Rep:Mod:01342206
NH3
| Name | NH3 |
|---|---|
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Final Energy (au) | -56.55776873 |
| RMS Gradient (au) | 0.00000485 |
| Point Group | C3V |
Optimised N-H bond length in NH3 : 1.0179Å
Optimised H-N-H bond angle : 105.74115°
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
NH3 |
The optimisation file is liked to here
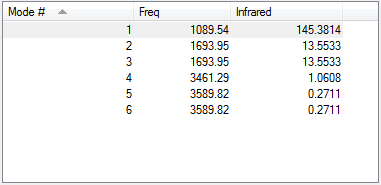
- Modes 5 and 6, as well as 2 and 3 are degenerate.
- Using the 3N-6 rule, it can be expected that there will be 6 vibrations as the value of N will be 4.
- Modes 1,2 and 3 are bending vibrations while 4,5, and 6 are bond stretches.
- Mode 1 is the umbrella vibrational mode.
- Mode 4 is highly symmetric
- 4 should be seen as there are 2 degenerate modes and 2 other peaks. However 4,5 and 6 may be too small to be seen and differentiated.
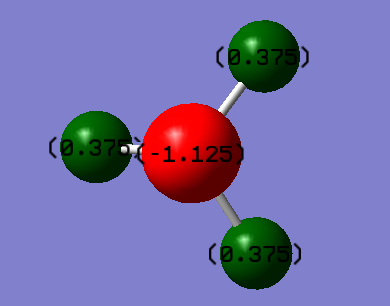
- The charge on N is -1.125 and the charge on the H is 0.375.
- As expected there is a partially negative charge on N as it is more electronegative than H.Therefore it will attract more electron density.
N2
| Name | N2 |
|---|---|
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Final Energy (au) | -109.52412868 |
| RMS Gradient (au) | 0.00000060 |
| Point Group | D*H |
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
The optimisation file is liked to here
1 Vibrational mode is present for N2 at 2457.
H2
| Name | H2 |
|---|---|
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Final Energy (au) | -1.17853936 |
| RMS Gradient (au) | 0.00000017 |
| Point Group | D*H |
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES
The optimisation file is liked to here
1 Vibrational mode is present for H2 at 4466.
Energy Calculations
- E(NH3)=-148492.421801kJmol-1
- 2*E(NH3)=-296984.843602kJmol-1
- E(N2)=-287555.599849kJmol-1
- E(H2)=-3094.25508968kJmol-1
- 3*E(H2)=-9282.76526904kJmol-1
- ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]=-146.478602kJmol-1
Literature value comparisons
The reactants are more stable. The literature value is -46kJmol-1. Literature values are taken from experimental observation. There is a difference between the literature value and the quantum mechanical estimation due to several reasons. One of them being that quantum mechanical estimations do not take real world imperfections into considerations. Also when calculating literature values, there is more than one molecule present, therefore there will be collisions and interactions between the molecules, and not just an energy value for a single molecule in space.
ClF3
| Name | ClF3 |
|---|---|
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Final Energy (au) | -759.38175725 |
| RMS Gradient (au) | 0.06637914 |
| Point Group | D3H |
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000011 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000007 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000049 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000032 0.001200 YES
The optimisation file is liked to here
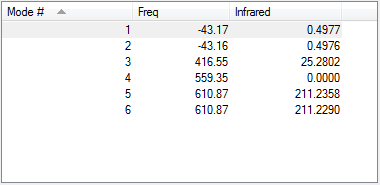
ClF3 |
Charge on Cl is 1.188, charge on F is -0.395.
F is more electronegative than Cl and attracts electron density towards itself.
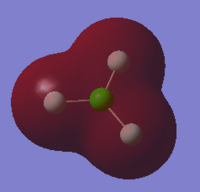
Molecular Orbitals of ClF3
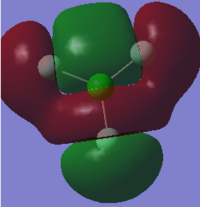

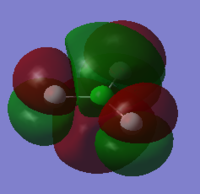
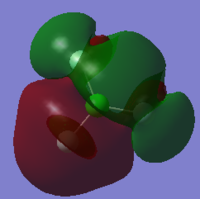
Cl2
| Name | Cl2 |
|---|---|
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Final Energy (au) | -920.34987886 |
| RMS Gradient (au) | 0.00002511 |
| Point Group | D*H |
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000043 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000043 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000121 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000172 0.001200 YES
The optimisation file is liked to here
F2
| Name | F2 |
|---|---|
| Calculation Method | RB3LYP |
| Basis Set | 6-31G(d,p) |
| Final Energy (au) | -199.49825218 |
| RMS Gradient (au) | 0.00007365 |
| Point Group | D*H |
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000128 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000128 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000156 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000221 0.001200 YES
The optimisation file is liked to here
Energy Calculations
- E(ClF3)= -759.38175725
- 2*E(ClF3)= -1518.76351 au
- E(Cl2)= -920.34987886 au
- E(F2)=-199.49825218 au
- 3*E(F2)= -598.494757 au
- ΔE=2*E(ClF3)-[E(Cl2)+3*E(F2)]=0.08113 au = +213.006815kJmol-1