Rep:Mod:01341438
NH3 Molecule
Summary
Calculation Method RB3LYP
Basis Method 6-31G(d.p)
Final energy E(RB3LYP) -56.55776873 a.u.
RMS gradient 0.00000485a.u.
Point group C3V
Bond Length (N-H) 1.01798 Å
Optimised Bond Angle (H-N-H) 105.741°
Item table
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-5.986288D-10
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R2 R(1,3) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! R3 R(1,4) 1.018 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A1 A(2,1,3) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A2 A(2,1,4) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! A3 A(3,1,4) 105.7412 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
! D1 D(2,1,4,3) -111.8571 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
Optimised NH3 molecule |
Vibrations

How many modes do we expect 6
Which modes are degenerate 2 and 3; 5 and 6
Which modes are bending 1 and 2 and 3
Which modes are bond strength 4 and 5 and 6
Which mode is highly symmetric 4 Which mode is the umbrella mode 1 How many bands do we expect in the experimental spectrum of gaseous ammonia 2
Charges
Charge on the N atom -1.125
Charge on each of the H atoms 0.375
Explaining charges It is as expected that the N would have a negative charge and that the Hs would be positive as N is the more electronegative atom. The molecule is neutral overall and the 3 Hs are equivalent so the -1.125 charge is stabilised equally by the 3 Hs (1.125/3=0.375).
N2 Molecule
Summary
Calculation Method RB3LYP
Basis Method 6-31G(d,p)
Final energy E(RB3LYP) -109.52412868 a.u.
RMS gradient 0.0000060 a.u.
Point group D*H
Bond Length (N-N) 1.10550 Å
Optimised Bond Angle (N-N) 180°
Item table
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-3.401107D-13
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.1055 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
Optimised N2 molecule |
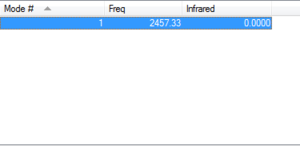
Vibrations
How many modes do we expect 1
Which modes are degenerate Not applicable
Which modes are bending 0
Which modes are bond strength 1
Which mode is highly symmetric 1
Which mode is the umbrella mode Not applicable
How many bands do we expect in the experimental spectrum of gaseous Nitrogen 0
Charges
Charge on each N atom 0
Explaining charges Nitrogen is a neutral molecule, both Ns are equivalent so both have 0 charge.
H2 Molecule
Calculation Method RB3LYP
Basis Set 6-31G(d,p)
Final energy E(RB3LYP) -1.17853936 a.u.
RMS gradient 0.00000017 a.u.
Point group D*H
Bond Length (H-H) 0.74279 Å
Optimised Bond Angle (H-H) 180°
Item table
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.164080D-13
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 0.7428 -DE/DX = 0.0 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
Optimised H2 molecule |
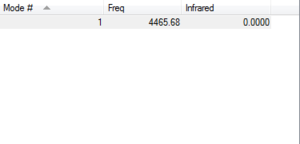
Vibrations
How many modes do we expect 1
Which modes are degenerat Not applicable
Which modes are bending 0
Which modes are bond strength 1
Which mode is highly symmetric 1
Which mode is the umbrella mode Not applicable
How many bands do we expect in the experimental spectrum of gaseous Hydrogen 0
Charge on each H atom 0
Explaining charges
Hydrogen is a neutral molecule, both Hs are equivalent so both have 0 charge.
Reaction Energies
E(NH3)= -56.55776873 a.u. 2*E(NH3)= -113.1155375 a.u. E(N2)= -109.52412868 a.u. E(H2)= -1.17853936 a.u. 3*E(H2)= -3.53561808 a.u. ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]= -0.0557907 a.u.
-0.0557907 a.u. x 2625.5 = -146.4784829 kJ/mol
Explanation This is an exothermic reaction, so the products are more stable than the reactants.
Literature The value in the literature was -99.2 kJ/mol. This is not too far off our value however, there may be differences due to limitations in the computers optimization. [1]
O2 Molecule
Summary
Calculation Method RB3LYP
Basis Set 6-31G(d,p)
Final energy E(RB3LYP) -150.25742434 a.u.
RMS gradient 0.00007502 a.u.
Point group D*H
Bond Length (N-H) 1.21602 Å
Optimised Bond Angle (H-N-H) 180°
Item table
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000130 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000130 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000080 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000113 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-1.033738D-08
Optimization completed.
-- Stationary point found.
----------------------------
! Optimized Parameters !
! (Angstroms and Degrees) !
-------------------------- --------------------------
! Name Definition Value Derivative Info. !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! R1 R(1,2) 1.216 -DE/DX = -0.0001 !
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGradGrad
Optimised O2 molecule |
Vibrations
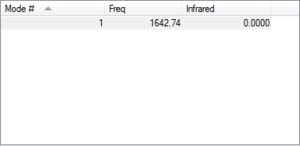
How many modes do we expect 1
Which modes are degenerate Not applicable
Which modes are bending 0
Which modes are bond strength 1
Which mode is highly symmetric 1
Which mode is the umbrella mode Not applicable
How many bands do we expect in the experimental spectrum of gaseous oxygen 0
Charges
Charge on each O atom 0.375
Explaining charges Oxygen is a neutral molecule, both Os are equivalent so both have 0 charge.
Molecular orbitals



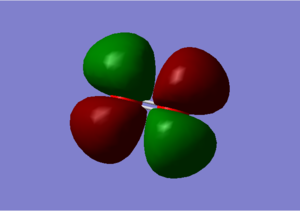
In the transparent orbital pictures we can determine some information about the orbitals above.
1) These orbitals are not interacting. It's occupied. 2) These MOs are made of 2 s orbitals, they are out of phase therefore they are antibonding orbitals. It's occupied. 3) These MOs are made up from the 2p AOs. It's occupied. 4) These MOs are pi orbitals; made of p AOs. It's occupied. 5) These MOs are 2 p orbitals out of phase, therefore they are antibonding. They are unoccupied. This is the LUMO as it is the lowest energy orbital without any electrons in.
References
[1] Periodicity, Quantitative equilibrium and Functional group chemistry Nelson Advanced Science Series
