Rep:Mod:04050310
NH3 Molecule
Optimisation
| Calculation type | Result |
|---|---|
| File Name | ANMOL_PHUNT_NH3_OPTF_POP |
| File Type | .log |
| Calculation Type | OPT FREQ |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Charge | 0 |
| Spin | Singlet |
| E(RB3LYP) | -56.55776873 |
| RMS Gradient Norm | 0.00000485 |
| Imaginary Freq | 0 |
| Dipole Moment | 1.8466 |
| Point Group | C3V |
| Job cpu time: | 0 days 0 hours 0 minutes 9.0 seconds |
| N-H bond distance: | 1.01798 |
| H-N-H bond angle: | 105.741 |
"Item" Table
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-5.986276D-10
Optimisation link
NH3 molecule |
The optimisation file is linked here
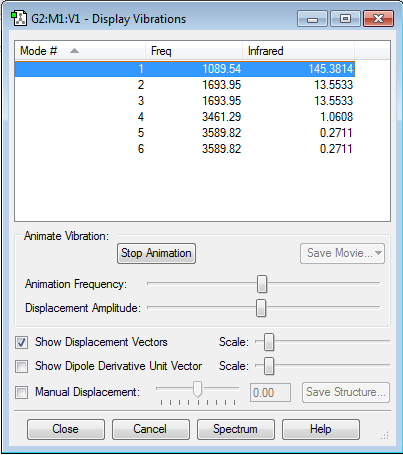
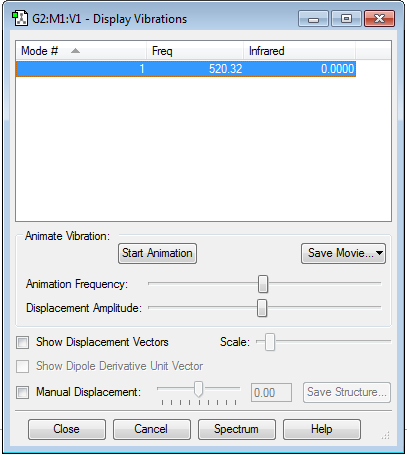
Vibration Modes
No negative frequencies shows that the energy of the molecule is at its local minimum. The absence of a net dipole moment results in no IR active vibrational modes.
Atomic Charge
| Atom | Charge |
|---|---|
| Hydrogen | +0.375 |
| Nitrogen | -1.125 |
The above image shows that nitrogen is more electronegative than hydrogen causing it to have a negative charge and the hydrogens to have a positive charge.
| Number of Modes (based on 3N-6 rule) | 6 |
|---|---|
| Degenerate Modes | 2 and 3, 5 and 6 |
| "Bending" Vibrations | 1089.54 Hz (1), 1693.95 Hz (2 and 3) |
| "Bond Stretch" Vibrations | 3461.29 Hz (4), 3589.82 Hz (5 and 6) |
| Highly Symmetric Mode | 4 |
| "Umbrella" Mode | 1 |
| Bands Expected in an Experimental Spectrum | 4 |
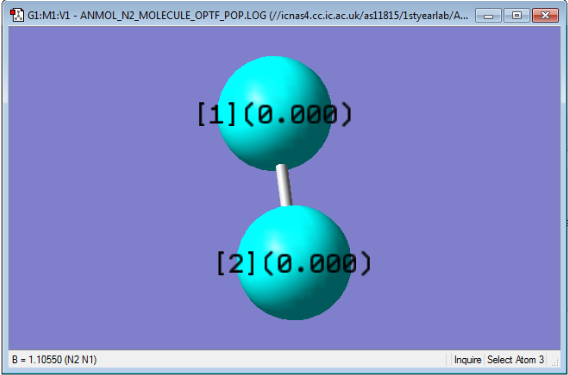
N2 Molecule
Optimisation
| Calculation type | Result |
|---|---|
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Point Group | D∞h |
| Final Energy E(RB3LYP)/a.u. | -109.52412868 |
| RMS Gradient/a.u. | 0.00000060 |
| Spin | Singlet |
| Bond Length/Å | 1.10550 |
"Item" Table
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-1.076088D-15
Optimisation link
N2 molecule |
The optimisation file is linked here
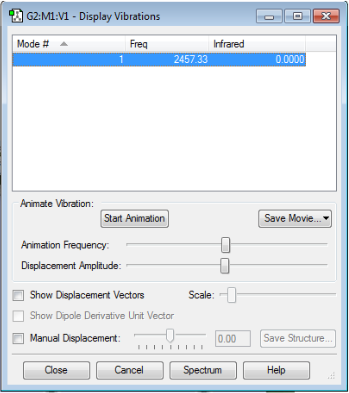
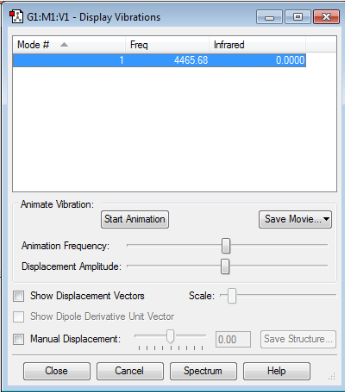
Vibration Modes
No negative frequencies shows that the energy of the molecule is at its local minimum. The absence of a net dipole moment results in no IR active vibrational modes.
