Rep:Mod:888
Bonding and Molecular Orbitals in Main Group Compounds
Optimisation, Frequency Analysis and Population Analysis of Simple Molecules
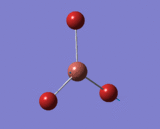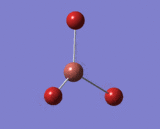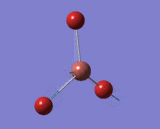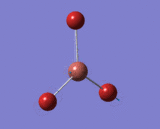
Optimisation of BH3
Calculation Setup and Summary
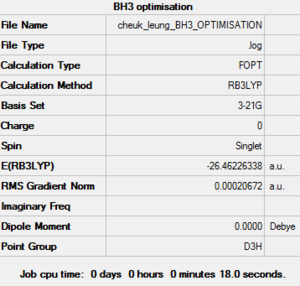
| Job Type | Optimisation |
|---|---|
| File Type | .log |
| Calculation Type | FOPT |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 3-21G |
| Keywords | # opt b3lyp/3-21g geom=connectivity |
| Final Energy (a.u.) | -26.46226338 |
| Gradient (a.u.) | 0.00020672 |
| Dipole Moment (debye) | 0.00 |
| Point Group | D3H |
| Calculation Time (sec) | 18.0 |
Results
Log File of BH3 Optimisation using 3-21G Basis Set
| B-H Bond Distance in BH3 | 1.193 Å |
|---|---|
| H-B-H Bond Angle in BH3 | 120.0° |
Item Table of BH3 Optimisation with basis set 3-21G:
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000413 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000271 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.001610 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.001054 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.071764D-06
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.1935 -DE/DX = 0.0004 !
! R2 R(1,3) 1.1935 -DE/DX = 0.0004 !
! R3 R(1,4) 1.1935 -DE/DX = 0.0004 !
! A1 A(2,1,3) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(2,1,4) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(3,1,4) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(2,1,4,3) 180.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Discussion
BH3 was first optimised using 3-21G basis set. Forces and displacements were successfully converged as shown in the item table. All B-H bond lengths and H-B-H angles are equivalent as expected.
Optimisation of BH3 using a better basis set
Calculation Setup and Summary

| Job Type | Optimisation |
|---|---|
| File Type | .log |
| Calculation Type | FOPT |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d.p) |
| Keywords | # opt b3lyp/6-31g(d.p) geom=connectivity |
| Final Energy (a.u.) | -26.61532363 |
| Gradient (a.u.) | 0.00000235 |
| Dipole Moment (debye) | 0.00 |
| Point Group | D3H |
| Calculation Time (sec) | 10.0 |
Results
Log File of BH3 Optimisation using 6-31G(d.p) Basis Set
| B-H Bond Distance in BH3 | 1.193 Å |
|---|---|
| H-B-H Bond Angle in BH3 | 120.0° |
Item Table of BH3 Optimisation with basis Set: 6-31G(d.p):
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000005 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000003 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000019 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000012 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.304899D-10
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.1923 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R2 R(1,3) 1.1923 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R3 R(1,4) 1.1923 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A1 A(2,1,3) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(2,1,4) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(3,1,4) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(2,1,4,3) 180.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Discussion
After optimising BH3 using 3-21G basis set, it was further optimised using a higher level basis set, 6-31G(d,p). All forces and displacements were converged. A lower level basis set was used first to avoid long calculation time and the higher level basis set provides a more accurate structure of the molecule. By using 6-31G(d,p) basis set, the energy of the molecule has decreased by 401.9 kJ/mol-1 which is a large difference. Bond angle and lengths have stayed the same. Although the bond lengths varied in the last two decimal places between the two basis sets, these were not reported as bond lengths are only accurate to 0.01 Å.
| Basis Set | Energy |
|---|---|
| 3-21G | -26.46226338 a.u. |
| 6-31G(d,p) | -26.61532363 a.u. |
| Δ Energy | 0.15306025 a.u. |
| Δ Energy | 401.9 kJ/mol-1 |
Optimisation of TIBr3 using HPC
Calculation Setup and Summary
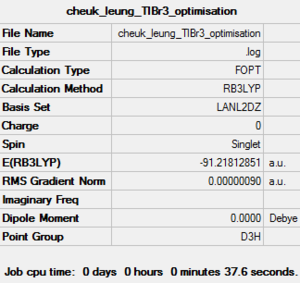
| Job Type | Optimisation |
|---|---|
| File Type | .log |
| Calculation Type | FOPT |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | LANL2DZ |
| Keywords | # opt b3lyp/lanl2dz geom=connectivity |
| Final Energy (a.u.) | -91.21812851 |
| Gradient (a.u.) | 0.00000090 |
| Dipole Moment (debye) | 0.00 |
| Point Group | D3H |
| Calculation Time (sec) | 37.6 |
Results
| Tl-Br Bond Distance in TIBr3 | 2.651 Å |
|---|---|
| Br-Tl-Br Bond Angle in TIBr3 | 120.0° |
Item Table of TIBr3 Optimisation:
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000002 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000022 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000014 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-6.084061D-11
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 2.651 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R2 R(1,3) 2.651 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R3 R(1,4) 2.651 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A1 A(2,1,3) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(2,1,4) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(3,1,4) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(2,1,4,3) 180.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Discussion
For the heavier molecule, TLBr3, calculations were more complicated than those of BH3 so they were not submitted to Gassview but to HPC to avoid long calculation time. Prior to submitting the calculations, symmetry was restricted to D3H with a high tollerance of 0.0001 in order to obtain more accurate vibrations and MOs later. Lan2DZ basis set was used and this uses D95V (medium level) on first row atoms and Los Alamos ECP (pseudo potentials) on heavier elements. Forces and displacements were successfully converged. All TL-Br bond lengths and Br-TL-Br angles are equivalent. The literature value of Tl-Br bond length is similar to the value obtained through gaussian, further supporting its accuracy.
| Optimised Tl-Br bond distance | Literature Tl-Br bond distance |
|---|---|
| 2.651Å | 2.51 Å [1] |
Optimisation of BBr3 using HPC
Calculation Setup and Summary

