Rep:Mod:01349934
NH3 Investigation
NH3 Molecule
Summary
What is the molecule?: NH3
What is the calculation method?: RB3LYP
What is the basis set?: 6-31G(d,p)
What is the final energy E(RB3LYP)(au)?: -56.55776873
What is the RMS gradient(au)?: 0.00000485
What is the point group of your molecule?: C3V
What is the optimised N-H bond distance(Å)?: 1.01798
What is the optimised H-N-H bond angle(°)?: 105.741
Item Table
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
Optimised NH3 Molecule
Optimised NH3 |
The optimisation file is linked to here
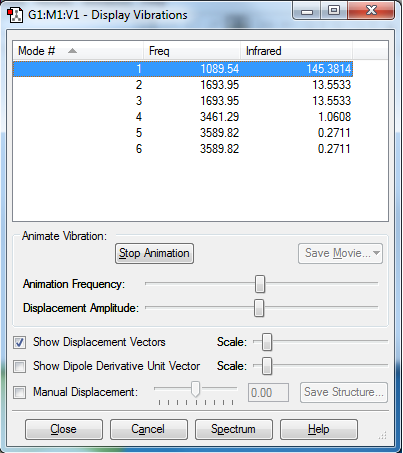
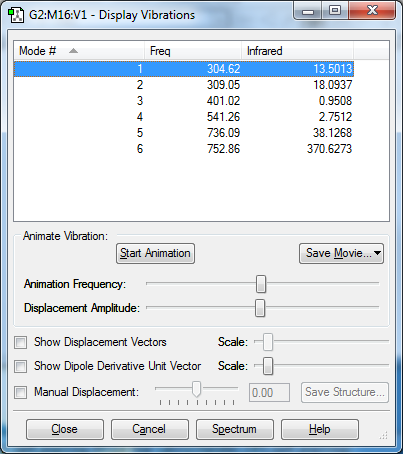
Vibrations Display
What vibration does each mode correspond to?:
Mode 1 = N-H Wagging Bend (active - change in dipole moment)
Mode 2 = H-N-H Scissoring Bend (active - change in dipole moment)
Mode 3 = H-N-H Scissoring Bend (active - change in dipole moment)
Mode 4 = N-H Symmetric Stretch (active - change in dipole moment)
Mode 5 = N-H Asymmetric Stretch (active - change in dipole moment)
Mode 6 = N-H Asymmetric Stretch (active - change in dipole moment)
How many modes do you expect from the 3N-6 rule?: 3(4)-6 = 6
Which modes are degenerate (i.e. have the same energy)?: Using the mode numbers on the Display Vibrations window - 2&3 and 5&6
Which modes are "bending" vibrations and which are "bond stretch" vibrations?: Bending = 1,2,3 and Stretching = 4,5,6
Which mode is highly symmetric?: Mode 4
One mode is known as the "umbrella" mode, which one is this?: Mode 1
How many bands would you expect to see in an experimental spectrum of gaseous ammonia?: You would expect to see 4 bands.
Charge Distribution
What is the charge on the Nitrogen atom?: -1.125
What charge would you expect for the Nitrogen atom?: Negative charge
What is the charge on the Hydrogen atoms?: 0.375
What charge would you expect on the Hydrogen atoms?: Positive charge
N2 Molecule
Summary
What is the molecule?: N2
What is the calculation method?: RB3LYP
What is the basis set?: 6-31G(d,p)
What is the final energy E(RB3LYP)in atomic units(au)?: -109.52412868
What is the RMS gradient(au)?: 0.00000060
What is the point group of your molecule?: D∞h
What is the optimised N-N bond distance(Å)?: 1.10550
Item Table
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
Optimised N2 Molecule
Optimised N2 |
The optimisation file is linked to here
Frequency of Vibration
The frequency of the vibrational mode is 2457.33 Hz. This is positive so the molecule is fully optimised.
H2 Molecule
Summary
What is the molecule?: H2
What is the calculation method?: RB3LYP
What is the basis set?: 6-31G(d,p)
What is the final energy E(RB3LYP)in atomic units(au)?: -1.17853936
What is the RMS gradient (au)?: 0.00000017
What is the point group of your molecule?: D∞h
What is the optimised H-H bond distance (Å)?: 0.74279
Item Table
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES
Optimised H2 Molecule
Optimised H2 |
The optimisation file is linked to here
Frequency of Vibration
The frequency of the vibrational mode is 4465.68 Hz. This is positive so the molecule is fully optimised.
Reaction Energies - The Haber-Bosch process
The energy change for the reaction is negative, meaning that the reaction is exothermic. This means that the product (gaseous ammonia) is more stable than the reactants (gaseous nitrogen and gaseous hydrogen)as the product is at a lower energy state.
F2 Investigation
Summary
What is the molecule?: F2
What is the calculation method?: RB3LYP
What is the basis set?: 6-31G(d,p)
What is the final energy E(RB3LYP)(au)?: -199.49825218
What is the RMS gradient(au)?: 0.00007365
What is the point group of your molecule?: D∞h
What is the optimised F-F bond distance(Å)?: 1.40281
Item Table
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000128 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000128 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000156 0.001800 YES
Optimised F2 Molecule
Optimised F2 |
The optimisation file is linked to here
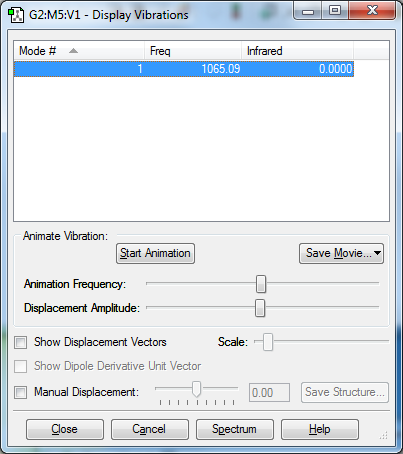
Vibrations Display
This vibrational mode frequency refers to the symmetric stretch vibration. The value is positive and so the molecule is fully optimised.
