Rep:Mod:01333428
NH3 molecule.
Calculation method: RB3LYP
Basis set: 6-31G(d,p)
Final energy in atomic units (a.u): -56.55776873 Bond length: 1.01798 Bond angle (degrees): 105.741°
The bond angle should be 107° because ammonia has a trigonal pyramidal shape1.
Point group: C3v
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
Predicted change in Energy=-5.986276D-10
test molecule |
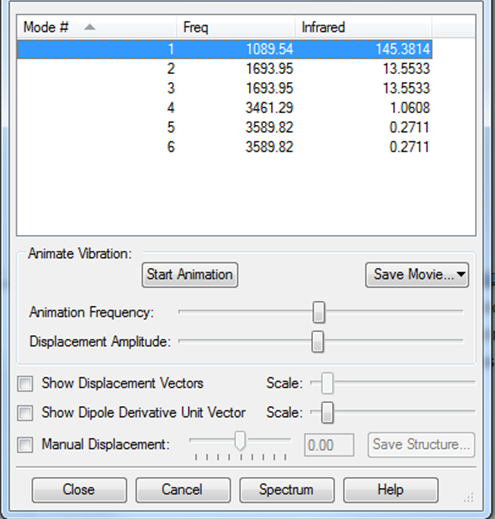
Modes of vibrations: 6 Modes 2 and 3 are degenerate. Modes 5 and 6 are degenerate. Modes 1,2 and 3 are bending vibrations. Modes 4,5 and 6 are bond-stretch vibrations. Mode 4 is highly symmetric. Mode 1 is the umbrella. Ammonia is infrared active because there is a change in dipole. There would be 2 bands in the experimental spectrum of gaseous ammonia. The charge on the nitrogen atom is -1.125 and the charge on the hydrogen atoms is 0.375. Nitrogen would have a negative charge because it gains 3 electrons to achieve a full octet. Hydrogen would have a positive charge because it loses an electron to the nitrogen atom.
Nitrogen molecule.
Calculation method: RB3LYP
Basis set: 6-31G(d,p)
Final energy E(RB3LYP) in atomic units (au): -150.25742434
RMS gradient: 0.00008890
Point group: dinfh
Bond length: 1.21584
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000006 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000006 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000002 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000003 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-1.248809D-11
test molecule |
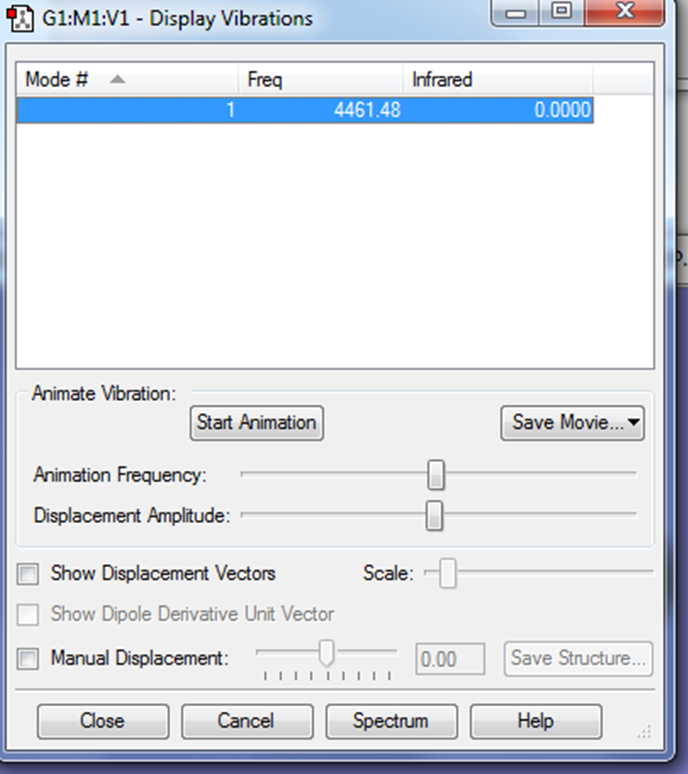
 There is only 1 mode of vibration. It is a bond stretch vibration. No bands will be seen in the IR spectrum as nitrogen is not infrared active because there is no change in dipole.
There is only 1 mode of vibration. It is a bond stretch vibration. No bands will be seen in the IR spectrum as nitrogen is not infrared active because there is no change in dipole.