| Job Type | Optimisation |
|---|---|
| File Type | .log |
| Calculation Type | FOPT |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | GEN |
| Keywords | # opt b3lyp/gen geom=connectivity gfinput pseudo=read |
| Final Energy (a.u.) | -64.43645296 |
| Gradient (a.u.) | 0.00020672 |
| Dipole Moment (debye) | 0.00 |
| Point Group | D3H |
| Calculation Time (sec) | 36.1 |
Results
| B-Br Bond Distance in BBr3 | 1.933 Å |
|---|---|
| Br-B-Br Bond Angle in BBr3 | 120.0° |
Item Table of BBr3 Optimisation
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000008 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000005 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000036 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000023 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-4.026903D-10
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.934 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R2 R(1,3) 1.934 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R3 R(1,4) 1.934 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A1 A(2,1,3) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(2,1,4) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(3,1,4) 120.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(2,1,4,3) 180.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Discussion
Calculations were submitted to HPC and basis set GEN was used. All forces and displacements have converged and all B-Br bond lengths and Br-B-Br angles were equivalent.
BH3, BBr3 and TiBr3 Comparison
As the molecule becomes larger, the bond length increases while the bond angle stays the same.
| Molecule | Bond Distance (Å) | Bond Angle (°) |
|---|---|---|
| BH3 | 1.193 | 120.0 |
| BBr3 | 1.933 | 120.0 |
| TlBr3 | 2.651 | 120.0 |
Bond Angle: BH3, BBr3 and TlBr3 all adopt trigonal planar structure. Here, bond angle is not affected by the ligand or the central atom. All bonds within each structure are equivalent therefore bond angle does not change.
Bond Distance: The larger the molecule, the greater the number of electrons and the longer the bond lengths. This is observed when larger ligands were used (BH3 to BBr3 where H was replaced by Br) and also when a larger central atom was used (BBr3 to TlBr3 where B was replaced by TI). In both cases, an increase in bond length was observed.
Bonding in Gaussview: A bond is the attractive interaction between atoms. Its strength could be affected by several factors, such as distance, attractive forces between positively and negatively charged ions or the repulsion of the positively charged nucleus. A bond is not shown on Gaussview when this attractive interaction is too low. However, this does not imply that there is no interaction between the atoms although they may be very weak.
Frequency Analysis of BH3
Calculation Setup and Summary
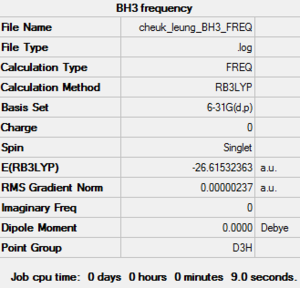
| Job Type | Frequency |
|---|---|
| File Type | .log |
| Calculation Type | FREQ |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Keywords | # freq b3lyp/6-31G(d.p)geom=connectivity |
| Final Energy (a.u.) | -26.61532363 |
| Gradient | 0.00000237 |
| Dipole Moment (debye) | 0.00 |
| Point Group | D3H |
| Calculation Time (sec) | 9.0 |
Results
Log File of BH3 Frequency Analysis
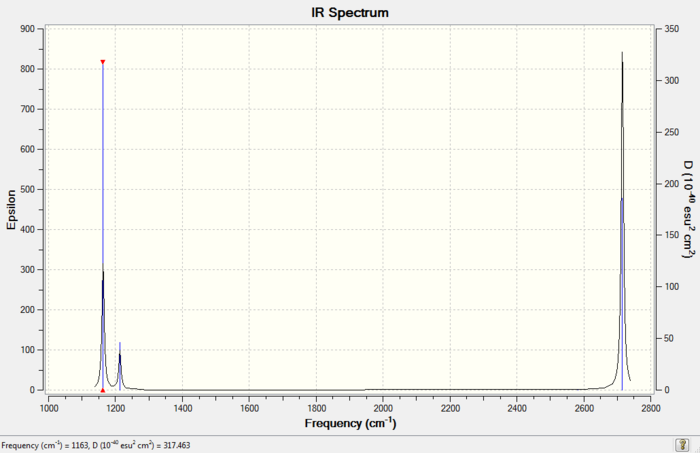

Low frequencies --- -0.9033 -0.7343 -0.0054 6.7375 12.2491 12.2824 Low frequencies --- 1163.0003 1213.1853 1213.1880
Discussion
Missing Peaks: There are two pairs of vibrations that have nearly identical frequencies, symmetrical stretching (No.2) and rocking (No.3) at 1213 cm-1 and also asymmetrical stretching (No.5) and symmetrical stretching (No.6) at 2715cm-1. Each pair of the vibrations have merged to give one single peak in the IR spectrum and can only be seen when the spectrum is expanded. The last missing peak is due to the extremely low intensity (0) of symmetric stretching (No.4).
Frequency Analysis of TIBr3
Calculation Setup and Summary

| Job Type | Frequency |
|---|---|
| File Type | .log |
| Calculation Type | FREQ |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | LANL2DZ |
| Keywords | # freq b3lyp/lanl2dz geom=connectivity |
| Final Energy (a.u.) | -91.21812851 |
| Gradient (a.u.) | 0.00000088 |
| Dipole Moment (debye) | 0.00 |
| Point Group | D3H |
| Calculation Time (sec) | 32.0 |
Results

