Rep:Mod:01366863
Intro to Molecule Modelling 2
Below, two molecules(NH3 and F2) will be analysed using GaussView.
Analyzed Molecule:NH3
Summary
Molecule name = NH3(ammonia)
Calculation method = RB3LYP
Basis set = 6-31G(d,p)
Final energy = -56.44397188 a.u.
Point Group = C3V
Dipole Moment = 1.5008 Debye
Bond Length = 1.3 angstrom
Bond Angle(H-N-H) = 105.74 degree
Spin = Singlet
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-5.986292D-10
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
The *.log file of NH3:File:NH3 OPTF.LOG
Vibrations
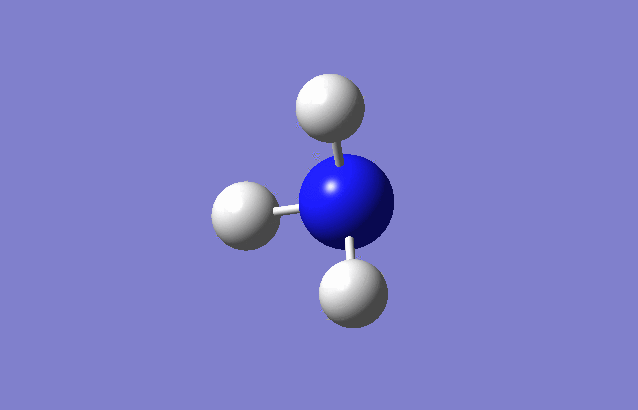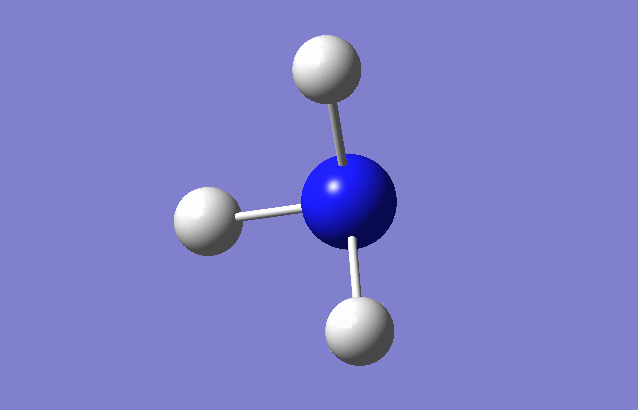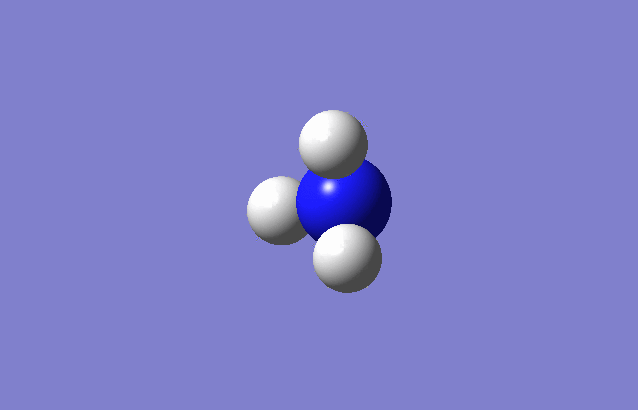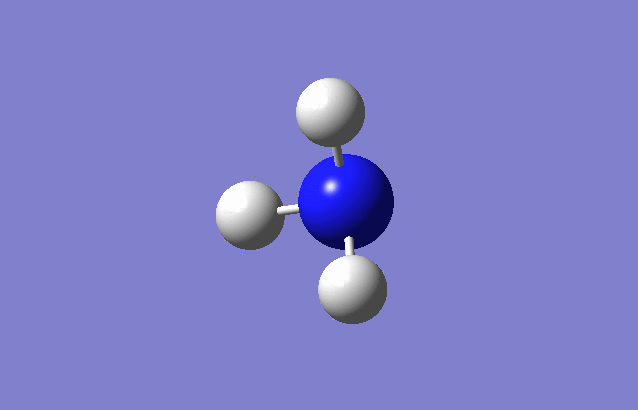
NH3 has 6 vibration modes.
- According to the table, the second and the third mode, also the fifth and the sixth mode are degenerate since they have the same frequency hence energy.
- Running the GaussView and animating the vibration function, it is clearly shown that Mode1,2&3 are "bending" vibrations and Mode4,5&6 are "stretching" vibrations.
- The highly vibrating mode is mode 4. N-H bonds are stretching along with their own direction and the dipole moment can cancel out in this case.
- The "umbrella" mode is mode 1, since the three N-H bonds are bending towards the same direction like an umbrella lid does.
- Four bands are expected to be seen in the spectrum because despite the degenerate modes, there are four modes with different energies.
