Rep:Mod:01356531
NH3 molecule
test molecule |
Summary
Molecule:NH3
Caculation method:RB3LYP
Basis set:6-31G(d.p)
The final energy(RB3LYP) in au:-56.55664124
The RMS gradient in au:0.00836083
The point group:C3v
optimised N-H bond distance:1.00000
optimised H-N-H bond angle:109.471
Item Table
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000006 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000014 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000009 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-1.141680D-10
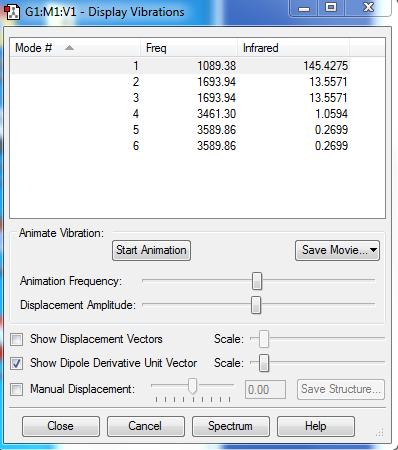
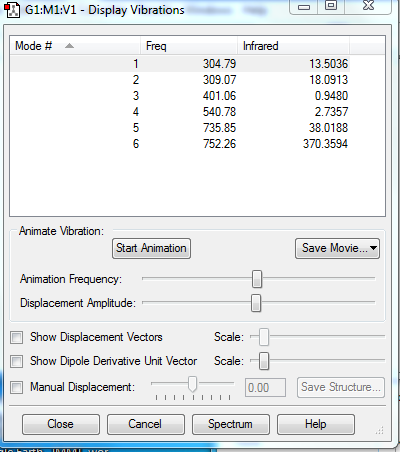
Display Vibrations
Charges
Charge on N atom is-1.125 and charges on H atom are 0.375.
Negative charge is expected on N atom and positive charge is expected on H atm because N atom is more electroneative than H atom.
Questions for NH3 Vibrations
1.how many modes do you expect from the 3N-6 rule?
3*4-6=6 modes
2.which modes are degenerate (ie have the same energy)?
mode3&4,mode5&6.
3.which modes are "bending" vibrations and which are "bond stretch" vibrations?
"Bending" vibrations modes:mode 1,2,3. "bond stretch" vibrations modes:mode 4,5,6.
4.which mode is highly symmetric?
mode 4 is highly symmetric.
5.one mode is known as the "umbrella" mode, which one is this?
mode 1 is the "umbrella" mode.
6.how many bands would you expect to see in an experimental spectrum of gaseous ammonia?
4 bands are expected to see in an experimental spectrum of gaseous ammonia.
N2 molecule
test molecule |
Summary
Molecule:N2
Caculation method:RB3LYP
Basis set:6-31G(d.p)
The final energy(RB3LYP) in au:-109.52359111
The RMS gradient in au:0.02473091
The point group:D*H
Optimised N-N bond distance:1.10550
Item Table
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-3.401010D-13
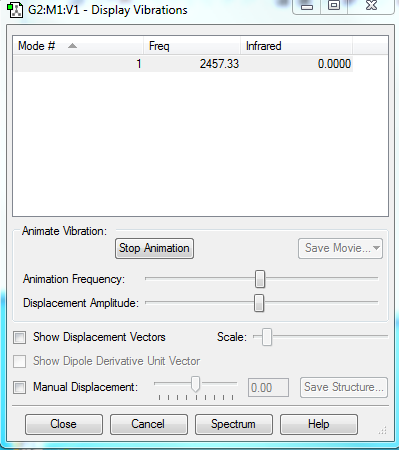
Display Vibrations
Charges
N2 does not have charge distribution.
H2 molecule
test molecule |
Summary
Molecule:H2
Caculation method:RB3LYP
Basis set:6-31G(d.p)
The final energy(RB3LYP) in au:-1.15928020
The RMS gradient in au:0.09719500
The point group:D*H
optimised H-H bond distance:0.74279
Item Table
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-1.164080D-13
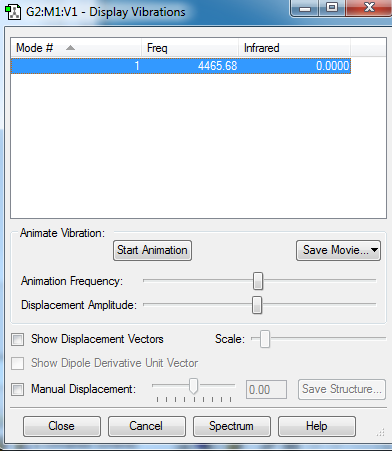
Display Vibrations
Charges
H2 does not have charge distribution.