Low frequencies --- -3.4213 -0.0026 -0.0004 0.0015 3.9367 3.9367 Low frequencies --- 46.4289 46.4292 52.1449
BH3 and TIBr3 Frequency Comparison
| Form of Vibration | BH3 (cm-1) | TIBr3 (cm-1) |
|---|---|---|
| Scissoring | 1213 | 46 |
| Rocking | 1213 | 46 |
| Wagging | 1163 | 52 |
| All symmetric stretching | 2582 | 165 |
| Asymmetrical Stretching | 2715 | 211 |
| 2 symmetric, 1 asymmetric stretch | 2715 | 211 |
BH3 has higher vibrational energy as the magnitude of its frequencies are much larger than those of TIBr3. This is because more energy is needed to move the heavier TIBr3 molecule and if the same amount of energy was supplied to both molecules, BH3 would move faster. Vibrational modes are not in the same order for the two molecules. This could be due to the change in mass as frequencies are sensitive to the mass of the molecule. The IR spectra look similar, with one intense peak on the right and two smaller peaks on the left.
The same method and basis set were used for both the optimisation and frequency analysis calculations to allow meaningful comparison of the results. Results can be compared if they have the same calculation setup as this would give rise to the same accuracy. However, if different methods were used, the error of the results would be different and any comparison would not be fair.
Frequency analysis is a means to check that the structure of the molecule has been successfully optimised. The first derivative should be close to zero and for the second derivative to be a minimum, it has to have a positive value.
Molecular Orbitals of BH3

| Job Type | Energy |
|---|---|
| File Type | .log |
| Calculation Type | SP |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Keywords | # b3lyp/6-31G(d.p) pop=(nbo.full) geom=connectivity |
| Final Energy (a.u.) | -26.61532363 |
| Dipole Moment (debye) | 0.00 |
| Point Group | D3H |
| Calculation Time (sec) | 31.1 |
Results and Discussion
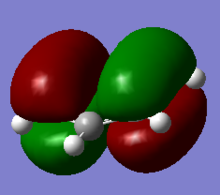
Additional Keyword, pop=full, was added with type under NBO set to "Full NBO". The real and LCAO MOs look very similar, validating the accuracy of the computer generated MOs.
Log File of BH3 Molecular Orbital Analysis
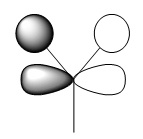
| Symmetry Labels | Calculated MO | Predicted MO |
|---|---|---|
| a1' |  |
|
| a1' |  |
|
| e' |  |
|
| e' | 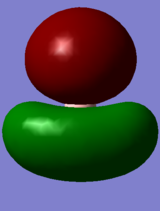 |
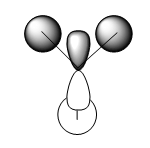
|
| a2' | 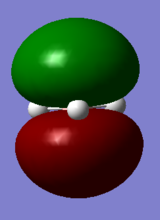 |
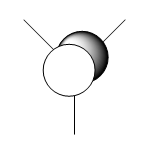
|
Optimisation of NH3
Calculation Setup and Summary

| Job Type | Optimisation |
|---|---|
| File Type | .log |
| Calculation Type | FOPT |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d.p) |
| Keywords | # opt b3lyp/6-31g(d.p) nosymm geom=connectivity |
| Final Energy (a.u.) | -56.55776856 |
| Gradient (a.u.) | 0.00000885 |
| Dipole Moment (debye) | 1.85 |
| Point Group | C1 |
| Calculation Time (sec) | 13.0 |
Results
Item Table of NH3 Optimisation
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000024 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000012 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000079 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000053 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.629730D-09
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R2 R(1,3) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R3 R(1,4) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A1 A(2,1,3) 105.7413 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(2,1,4) 105.7486 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(3,1,4) 105.7479 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(2,1,4,3) -111.8631 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Frequency Analysis of NH3
Calculation Setup and Summary

| Job Type | Frequency |
|---|---|
| File Type | .log |
| Calculation Type | FREQ |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Keywords | # freq b3lyp/6-31G(d.p) nosymm geom=connectivity |
| Final Energy (a.u.) | -56.55776856 |
| Gradient | 0.00000888 |
| Dipole Moment (debye) | 1.85 |
| Point Group | C1 |
| Calculation Time (sec) | 10.0 |
Results
Log file of NH3 Frequency Analysis
Low frequencies --- -30.7764 0.0013 0.0015 0.0019 20.3142 28.2484 Low frequencies --- 1089.5557 1694.1237 1694.1868
Molecular Orbitals of NH3
Calculation Setup and Summary

| Job Type | Energy |
|---|---|
| File Type | .log |
| Calculation Type | SP |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Keywords | # b3lyp/6-31G(d.p) pop=(nbo.full) geom=connectivity |
| Final Energy (a.u.) | -56.55776856 |
| Dipole Moment (debye) | 1.85 |
| Point Group | C1 |
| Calculation Time (sec) | 3.0 |
Results and Discussion
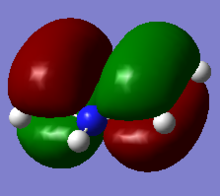
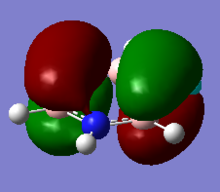
Log File of NH3 Molecular Orbital Analysis
NBO colour range was set from -1.000 to 1.000 and NBO charges for the nitrogen and hydrogen atoms are:
Using the additional keyword "nosymm" in the calculation takes the symmetry away from the molecule, therefore the point group appears to be C1|. Taking symmetry away from the molecule allows quicker calculation.
Optimisation of NH3BH3
Calculation and Setup

