Rep:Mod:7317
Appearance
Introduction To Molecular Modelling 2
NH3 Molecule
- Molecule= NH3
- Calculation Method=RB3LYP
- Basis Step= 6-31G(d,p)
- Final energy E(RB3LYP)= -56.55776873 a.u.
- RMS gradient= 0.00000485 a.u.
- Point Group= C3V
- N-H Bond Distance= 1.01798 Å
- H-N-H bond angle= 105.741°
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
NH3 Animation
test molecule |
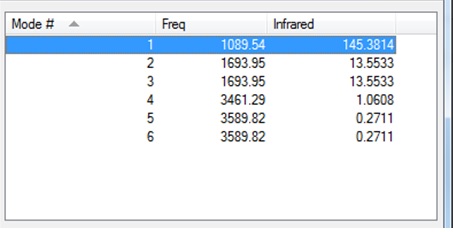
Vibrational Modes of NH3 molecule
- From the 3N-6 rule, I would expect 6 nodes for a molecule of NH3.
- The 2nd and 3rd, and the 5th and 6th vibrational modes are degenerate with respect to each other.
- The 1st,2nd and 3rd modes are bending vibrations, while the 4th,5th and 6th modes are stretching.
- The 4th vibrational mode is highly symmetric.
- The 1st vibrational mode is known as the 'umbrella mode'.
- I would expect to see 2 bands in an experimental spectrum of gaseous ammonia- the 1st vibrational mode, and the 2nd and 3rd which are degenerate. This is because the 4th,5th and 6th vibrational modes have a very low intensity compared to the first 3 vibrational modes so wouldn't be seen in the experimental spectrum.
Charge Distribution of NH3 molecule
- The charge on the nitrogen atom is -1.125
- The charge on the hydrogen atoms is +0.375.
- I would have expected that the charge of the nitrogen atom would be negative, while the charge on the hydrogen atoms would be positive. This charge distribution has agreed with my expectations.
H2 Molecule
- Calculation Method- RB3LYP
- Basis Step- 6-31G(d,p)
- Final Energy- -1.17853936 au
- RMS Gradient- 0.00000017 au
- Point Group- D*H
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES
- There is one vibrational mode at a frequency of 4465.68 cm-1
N2 molecule
- Calculation Method- RB3LYP
- Basis Step- 6-31G(d,p)
- Final Energy- -109.52412868 au
- RMS gradient- 0.000000326 au
- Point Group- D*H
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000006 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000006 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000002 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000002 0.001200 YES
- There is one vibrational mode at a frequency of 2457.35 cm-1
Calculating the Energy Change for the Haber process
- E(NH3)= -56.55776873 au
- 2*E(NH3)= -113.1155375 au
- E(N2)= -109.52412868 au
- E(H2)= -1.17853936 au
- 3*E(H2)= -3.53561808 au
- ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]= -0.05579074au = -146.48 kJ/mol
- The ammonia product is more stable than the gaseous reactants.
Project Molecule[CN-]
Optimization Information
- Calculation Method- RB3LYP
- Basis Step- 6-31G(d,p)
- Final Energy- -92.82453153 au
- RMS Gradient- 0.00001661 au
- Point Group- C*V
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000029 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000029 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000013 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000018 0.001200 YES
CN- Animation
test molecule |
Vibrational Modes
- There is only one vibrational mode for CN-, which occurs at a frequency of 2139.14 cm-1. This is a bond stretch vibration.
Charge Distribution in CN- molecule
- The charge on the carbon atom is -0.246.
- The charge on the nitrogen atom is -0.754.
- I expected that the charge on the nitrogen atom would be more negative than on the carbon atom, as it is a more electronegative atom. The calculated charges confirm my expectations.
Molecular Orbitals
- This bonding molecular orbital (σ bond) is formed from two 2s atomic orbitals, combining in the same phase. It is occupied and deep in energy.
- It has a node near the carbon atom because the 2s orbitals are slightly hybridised with 2p orbitals, which influence the electron density.
- This anti-bonding molecular orbital (σ* bond) is formed from two 2s atomic orbitals, combining out of phasse. It is occupied and deep in energy.
- It has a node near the nitrogen atom because of the influence of 2p orbitals.
- This anti-bonding molecular orbital (π* orbital) is formed from two Py or two Pz orbitals, combining out of phase. It is the LUMO.
- This bonding molecular orbital (σ bond) is formed from two 2Px orbitals, combining in phase. It is the HOMO.
- This bonding molecular orbital (π bond) is formed from two Py or two Pz orbitals, combining in phase. It is occupied and deep in energy.