Rep:Mod:1179
NH3 Molecule
Information
Molecule: NH3
Calculation Method: RB3LYP
Basis Set: 6-31G(d,p)
Final Energy E(RB3LYP): -56.55776873 a.u.
RMS gradient: 0.00000485 a.u.
Point Group: C3V
N-H Bond Length: 1.01798 Å
H-N-H Bond Angle: 105.74115°
N-atom charge:-1.125 H-atom charge:0.375
The N atom is more electronegative; it will pull electrons towards itself and have a negative charge.
The H atom will have a positive charge.
Optimisation
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
NH3 |
The optimisation file is linked here
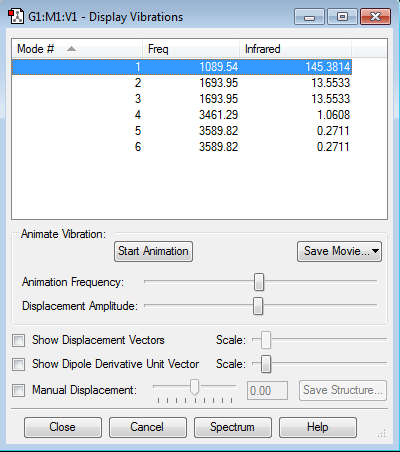
Vibrational Modes
The 3N-6 rule predicts a total of 6 vibrational modes.
Degenerate modes: 1693.95 (modes 2 and 3) and 3589.82 (modes 5 and 6).
Bending modes: 1,2,3
Stretching modes: 4,5,6
Mode 4 (stretching) is highly symmetric.
The umbrella mode is number 1, symmetric bend.
4 bands, as there are 4 distinct frequencies.
N2 molecule
Information
Molecule: N2
Calculation Method: RB3LYP
Basis Set: 6-31G(d,p)
Final Energy E(RB3LYP): -109.52412868 a.u.
RMS gradient: 0.00000060 a.u.
Point Group: D∞h
N-N bond length: 1.10550 Å
Optimisation
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
N2 |
The optimisation file is linked here
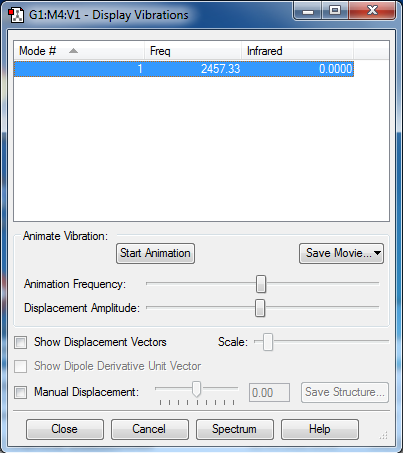
Frequencies
2457.33, stretching mode.
No negative frequencies.
H2 molecule
Information
Molecule: H2
Calculation Method: RB3LYP
Basis Set: 6-31G(d,p)
Final Energy E(RB3LYP): -1.17853936 a.u.
RMS gradient: 0.00000017 a.u.
Point Group: D∞h
H-H bond length: 0.74279 Å
Optimisation
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES
H2 |
The optimisation file is linked here
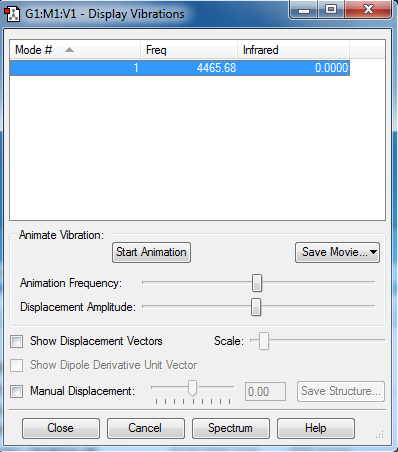
Frequencies
4465.68, stretching mode.
No negative frequencies.
Haber-Bosch reaction
N2 + 3H2 -> 2NH3
E(NH3)= -56.55776873 a.u.
2*E(NH3)= -113.11553746 a.u.
E(N2)= -109.52412868 a.u.
E(H2)= -1.17853936 a.u.
3*E(H2)= -3.53561808 a.u.
ΔE= -0.0557907 a.u.