| Job Type | Optimisation |
|---|---|
| File Type | .log |
| Calculation Type | FOPT |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d.p) |
| Keywords | # opt b3lyp/6-31g(d.p) geom=connectivity |
| Final Energy (a.u.) | -83.22468918 |
| Gradient (a.u.) | 0.00006806 |
| Dipole Moment (debye) | 5.57 |
| Point Group | C1 |
| Calculation Time (sec) | 52.0 |
Results
Log file of NH3BH3 Optimisation
Item Table of NH3BH3 Optimisation:
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000137 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000063 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000606 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000336 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.994009D-07
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,7) 1.0186 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! R2 R(2,7) 1.0186 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! R3 R(3,7) 1.0186 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! R4 R(4,8) 1.2101 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! R5 R(5,8) 1.2101 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! R6 R(6,8) 1.2101 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! R7 R(7,8) 1.668 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! A1 A(1,7,2) 107.87 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(1,7,3) 107.8652 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(1,7,8) 111.0329 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A4 A(2,7,3) 107.8697 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A5 A(2,7,8) 111.0286 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A6 A(3,7,8) 111.0291 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A7 A(4,8,5) 113.8693 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A8 A(4,8,6) 113.8721 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A9 A(4,8,7) 104.6003 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A10 A(5,8,6) 113.8747 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A11 A(5,8,7) 104.6003 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A12 A(6,8,7) 104.5984 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(1,7,8,4) -179.9867 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D2 D(1,7,8,5) -59.9892 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D3 D(1,7,8,6) 60.0135 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D4 D(2,7,8,4) -59.9839 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D5 D(2,7,8,5) 60.0136 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D6 D(2,7,8,6) -179.9837 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D7 D(3,7,8,4) 60.0161 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D8 D(3,7,8,5) -179.9864 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D9 D(3,7,8,6) -59.9837 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Frequency Analysis of NH3BH3
Calculation Setup and Summary
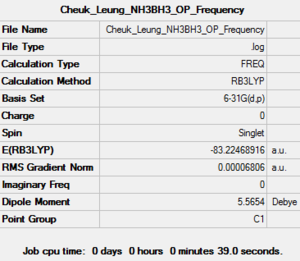
| Job Type | Frequency |
|---|---|
| File Type | .log |
| Calculation Type | FREQ |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d.p) |
| Keywords | # freq b3lyp/6-31G(d.p) geom=connectivity |
| Final Energy (a.u.) | -83.22468916 |
| Gradient (a.u.) | 0.00006806 |
| Dipole Moment (debye) | 5.57 |
| Point Group | C1 |
| Calculation Time (sec) | 39.0 |
Results
Log file of NH3BH3 Frequency Analysis
Low frequencies --- -0.0009 -0.0009 -0.0007 17.1076 22.5380 38.6973 Low frequencies --- 265.8489 632.3775 639.0687
Energy Analysis
A difference in energy is observed between NH3BH3 and the sum of NH3 and BH3. The difference is -135.5 kJ/mol-1 as reported below.
| NH3 | -56.55776856 a.u. |
|---|---|
| BH3 | -26.61532363 a.u. |
| NH3BH3 | -83.22468918 a.u. |
| NH3BH3 - [NH3 + BH3] | -0.05159699 a.u. |
| NH3BH3 - [NH3 + BH3] | -135.467897 kJ/mol-1 |
Optimisation and Analysis of Aromatic Molecules
Optimisation of Benzene
Calculation Setup and Summary
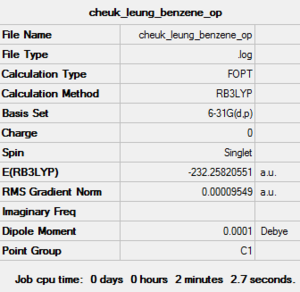
| Job Type | Optimisation |
|---|---|
| File Type | .log |
| Calculation Type | FOPT |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d.p) |
| Keywords | # opt b3lyp/6-31g(d.p) geom=connectivity |
| Final Energy (a.u.) | -232.25820551 |
| Gradient (a.u.) | 0.00009549 |
| Dipole Moment (debye) | 0.00 |
| Point Group | C1 |
| Calculation Time | 2 minutes 2.7 seconds |
Results
Item Table of Benzene Optimisation with basis Set: 6-31G(d.p):
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000212 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000085 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000991 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000315 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-5.157454D-07
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.3963 -DE/DX = 0.0001 !
! R2 R(1,6) 1.3961 -DE/DX = 0.0002 !
! R3 R(1,7) 1.0861 -DE/DX = 0.0002 !
! R4 R(2,3) 1.3961 -DE/DX = 0.0002 !
! R5 R(2,8) 1.0861 -DE/DX = 0.0002 !
! R6 R(3,4) 1.3963 -DE/DX = 0.0001 !
! R7 R(3,9) 1.086 -DE/DX = 0.0002 !
! R8 R(4,5) 1.3961 -DE/DX = 0.0002 !
! R9 R(4,10) 1.086 -DE/DX = 0.0002 !
! R10 R(5,6) 1.3963 -DE/DX = 0.0001 !
! R11 R(5,11) 1.0861 -DE/DX = 0.0002 !
! R12 R(6,12) 1.0861 -DE/DX = 0.0002 !
! A1 A(2,1,6) 119.9972 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(2,1,7) 119.9949 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(6,1,7) 120.0079 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A4 A(1,2,3) 120.0079 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A5 A(1,2,8) 119.9881 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A6 A(3,2,8) 120.004 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A7 A(2,3,4) 119.9948 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A8 A(2,3,9) 120.0086 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A9 A(4,3,9) 119.9966 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A10 A(3,4,5) 119.9972 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A11 A(3,4,10) 119.9934 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A12 A(5,4,10) 120.0094 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A13 A(4,5,6) 120.0083 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A14 A(4,5,11) 120.0014 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A15 A(6,5,11) 119.9904 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A16 A(1,6,5) 119.9946 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A17 A(1,6,12) 120.0106 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A18 A(5,6,12) 119.9948 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(6,1,2,3) -0.0059 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D2 D(6,1,2,8) 180.0023 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D3 D(7,1,2,3) -180.01 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D4 D(7,1,2,8) -0.0019 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D5 D(2,1,6,5) -0.0055 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D6 D(2,1,6,12) -179.9972 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D7 D(7,1,6,5) -180.0013 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D8 D(7,1,6,12) 0.007 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D9 D(1,2,3,4) 0.0117 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D10 D(1,2,3,9) -179.9914 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D11 D(8,2,3,4) 180.0036 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D12 D(8,2,3,9) 0.0005 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D13 D(2,3,4,5) -0.0062 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D14 D(2,3,4,10) -180.0059 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D15 D(9,3,4,5) 179.9969 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D16 D(9,3,4,10) -0.0028 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D17 D(3,4,5,6) -0.0051 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D18 D(3,4,5,11) 180.0058 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D19 D(10,4,5,6) -180.0055 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D20 D(10,4,5,11) 0.0054 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D21 D(4,5,6,1) 0.011 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D22 D(4,5,6,12) 180.0027 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D23 D(11,5,6,1) -179.9999 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D24 D(11,5,6,12) -0.0082 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Frequency Analysis of Benzene
Calculation Setup and Summary
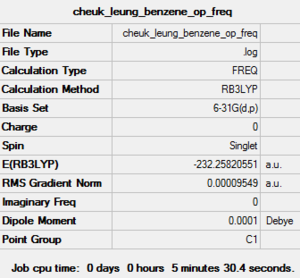
| Job Type | Frequency |
|---|---|
| File Type | .log |
| Calculation Type | FREQ |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d.p) |
| Keywords | # freq b3lyp/6-31G(d.p) geom=connectivity |
| Final Energy (a.u.) | -232.25820551 |
| Gradient (a.u.) | 0.00009549 |
| Dipole Moment (debye) | 0.00 |
| Point Group | C1 |
| Calculation Time | 5 minutes 30.4 seconds |
Results
Low frequencies --- -17.2788 -14.5868 -9.6527 -0.0010 -0.0009 0.0004 Low frequencies --- 413.7971 414.4697 620.8545
Molecular Orbitals of Benzene
Calculation Setup and Summary