The energy for the reaction of N2 + 3H2 -> 2NH3
E(NH3)=-56.55664124a.u.
2*E(NH3)=-113.1132825a.u.
E(N2)=-109.52359111a.u.
E(H2)=-1.15928020a.u.
3*E(H2)=-3.47778406a.u.
ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]=-0.11190733a.u.=-293.81kJ/mol
Because the energy difference is negative,so ammonia is more stable.
F2 molecule
test molecule |
Summary
Molecule:F2
Caculation method:RB3LYP
Basis set:6-31G(d.p)
The final energy(RB3LYP) in au:-199.42620785
The RMS gradient in au:0.23253407
The point group:D*H
optimised F-F bond distance:1.16000
Item Table
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000128 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000128 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000156 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000221 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-1.995025D-08
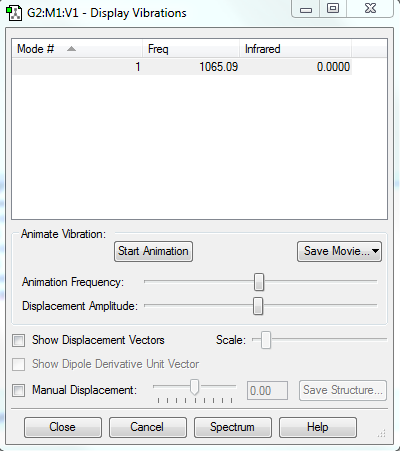
Display Vibrations
Charges
F2 does not have charge distribution.
Five MOs in F2
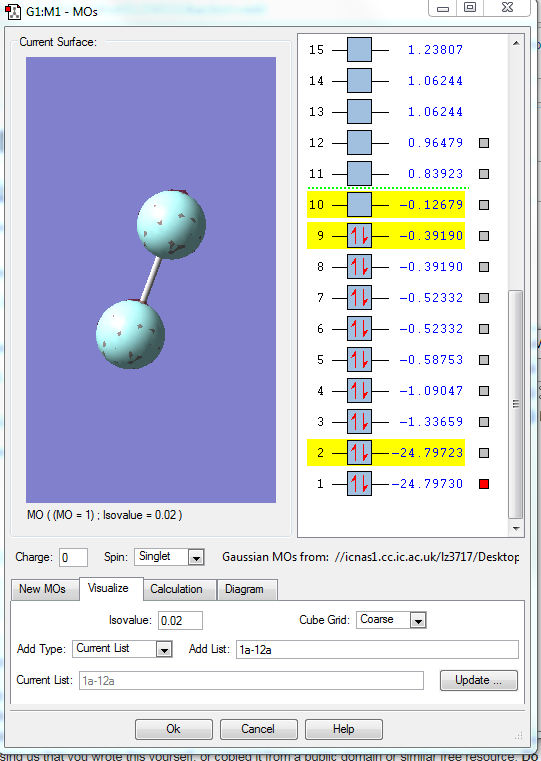
MO1
1.what AOs contribute to the MO?
Two 1s orbitals of two F elements.
2.Is the MO bondng, antibonding or a mixture?
This MO is non-bonding orbital.
3. Is the MO deep in energy, in the HOMO/LUMO region or high in energy?
This MO has the lowest energy in the HOMO region.(-24.79730)
4.Is the MO occupied or unoccupied?
It is occupied.
5.What effect will your MOs have on bonding?
It is the non-bonding orbital.
MO4
1.what AOs contribute to the MO?
Two 2s orbitals of two F elements.
2.Is the MO bondng, antibonding or a mixture?
This MO is anti-bonding orbital.
3. Is the MO deep in energy, in the HOMO/LUMO region or high in energy?
This MO has the relative low energy in the HOMO region.(-1.09047)
4.Is the MO occupied or unoccupied?
It is occupied.
5.What effect will your MOs have on bonding?
It strengthen the antibonding character and weaken the bonding character. It is the antibonding of sigma bond.