Atomic Charge
| Atom | Charge |
|---|---|
| Nitrogen | 0.000 |
The above image shows that the charge is equally shared between the atoms as there is no electronegativity difference between two identical N atoms.
H2 Molecule
Optimisation
| Calculation type | Result |
|---|---|
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Point Group | D∞h |
| Final Energy E(RB3LYP)/a.u. | -1.17853936 |
| RMS Gradient/a.u. | 0.00000222 |
| Spin | Singlet |
| Bond Length/Å | 0.74280 |
"Item" Table
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-1.164080D-13
Optimisation link
H2 molecule |
The optimisation file is linked here
Vibration Modes
No negative frequencies shows that the energy of the molecule is at its local minimum. The absence of a net dipole moment results in no IR active vibrational modes.
Atomic Charge
| Atom | Charge |
|---|---|
| Hydrogen | 0.000 |
The above image shows that the charge is equally shared between the atoms as there is no electronegativity difference between two identical H atoms.
Energetics of Haber-Bosch process
N2 + 3H2 → 2NH3
| Energy | Value in a.u. |
|---|---|
| E(NH3) | -56.55776873 |
| 2*E(NH3) | -113.11553746 |
| E(N2) | -109.52412868 |
| E(H2) | -1.17853936 |
| 3*E(H2) | -3.53561808 |
| ΔE=2*E(NH3) - [E(N2) + 3*E(H2)] | -0.05579070 |
The energy change is ΔE= -0.05579070×2625.5= -146.48 kJmol-1. Since the enthalpy change is negative, the reaction is exothermic. Since the energy decreases, it can be confirmed that ammonia is more stable than nitrogen and hydrogen.
Cl2 Molecule
| Calculation type | Result |
|---|---|
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Point Group | D∞h |
| Final Energy E(RB3LYP)/a.u. | -920.34987886 |
| RMS Gradient/a.u. | 0.00002510 |
| Spin | Singlet |
| Bond Length/Å | 2.04174 |
"Item" Table
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000043 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000043 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000121 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000172 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-5.277246D-09
Optimisation link
Cl2 molecule |
The optimisation file is linked here
Vibration Modes
No negative frequencies shows that the energy of the molecule is at its local minimum. The absence of a net dipole moment results in no IR active vibrational modes.
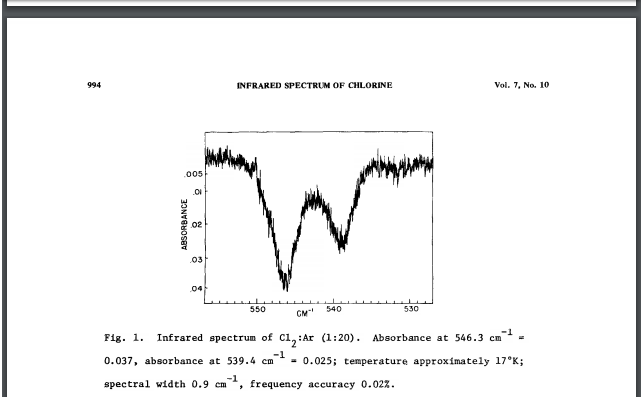
This is an IR spectrum of chlorine.[1]
Atomic Charge
| Atom | Charge |
|---|---|
| Chlorine | 0.000 |
The above image shows that the charge is equally shared between the atoms as there is no electronegativity difference between two identical Cl atoms.
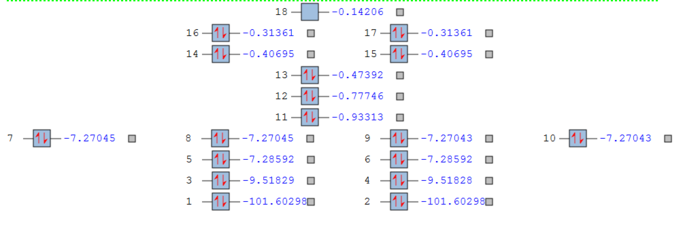
Molecular Orbitals
In GaussView, a degeneracy threshold of 0.001 was used to create an MO diagram of degeneracy.
Table of some occupied MOs.
References
- ↑ 'Infrared spectrum of chlorine in concentrated matrices' M.R. Clarke. G. Mamantov. Department of Chemistry, University of Tennessee, Knoxville, Tennessee 37916, USA