| Job Type | Energy |
|---|---|
| File Type | .log |
| Calculation Type | SP |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Keywords | # rb3lyp/6-31G(d.p) pop=(nbo.full) geom=connectivity |
| Final Energy (a.u.) | -232.25820551 |
| Dipole Moment (debye) | 0.00 |
| Point Group | C1 |
| Calculation Time | 1 minute 5.2 seconds |
Optimisation of Boratabenzene
Calculation Setup and Summary

| Job Type | Optimisation |
|---|---|
| File Type | .log |
| Calculation Type | FOPT |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d.p) |
| Keywords | # opt b3lyp/6-31g(d.p) geom=connectivity |
| Final Energy (a.u.) | -219.02052962 |
| Gradient (a.u.) | 0.00016240 |
| Dipole Moment (debye) | 2.84 |
| Point Group | C1 |
| Calculation Time | 4 minutes 4.0 seconds |
Results
Item Table of Boratabenzene Optimisation with basis Set: 6-31G(d.p):
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000244 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000077 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.001093 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000402 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-8.683304D-07
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.4053 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! R2 R(1,5) 1.3988 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R3 R(1,6) 1.0968 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R4 R(2,3) 1.4053 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! R5 R(2,7) 1.0917 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! R6 R(3,4) 1.3989 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R7 R(3,8) 1.0968 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R8 R(4,9) 1.0971 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! R9 R(4,12) 1.5139 -DE/DX = 0.0001 !
! R10 R(5,11) 1.0971 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! R11 R(5,12) 1.5139 -DE/DX = 0.0001 !
! R12 R(10,12) 1.2178 -DE/DX = 0.0002 !
! A1 A(2,1,5) 122.1404 -DE/DX = 0.0001 !
! A2 A(2,1,6) 117.4328 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(5,1,6) 120.4268 -DE/DX = -0.0002 !
! A4 A(1,2,3) 120.4471 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! A5 A(1,2,7) 119.7758 -DE/DX = 0.0001 !
! A6 A(3,2,7) 119.777 -DE/DX = 0.0001 !
! A7 A(2,3,4) 122.1409 -DE/DX = 0.0001 !
! A8 A(2,3,8) 117.4337 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A9 A(4,3,8) 120.4254 -DE/DX = -0.0002 !
! A10 A(3,4,9) 115.9348 -DE/DX = 0.0002 !
! A11 A(3,4,12) 120.0926 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! A12 A(9,4,12) 123.9726 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! A13 A(1,5,11) 115.9367 -DE/DX = 0.0002 !
! A14 A(1,5,12) 120.0927 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! A15 A(11,5,12) 123.9706 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! A16 A(4,12,5) 115.0862 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A17 A(4,12,10) 122.4584 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A18 A(5,12,10) 122.4555 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(5,1,2,3) -0.0021 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D2 D(5,1,2,7) -180.001 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D3 D(6,1,2,3) -180.0013 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D4 D(6,1,2,7) -0.0002 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D5 D(2,1,5,11) 180.0009 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D6 D(2,1,5,12) 0.0003 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D7 D(6,1,5,11) 0.0001 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D8 D(6,1,5,12) -180.0005 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D9 D(1,2,3,4) 0.0028 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D10 D(1,2,3,8) 180.0006 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D11 D(7,2,3,4) 180.0017 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D12 D(7,2,3,8) -0.0006 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D13 D(2,3,4,9) -180.002 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D14 D(2,3,4,12) -0.0017 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D15 D(8,3,4,9) 0.0003 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D16 D(8,3,4,12) 180.0007 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D17 D(3,4,12,5) -0.0001 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D18 D(3,4,12,10) -179.9997 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D19 D(9,4,12,5) 180.0002 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D20 D(9,4,12,10) 0.0006 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D21 D(1,5,12,4) 0.0008 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D22 D(1,5,12,10) 180.0004 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D23 D(11,5,12,4) -179.9999 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D24 D(11,5,12,10) -0.0003 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Frequency Analysis of Boratabenzene
Calculation Setup and Summary