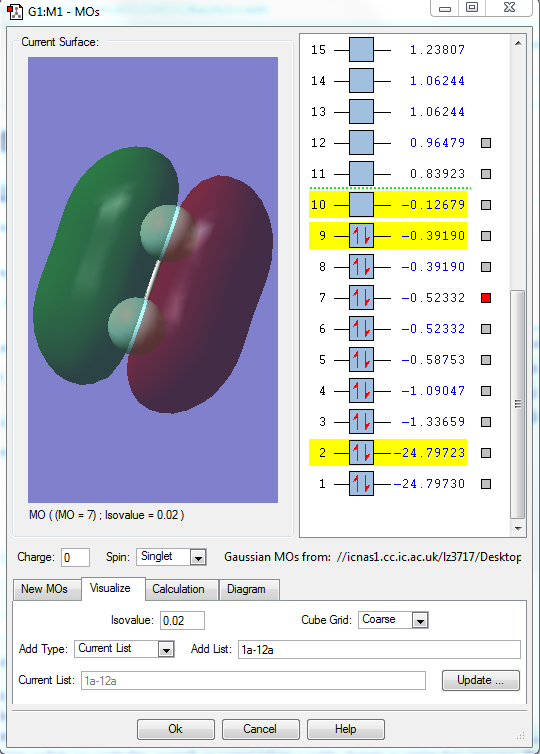
MO7
1.what AOs contribute to the MO?
Two 2p orbitals of two F elements.
2.Is the MO bondng, antibonding or a mixture?
This MO is bonding orbital.
3. Is the MO deep in energy, in the HOMO/LUMO region or high in energy?
This MO has the relative high energy in the HOMO region.(-0.52332)
4.Is the MO occupied or unoccupied?
It is occupied.
5.What effect will your MOs have on bonding?
It strengthen the bonding character and weaken the antibonding character. It contributes to a pi bond.
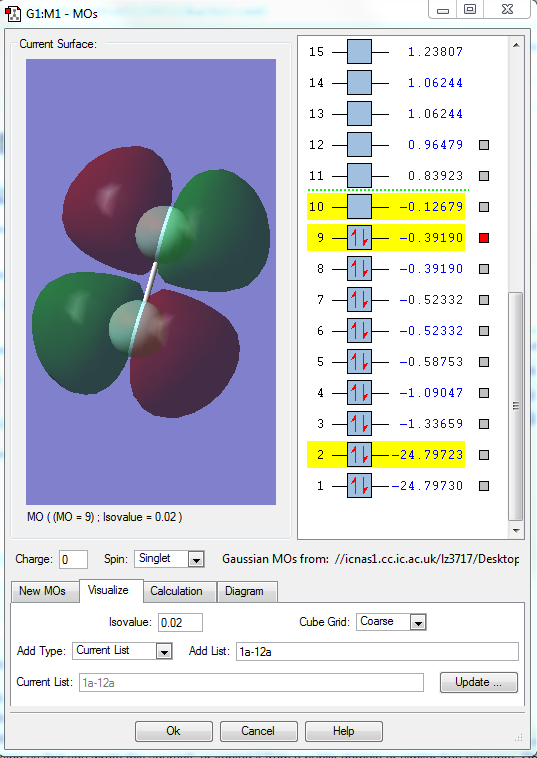
MO9
1.what AOs contribute to the MO?
Two 2p orbitals of two F elements.
2.Is the MO bondng, antibonding or a mixture?
This MO is antibonding orbital.
3. Is the MO deep in energy, in the HOMO/LUMO region or high in energy?
This MO has the highest energy in the HOMO region.(-0.39190)
4.Is the MO occupied or unoccupied?
It is occupied.
5.What effect will your MOs have on bonding?
It strengthen the antibonding character and weaken the bonding character. It is the antibonding of pi bond.
MO10
1.what AOs contribute to the MO?
Two 2p orbitals of two F elements.
2.Is the MO bondng, antibonding or a mixture?
This MO is antibonding orbital.
3. Is the MO deep in energy, in the HOMO/LUMO region or high in energy?
This MO has the lowest energy in the LOMO region.(-0.12679)
4.Is the MO occupied or unoccupied?
It is unoccupied.
5.What effect will your MOs have on bonding?
It strengthen the antibonding character and weaken the bonding character. It is the antibonding of sigma bond.
CLF3 molecule
test molecule |
Summary
Molecule:CLF3
Caculation method:RB3LYP
Basis set:6-31G(d.p)
The final energy(RB3LYP) in au:-759.43206418
The RMS gradient in au:0.05217279
The point group:C2v
optimised CL-F bond distance:1.57000
optimised F-CL-F bond angle:90.000
Item Table
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000050 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000028 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000204 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000134 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-1.250235D-08
Display Vibrations
Charges
CLF3 does not have charge distribution.