Hydrogen molecule
Calculation method:RB3LYP
Basis set: 6-31G(d,p)
Final energy E(RB3LYP) in atomic units (au):-1.17853930
RMS gradient:0.00012170
Point group:dinfh
Bond length:0.74309
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000211 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000211 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000278 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000392 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-5.540678D-08
test molecule |
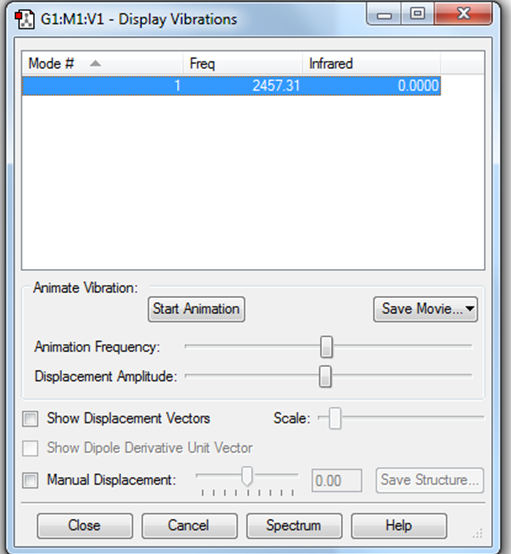
There is only 1 mode of vibration because the molecule is linear. It is a bond stretch. No bands will be seen in the IR spectrum as hydrogen is not infrared active because there is no change in dipole.
Haber-Bosch process calculation:
E(NH3)= -56.55776873
E(N2)=-109.52412868
E(H2)=-1.17853930
2*E(NH3)=-113.1155375
3*E(H2)=-3.5356179
ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]= -146.48 kJ/mol
The gaseous reactants are the most stable.
Oxygen molecule.
Calculation method: RB3LYP
Basis set: 6-31G(d,p)
Final energy E(RB3LYP) in atomic units (au):-150.25742434
RMS gradient: 0.00008890
Point group: dinfh
Bond length: 1.21584
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000154 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000154 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000094 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000133 0.001200 YES Predicted change in Energy=-1.449648D-08
test molecule |
 There is only 1 mode of vibration. It is a bond stretch vibration. No bands will be seen in the IR spectrum as oxygen is not infrared active because there is no change in dipole.
There is only 1 mode of vibration. It is a bond stretch vibration. No bands will be seen in the IR spectrum as oxygen is not infrared active because there is no change in dipole.
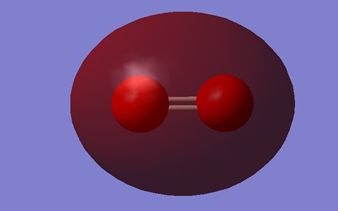 This is the bonding 2σg orbital. It is formed by the constructive overlap of 2 2s orbitals. It contains 2 electrons.
This is the bonding 2σg orbital. It is formed by the constructive overlap of 2 2s orbitals. It contains 2 electrons.
 This is the bonding 3σg orbital. It is formed by constructive overlap of 2 2pz orbitals which are linearly combined. It is higher in energy than the 2σg orbital.
This is the bonding 3σg orbital. It is formed by constructive overlap of 2 2pz orbitals which are linearly combined. It is higher in energy than the 2σg orbital.
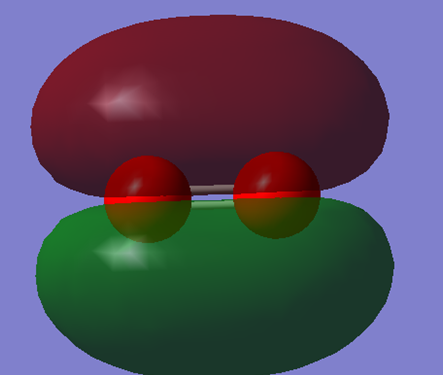 This is the bonding 1 πu (px) orbital. It is formed from the constructive overlap of 2 px orbitals.
This is the bonding 1 πu (px) orbital. It is formed from the constructive overlap of 2 px orbitals.
This is the other bonding 1 πu orbital. I It is formed by the constructive overlap of 2 py prbitals. The πu (px) and πu (py) are degenerate because of the symmetry of the molecule. The energies of the orbitals are slightly different on gaussian due to the d character of the orbitals.
This is the anti-bonding 1 πg orbital. It is formed by the deconstructive overlap of 2 px orbitals out of phase. The antibonding π orbital is higher in energy than the bonding π orbital. Gaussian shows that this orbital is occupied with 2 electrons, however according to molecular theory it should be singly occupied due to paramagnetism.
References:
1 P. Atkins, J, de Paula, Atkins’ Physical Chemistry, Oxford University Press