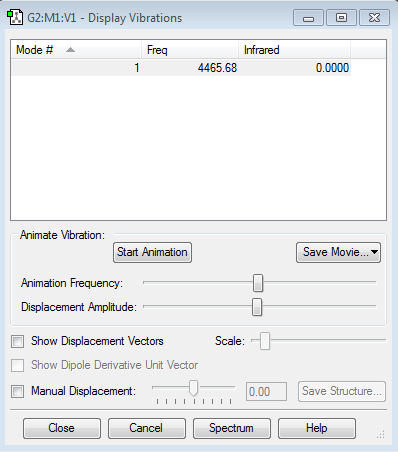
For oxygen, since molecule is linear and since there is no dipole movement, there is only one vibrational mode is produced.
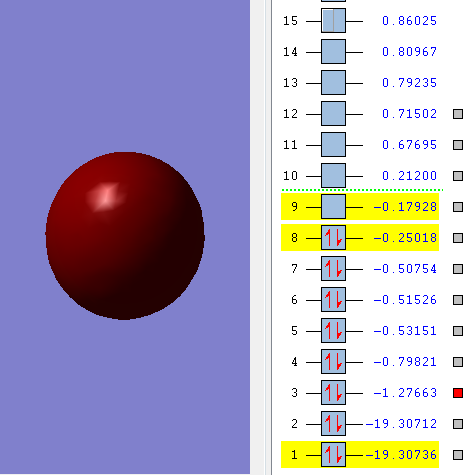
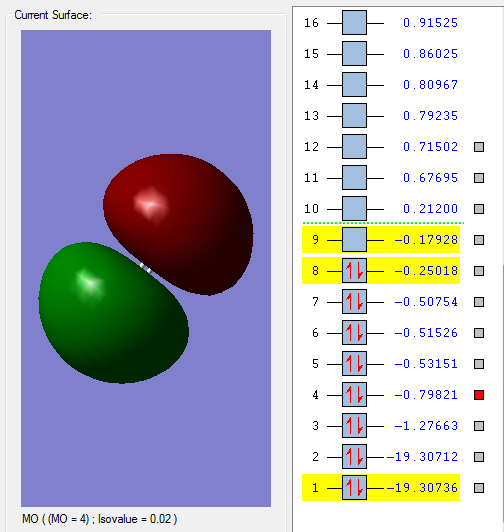
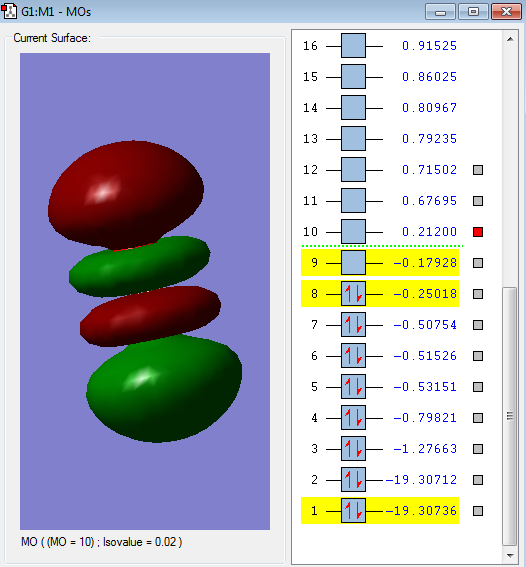
Molecular orbitals of Oxygen molecule
2σg MO
When the two 2S2 orbitals parallel to the bond mix in-phase, this MO is formed. This is a bonding MO and it is occupied. This is also comparatively low in energy.
2σ*u MO
When the two 2S2 orbitals overlap parallel to the bond in anti-phase manner. This is an anti-bonding orbital which is occupied. Higher in energy than above.
3σg MO
When the two 2px orbitals parallel to the bond overlap in phase way. This is a bonding MO which is occupied.
1π*g MO
When two 2py orbitals perpendicular to the bond overlap in anti-phase, this is formed. This is HOMO, highest occupied molecular orbital and also an anti-bonding orbital.
3σ*g MO
When two 2p orbitals parallel to the bond overlap in anti phase manner, this is formed. This is the lowest unoccupied molecular orbital.This is also an anti-bonding orbital.
The charge on each oxygen atom is zero.
Display vibrations
Independance section
Literature bond length of oxygen to 3 s.f = 1.21 A [1]
Bond length calculated by optimization = 1.21602 A
Percentage difference compared to literature value = 0.49752%
It is however not comparable as literature value is not as precise as the calculated value.
Reference;
[1] Chieh C. Bond Lengths and Energies. University of Waterloo http://www science uwaterloo ca/\ cchieh/cact/c120/bondel h tml. 2007