| Job Type | Frequency |
|---|---|
| File Type | .log |
| Calculation Type | FREQ |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d.p) |
| Keywords | # freq b3lyp/6-31G(d.p) geom=connectivity |
| Final Energy (a.u.) | -219.02052962 |
| Gradient (a.u.) | 0.00016237 |
| Dipole Moment (debye) | 2.85 |
| Point Group | C1 |
| Calculation Time | 5 minutes 35.1 seconds |
Results
Low frequencies --- -14.5333 -0.0008 -0.0006 -0.0005 15.8823 18.0033 Low frequencies --- 371.2529 404.2372 565.1706
Molecular Orbitals of Boratabenzene
Calculation Setup and Summary
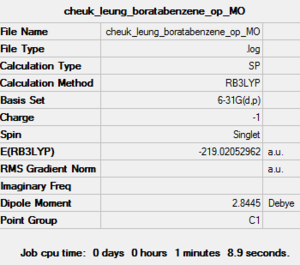
| Job Type | Energy |
|---|---|
| File Type | .log |
| Calculation Type | SP |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Keywords | # rb3lyp/6-31G(d.p) pop=(nbo.full) geom=connectivity |
| Final Energy (a.u.) | -219.02052962 |
| Dipole Moment (debye) | 2.84 |
| Point Group | C1 |
| Calculation Time | 1 minute 8.9 seconds |
Optimisation of Pyridinium
Calculation Setup and Summary
| Job Type | Optimisation |
|---|---|
| File Type | .log |
| Calculation Type | FOPT |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d.p) |
| Keywords | # opt b3lyp/6-31g(d.p) geom=connectivity |
| Final Energy (a.u.) | -248.66807397 |
| Gradient (a.u.) | 0.00003236 |
| Dipole Moment (debye) | 1.87 |
| Point Group | C1 |
| Calculation Time | 3 minutes 57.6 seconds |
Results
Item Table of Pyridinium Optimisation with basis Set: 6-31G(d.p):
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000059 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000020 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000685 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000162 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-5.641922D-08
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.3988 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R2 R(1,5) 1.3839 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R3 R(1,6) 1.0835 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R4 R(2,3) 1.3988 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R5 R(2,7) 1.0852 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R6 R(3,4) 1.3839 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R7 R(3,8) 1.0835 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R8 R(4,9) 1.0832 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R9 R(4,12) 1.3524 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R10 R(5,11) 1.0832 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R11 R(5,12) 1.3524 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R12 R(10,12) 1.0169 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A1 A(2,1,5) 119.0826 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(2,1,6) 121.4953 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! A3 A(5,1,6) 119.4221 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A4 A(1,2,3) 120.0564 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A5 A(1,2,7) 119.9711 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A6 A(3,2,7) 119.9725 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A7 A(2,3,4) 119.0823 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A8 A(2,3,8) 121.4967 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! A9 A(4,3,8) 119.4211 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A10 A(3,4,9) 123.9315 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A11 A(3,4,12) 119.2352 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A12 A(9,4,12) 116.8333 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A13 A(1,5,11) 123.9329 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A14 A(1,5,12) 119.2347 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A15 A(11,5,12) 116.8323 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A16 A(4,12,5) 123.3088 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A17 A(4,12,10) 118.3459 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A18 A(5,12,10) 118.3453 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(5,1,2,3) -0.0001 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D2 D(5,1,2,7) 180.0004 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D3 D(6,1,2,3) -180.0002 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D4 D(6,1,2,7) 0.0003 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D5 D(2,1,5,11) 180.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D6 D(2,1,5,12) -0.0004 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D7 D(6,1,5,11) 0.0001 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D8 D(6,1,5,12) -180.0003 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D9 D(1,2,3,4) 0.0004 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D10 D(1,2,3,8) 180.0002 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D11 D(7,2,3,4) -180.0001 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D12 D(7,2,3,8) -0.0003 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D13 D(2,3,4,9) -180.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D14 D(2,3,4,12) -0.0002 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D15 D(8,3,4,9) 0.0002 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D16 D(8,3,4,12) -180.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D17 D(3,4,12,5) -0.0003 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D18 D(3,4,12,10) 180.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D19 D(9,4,12,5) -180.0005 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D20 D(9,4,12,10) -0.0002 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D21 D(1,5,12,4) 0.0006 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D22 D(1,5,12,10) 180.0003 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D23 D(11,5,12,4) 180.0002 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D24 D(11,5,12,10) -0.0001 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Frequency Analysis of Pyridinium
Calculation Setup and Summary
| Job Type | Frequency |
|---|---|
| File Type | .log |
| Calculation Type | FREQ |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d.p) |
| Keywords | # freq b3lyp/6-31G(d.p) geom=connectivity |
| Final Energy (a.u.) | -248.66807397 |
| Gradient (a.u.) | 0.00003234 |
| Dipole Moment (debye) | 1.87 |
| Point Group | C1 |
| Calculation Time | 5 minutes 40.1 seconds |
Results
Low frequencies --- -7.1947 -0.0004 -0.0003 0.0006 17.4261 18.7048 Low frequencies --- 392.4494 404.0786 620.4749
Molecular Orbitals of Pyridinium
Calculation Setup and Summary
| Job Type | Energy |
|---|---|
| File Type | .log |
| Calculation Type | SP |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Keywords | # b3lyp/6-31G(d.p) pop=(nbo.full) geom=connectivity |
| Final Energy (a.u.) | -248.66807397 |
| Dipole Moment (debye) | 1.87 |
| Point Group | C1 |
| Calculation Time | 1 minute 12.2 seconds |
Optimisation of Borazine
Calculation Setup and Summary