Atomic Charges
q(N)= -1.132
q(H)= 0.377
The molecule NH3 is generally neutral.
Reaction Energies
E(NH3)= -56.56 a.u.
2*E(NH3)= -113.12 a.u.
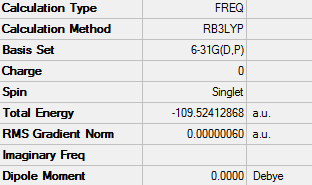
E(N2)= -109.52 a.u.
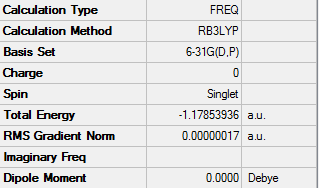
E(H2)= -1.16 a.u.
3*E(H2)= -3.48 a.u.
ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]= -0.12 a.u.
ΔE= -0.12*2625.5 = -315.06 kJ/mol
The energy for converting hydrogen and nitrogen gas into ammonia gas is -315.06 kJ/mol. It can be seen that the energy difference of the reaction is a negative value, which indicates that Haber-Bosch Process is exothermic and releases energy. Since less energy equals more stable, the gaseous product is more stable than the gaseous reactants.
Calculation of N2
The *.log file of N2:File:N2 OPTF.LOG
Calculation of H2
The *.log file of H2:File:H2 OPTF.LOG
Small Molecule:F2
Summary
Molecule name = F2(fluorine)
Calculation method = RB3LYP
Basis set = 6-31G(d,p)
Final energy = -199.42620785 a.u.
Point Group = D*H
Dipole Moment = 0.0000 Debye
Bond Length = 1.403 angstrom
Bond Angle = 180 degree
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000128 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000128 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000156 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000221 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.995024D-08
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
The .*log file of F2: File:F2 OPTF.LOG
Vibrations
-Only one vibration mode is expected because F2 is a linear molecule.
-The vibration mode is a "stretching" mode.
-It is highly symmetric and the dipole moment cancels out completely.
Atomic Charges
q(F)= 0.000
This diatomic molecule is symmetric and its atoms are identical, hence it gives the atomic charges of zero.
Reaction Energies
For the formation of HF:
E(F2)= -199.43 a.u.
E(H2)= -1.16 a.u.
E(HF)= -100.42 a.u.
2*E(HF)= -200.84 a.u.
ΔE=2*E(HF)-[E(H2)+E(F2)]= -0.25 a.u.
ΔE= -0.25*2625.5 = -656.38 kJ/mol
Molecular Orbitals
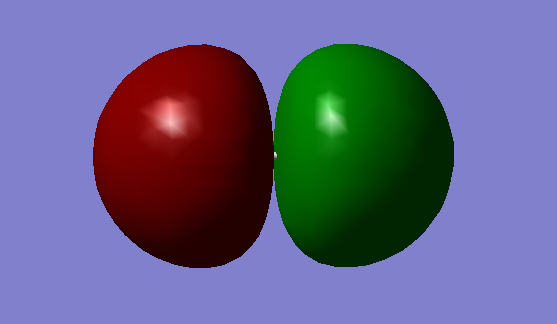
1.MO = 3
This MO is combined from two 2s AOs of F, and it is a σg bonding MO. It's quite deep in energy and it sure is occupied.
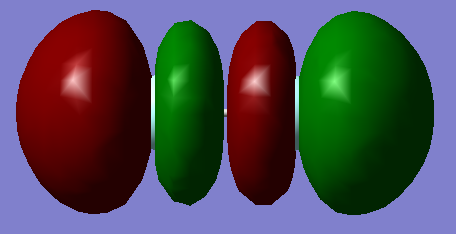
2.MO = 4
This MO is also combined from two 2s AOs of F, and it is a σ*u anti-bonding MO. It's also deep in energy but slightly higher than MO=3, and it is occupied.
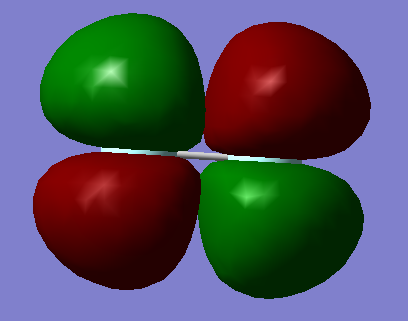
3.MO = 6
This MO is combined from two 2P AOs of F, and it is a πu bonding MO. It's deeper in energy than the HOMO and higher than the previous two, also it is occupied.
4.MO = 8
This MO is combined from two 2p AOs of F, and it is a π*g anti-bonding MO. This MO is π*g which means it's in HOMO region in this case and it is still occupied.
5.1.MO = 10
This MO is combined from two 2p AOs of F, and it is a σ*u bonding MO. It's right in the LUMO region (higher than all the MOs mentioned previously) and it is unoccupied since the occupied MOs are up to MO = 9.