Rep:Mod:01364634
NH3
Optimisation Information
Calculation Method:B3LYP, Basis Set:6-31G(d,p)
Molecule Information
Energy:-56.55776873, Point Group:C3V, Charge on N atom:-1.162, Charge on H atoms:0.387 Nitrogen if more electronegative than hydrogen, the nitrogen atom will therefore displace the bonding pairs towards itself, increasing electron density around itself and acquiring a negative charge. This leaves the hydrogen atoms to be positively charged, since electron density around them is lowered.
Image
test molecule |
RMS Force and Displacement
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
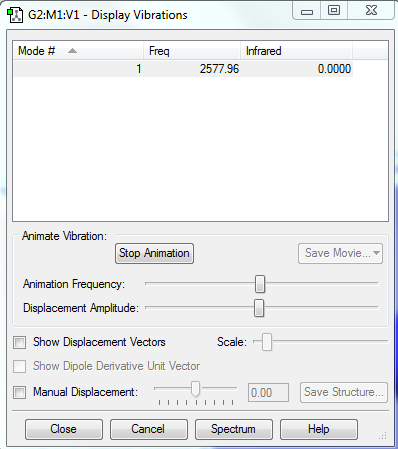
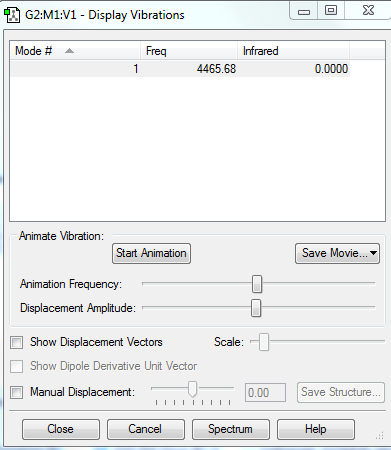
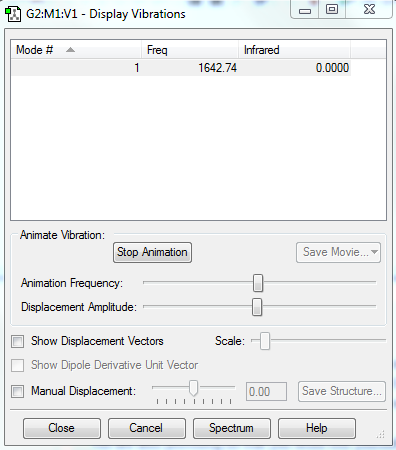
Vibrations
Link to file
N2
Optimisation Information
Calculation Method:B3LYP, Basis Set:6-31G(d,p)
Molecule Information
Energy:-109.52412868, Point Group:D*H
Image
test molecule |
RMS Force and Displacement
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
Vibrations
Link to file
H2
Optimisation Information
Calculation Method:B3LYP, Basis Set:6-31G(d,p)
Molecule Information
Energy: -1.17853936, Point Group:D*H
Image
test molecule |
RMS Force and Displacement
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES
Vibrations
Link to file
Haber Process Energy
E(NH3)=-56.55776873 2*E(NH3)=-113.1153746 E(N2)=-109.52412868 E(H2)=-1.17853936 3*E(H2)=-3.53561808 ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]=-0.05562784 Hartree= -146.05 kJ/mol
O2
Optimisation Information
Calculation Method:B3LYP, Basis Set:6-31G(d,p)
Molecule Information
Energy: -150.25742434 Point Group:D*H
Image
test molecule |
RMS Force and Displacement
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000130 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000130 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000080 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000113 0.001200 YES
Vibrations
Link to file
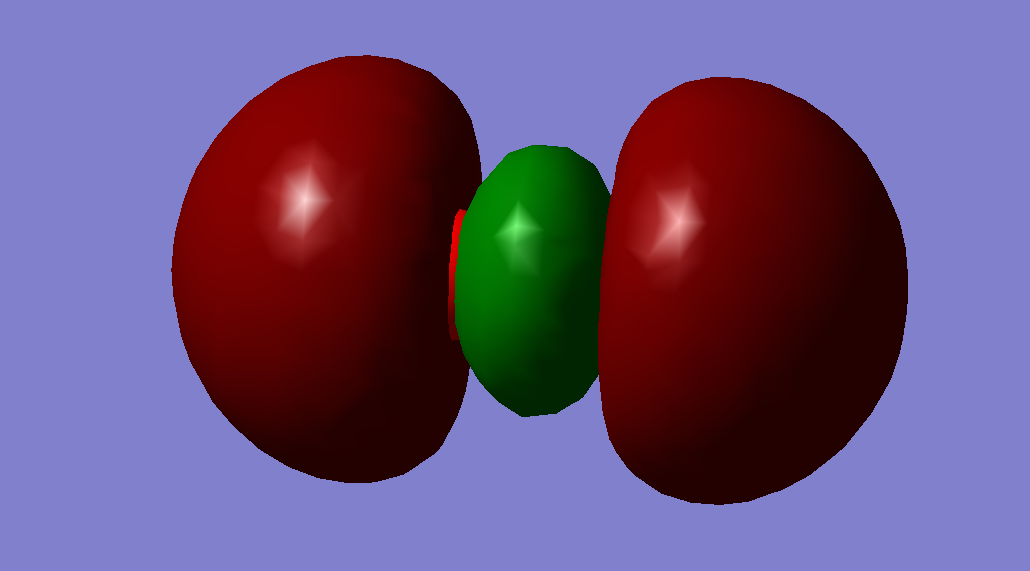
Molecular Orbitals
1σg
This is the 1σg orbital. It is a bonding orbital resulting from the linear combination of a 1s atomic orbital from each oxygen atom. It is the molecular orbital lowest in energy. Therefore, it has no effect on bonding. The orbital is occupied, filled with two electrons.
1σ*u
2σg
This is the 2σg orbital. It is a bonding orbital resulting from the linear combination of a 2s orbital from each oxygen atom. It is relatively higher in energy (-1.27663) than the two previously discussed ones. The orbital is occupied, filled with two electrons.
2σ*u
This is the 2σ*u orbital. It is an anti-bonding orbital resulting from the linear combination of a 2s orbital from each oxygen atom. It has an energy of -0.79812. The orbital is occupied, filled with two electrons.

3σg
This is the 3σg orbital. It is a bonding orbital resulting from the linear combination of a 2p orbital, which overlap head-on, from each oxygen atom. It has an energy of -0.53151. The orbital is occupied, filled with two electrons.