| Job Type | Optimisation |
|---|---|
| File Type | .log |
| Calculation Type | FOPT |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d.p) |
| Keywords | # opt b3lyp/6-31g(d.p) geom=connectivity |
| Final Energy (a.u.) | -242.68458731 |
| Gradient (a.u.) | 0.00009860 |
| Dipole Moment (debye) | 0.00 |
| Point Group | C1 |
| Calculation Time | 5 minutes 7.4 seconds |
Results
Item Table of Borazine Optimisation with basis Set: 6-31G(d.p):
align="centre"
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000123 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000047 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000597 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000125 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-2.274814D-07
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,8) 1.0098 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R2 R(2,12) 1.1949 -DE/DX = 0.0001 !
! R3 R(3,9) 1.0098 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R4 R(4,11) 1.1949 -DE/DX = 0.0001 !
! R5 R(5,7) 1.0098 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R6 R(6,10) 1.1949 -DE/DX = 0.0001 !
! R7 R(7,10) 1.4307 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! R8 R(7,11) 1.4307 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! R9 R(8,10) 1.4307 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! R10 R(8,12) 1.4307 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! R11 R(9,11) 1.4307 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! R12 R(9,12) 1.4307 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! A1 A(5,7,10) 118.563 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(5,7,11) 118.5556 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(10,7,11) 122.8814 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! A4 A(1,8,10) 118.5503 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A5 A(1,8,12) 118.5526 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A6 A(10,8,12) 122.8971 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! A7 A(3,9,11) 118.5576 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A8 A(3,9,12) 118.5593 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A9 A(11,9,12) 122.8832 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A10 A(6,10,7) 121.4456 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A11 A(6,10,8) 121.4465 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
! A12 A(7,10,8) 117.1079 -DE/DX = 0.0001 !
! A13 A(4,11,7) 121.4428 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A14 A(4,11,9) 121.434 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A15 A(7,11,9) 117.1232 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A16 A(2,12,8) 121.4432 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A17 A(2,12,9) 121.4496 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A18 A(8,12,9) 117.1072 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(5,7,10,6) -0.0002 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D2 D(5,7,10,8) 179.9997 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D3 D(11,7,10,6) -179.9992 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D4 D(11,7,10,8) 0.0008 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D5 D(5,7,11,4) 0.0007 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D6 D(5,7,11,9) -179.9994 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D7 D(10,7,11,4) 179.9996 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D8 D(10,7,11,9) -0.0005 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D9 D(1,8,10,6) -0.0002 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D10 D(1,8,10,7) 179.9999 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D11 D(12,8,10,6) 179.9995 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D12 D(12,8,10,7) -0.0005 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D13 D(1,8,12,2) -0.0007 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D14 D(1,8,12,9) 179.9996 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D15 D(10,8,12,2) 179.9996 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D16 D(10,8,12,9) -0.0001 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D17 D(3,9,11,4) 0.0002 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D18 D(3,9,11,7) -179.9997 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D19 D(12,9,11,4) 179.9998 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D20 D(12,9,11,7) -0.0001 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D21 D(3,9,12,2) 0.0003 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D22 D(3,9,12,8) -180.0 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D23 D(11,9,12,2) -179.9993 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D24 D(11,9,12,8) 0.0004 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Frequency Analysis of Borazine
Calculation Setup and Summary

| Job Type | Frequency |
|---|---|
| File Type | .log |
| Calculation Type | FREQ |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d.p) |
| Keywords | # freq b3lyp/6-31G(d.p) geom=connectivity |
| Final Energy (a.u.) | -242.68458742 |
| Gradient (a.u.) | 0.00009865 |
| Dipole Moment (debye) | 0.00 |
| Point Group | C1 |
| Calculation Time | 5 minutes 32.4 seconds |
Results
Low frequencies --- -16.7791 -10.4871 -4.9436 -0.0005 -0.0004 0.0007 Low frequencies --- 288.8561 289.6929 404.2203
Molecular Orbitals of Borazine
Calculation Setup and Summary

| Job Type | Energy |
|---|---|
| File Type | .log |
| Calculation Type | SP |
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Keywords | # b3lyp/6-31G(d.p) pop=(nbo.full) geom=connectivity |
| Final Energy (a.u.) | -242.68458731 |
| Dipole Moment (debye) | 0.00 |
| Point Group | C1 |
| Calculation Time (sec) | 1 minute 7.0 seconds |
Analysis
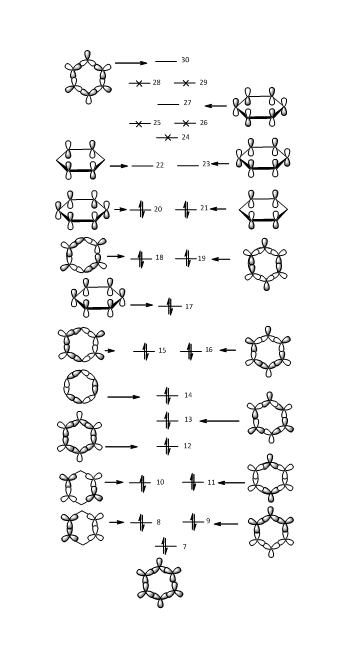
The LCAOs of benzene are shown below. The higher the symmetry of the molecule and the lower the number of nodal planes, the easier it is for the electrons to delocalise in the structure and so the lower the energy of the system.
Charge Distribution
| Molecule | Distribution by Charge (Number) | Distribution by Charge (Colour) |
|---|---|---|
| Benzene | 
|
|
| Boratabenzene | 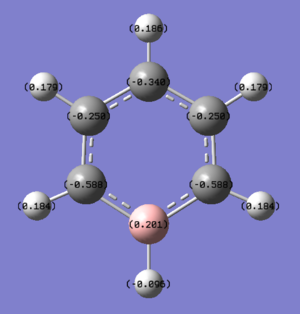
|