ΔE= -146.48 kJ/mol
ΔE<0, therefore the product (NH3) is more stable than the reactants (H2 and N2).
HCl molecule
Information
Molecule: HCl
Calculation Method: RB3LYP
Basis Set: 6-31G(d,p)
Final Energy E(RB3LYP): -460.80077875 a.u.
RMS gradient: 0.00005211 a.u.
Point Group: C∞v
H charge: 0.284
Cl charge: -0.284
H-Cl bond length = 1.28599 Å
Optimisation
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000090 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000090 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000139 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000197 0.001200 YES
HCl |
The optimisation file is linked here
Frequencies
Orbitals
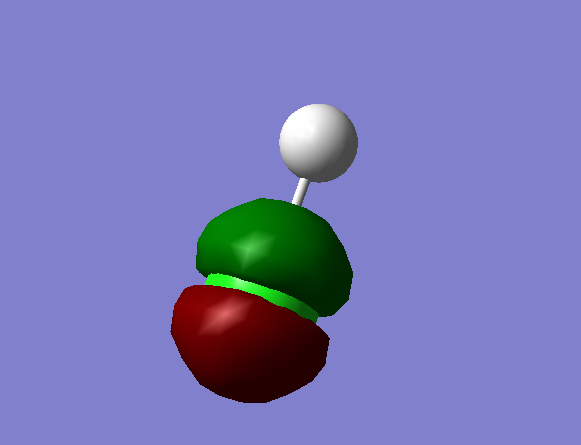
Non-bonding MO formed by the 2p orbital of Cl; high energy difference so no interaction between the 2p of Cl and the 1s of H.
Occupied.
Energy = -7.238 a.u.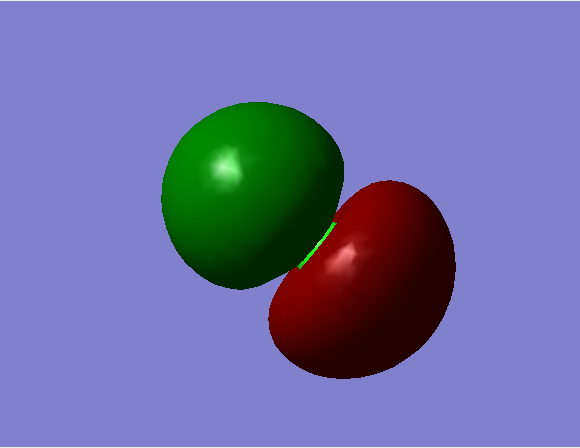
Bonding MO, with contributions from the 1s orbital of H and the 3pz orbital of Cl; occupied.
Energy = -0.474 a.u.
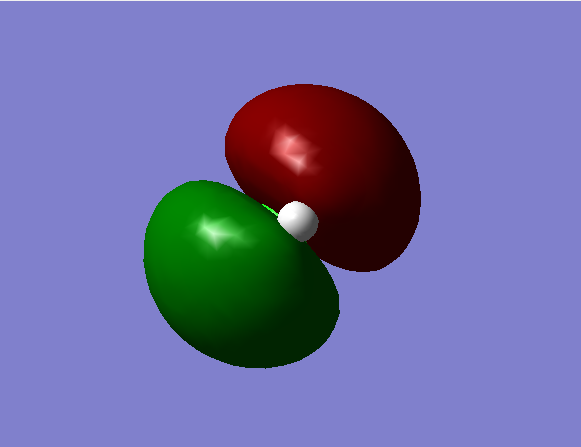
Non-bonding degenerate MOs from the 3px and 3pz orbitals of Cl.
HOMO.
Energy = -0.332 a.u.
Anti-bonding MO formed by the interaction between the 1s orbital of H and the 3pz orbital of Cl.
LUMO.
Energy = -0.013 a.u.
Cl2
Information
Molecule: Cl2
Calculation Method: RB3LYP
Basis Set: 6-31G(d,p)
Final Energy E(RB3LYP): -920.34987886 a.u.
RMS gradient: 0.00002510 a.u.
Point Group: D∞h
Cl charge: 0
Cl-Cl bond length = 2.042 Å
Optimization
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000043 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000043 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000121 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000172 0.001200 YES
Cl2 |