Charge Distribution
What charge would you expect for the Fluorine atoms?: No charge, this is because the molecule is diatomic where both atoms are equally electronegative and have an equally strong pull on the electrons.
What is the charge on the atoms?: No charge
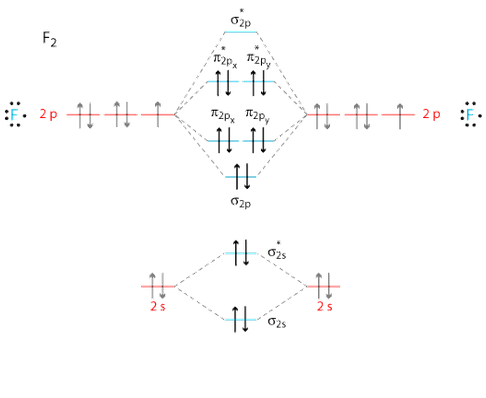
Molecular Orbitals
Molecular Orbital Diagram
Source:http://www.grandinetti.org/
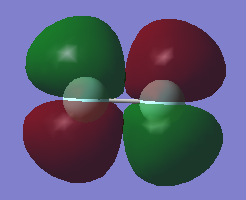
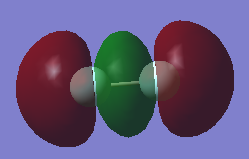
π*2p
What AOs contribute to the MO?: This MO is made up of the 2p AOs
Is the MO bonding, antibonding or a mixture?: This MO is antibonding
What is the energy of the MO?: -0.39190, this is the HOMO (highest occupied molecular orbital)
Is the MO occupied or unoccupied?: This MO is occupied
What effect will your MOs have on bonding?: The MO is antibonding and so will weaken the bonding. This cancels out the pi bonding orbitals and so no pi bond is formed.
σ*2p
What AOs contribute to the MO?: This MO is made up of the 2p AOs
Is the MO bonding, antibonding or a mixture?: This MO is antibonding
What is the energy of the MO?: -0.12679
Is the MO occupied or unoccupied?: The MO is unoccupied, it is the LUMO (lowest unoccupied molecular orbital)
What effect will your MOs have on bonding?: The MO is antibonding and so would weaken the bonding if occupied. This is unoccupied and so a sigma bond can form.
π2p
What AOs contribute to the MO?: This MO is made up of the 2p AOs
Is the MO bonding, antibonding or a mixture?: This MO is bonding
What is the energy of the MO?: -0.52332
Is the MO occupied or unoccupied?: This MO is occupied
What effect will your MOs have on bonding?: This is a bonding orbital and so will contribute to the bonding and strengthen it. This would form part of the pi bond, however the antibonding is also filled and so no pi bond is formed.
σ2p
What AOs contribute to the MO?: This MO is made up of 2p AOs
Is the MO bonding, antibonding or a mixture?: This MO is bonding
What is the energy of this MO?: -0.58753
Is the MO occupied or unoccupied?: This MO is occupied
What effect will your MOs have on bonding?: This MO is responsible for the sigma bond, it is bonding and so strengthens the bond.
σ*2s
What AOs contribute to the MO?: This MO is made up of 2s AOs
Is the MO bonding, antibonding or a mixture?: This MO is antibonding
What is the energy of the MO?: -1.09047
Is the MO occupied or unoccupied?: This MO is occupied
What effect will your MOs have on bonding?: This MO is antibonding and so weakens the bond. This cancels out the occupied 2s bonding orbital and so no sigma bond is formed from the 2s AOs.
ClF3 Investigation
Summary
What is the molecule?: ClF3
What is the calculation method?: RB3LYP
What is the basis set?: 6-31G(d,p)
What is the final energy E(RB3LYP)(au)?: -759.46531651
What is the RMS gradient(au)?: 0.00018431
What is the point group of your molecule?: CS
What is the optimised Cl-F bond distance(Å)?: 1.65132, 1.72899 and 1.72765
What is the optimised F-Cl-F bond angle(°)?: 87.168 and 87.138
Item Table
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000333 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000145 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000851 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000548 0.001200 YES
Optimised ClF3 Molecule
Optimised ClF3 |
The optimisation file is linked to here
Vibrations Display
What vibration does each mode correspond to?:
Mode 1 = F-Cl-F Scissoring Bend (active - change in dipole moment)
Mode 2 = F-Cl-F Scissoring Bend (active - change in dipole moment)
Mode 3 = F-Cl-F Wagging Bend (active - change in dipole moment)
Mode 4 = Cl-F Symmetric Stretch (active - change in dipole moment)
Mode 5 = Cl-F Symmetric Stretch (active - change in dipole moment)
Mode 6 = Cl-F Asymmetric Stretch (active - change in dipole moment)
How many modes do you expect from the 3N-6 rule?: 3(4)-6=6
Which modes are "bending" vibrations and which are "bond stretch" vibrations?: Bending = 1,2,3 and Stretching = 4,5,6
One mode is known as the "umbrella" mode, which one is this?: Mode 2
How many bands would you expect to see in an experimental spectrum of ClF3?: You would expect to see 6 bands.
Charge Distribution
What charge would you expect for the Chlorine atom?: Positive charge
What charge would you expect on the Fluorine atoms?: Negative charge as more electronegative so have a greater pull on the electrons in the bonds
What is the charge on the atoms?:
Chlorine = +1.225
Fluorine 1 = -0.455
Fluorine 2 = -0.316
Fluorine 3 = -0.454