|
| Pyridinium | 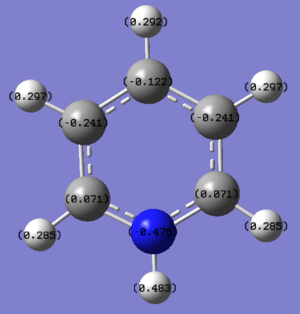
|
|
| Borazine | 
|
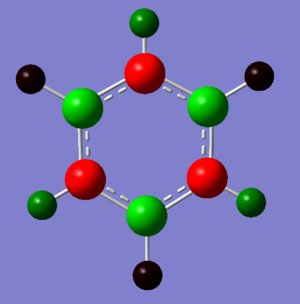
|
Benzene: Charge is distributed evenly in benzene as shown by both the colour and the numerical value of the distribution of charge. All C atoms have the same charge, -0.239, unlike boratabenzene and pyridinium as they both contain a heteroatom.
Boratabenzene: Compared to benzene, boratabenzene has a C-H unit replaced by a B-H unit, with B atom being more electropositive than C atom. This change is reflected in the distribution of charge with B atom being positively charge, +0.201. All the other C atoms, charges -0.588 (ortho), -0.340 (para) and -0.250 (meta) are more negatively charged compared to the C atoms in benzene. This is because electronegative C atoms pull electron density away from the B atom and is also caused by the delocalisation of the anionic charge.
The C atoms that are ortho and para to B atom have a larger negative charge, with ortho C being more negative than para C due to ortho C being closer to B than para C. The meta C have a smaller negative charge compared to the ortho and para C atoms due to resonance and delocalisation of the anionic charge. However the meta C atoms are still more negative than the C atoms in benzene.
The change in charge distribution is also reflected by the increased brightness of the red colour of the C atoms next to the B atom; brighter the red colour, more negatively charged the atom. It is worth mentioning that the H atom attached to the B atom is negatively charged, -0.095, unlike all the other H atoms in boratabenzene and benzene. This is due to the replacement of C atom by the electropositive B atom.
Pyridinium: Pyridinium on the other hand, has the same structure as benzene but with a C-H unit replaced by an N-H unit. N atom being more electronegative than C atom, pulls electron density away from the C thus N has a large negative charge, -0.476. This causes the C adjacent to the N to be more positively charged, +0.071, and they are the only positively charged C atoms in the three structures of benzene, boratabenzene and pyridinium. However due to cationic resonance, the C atoms at the meta position, -0.241, actually have a larger negative charge than the C atom at the para position, -0.122.
Borazine: Borazine is an aromatic compound with alternate N and B atoms replacing the 6 C atoms in benzene. The B atoms have large positive charge, +0.747, and N atoms have large negative charge, -1.102. Both atoms are more positive and more negatively charged than the B and N atoms in boratabenzene and pyridinium respectively. This is shown by the bright green and bright red colours of the B and N atoms. The molecule is physically stable but it is more likely to be attacked by nucleophiles or electrophiles. This is due to the high charges on each of the atoms on the aromatic molecule thus it is more reactive than benzene.
MO Comparison
MO 7 sigma: MO 7 is an all sigma bonding orbital. Even distribution can be seen in benzene where it adopts a symmetrical star shape, showing that all C atoms have the same share of the electron density. This uniform distribution is broken when a heteroatom is introduced into the aromatic system. In boratabenzene, the electron density has shifted away from the B atom which causes the B atom to be exposed. The other side of the ring (opposite to the B atom) has a similar shape compared to benzene. However it is more rounded as more electron density has been pushed to this side. The opposite is observed in pyridinium where electron density is shifted towards the N atom. The three C-H units that are opposite to the N atom are exposed along with the H atoms that are bonded to the adjacent C atoms. Unlike benzene, borazine adopts a triangular shape covering the N-H units and exposing the B-H units. This shows that electron density around N atoms is greater than that of the B atoms, which corresponds to the observation from the charge distribution.
MO 17 pi: MO 17 is an all pi bonding orbital. It adopts different signs above and below the plane of the molecule. For benzene the hexagonal shape is symmetrical which is expected as all C atoms have the same degree of electron density. Similar to MO 7 sigma, electron density around the B atom is less than that of the C atoms in boratabenzene. This results in a more rounded shape for the side that is opposite to the B atom compared to benzene. Again, the opposite is observed for pyridinium where electron density is shifted towards the N atom so less electron density is seen for the C-H units that are on the opposite side of the N atom. Borazine adopts a more rounded triangle shape where electron density for N atom is greater than that of the B atom.
MO 21 HOMO: The MOs are divided into four parts with two nodal planes. The shapes of the MOs in benzene are all similar. In contrast to that of the boratabenzene, one side of the molecule has two smaller rounded shape lobes with opposite signs. On the other side, the shape of the oppositely charged lobes is slightly triangular and larger. It also has a positive energy level so it is anti-bonding. This decreases the stability of the molecule since it is filled and so it exists as ligands in complexes or dimers. The lobes of pyridinium and borazine are more similar to benzene compared to boratabenzene, with all the lobes being more similar in size. The difference between these MOs is less than that of the difference between the 7 sigma MOs and also the 17 pi MOs because it has higher energy thus weaker interactions between sigma and pi orbitals.
References
1. J. Glaser, G. Johansson. Acta Chemica Scandinavica, 1982, 36a, Pp. 125-135.