Rep:Mod:01186302
NH3
Calculation Method:RB3LYP Basis Set:6-31G(d.p) Final Energy E(RB3LYP:-56.55776873 au RMS Gradient:0.00000485 au Point Group:C3V N-H Bond Distance:1.01798Å H-N-H Bond Angle:105.741°
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
NH3 |
The optimisation file is liked to here
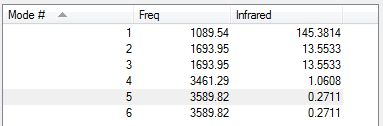
Expected Modes:6 Degenerate Modes:2/3 and 5/6 Bending Modes:1/2/3 Stretching Modes:4/5/6 Highly Symmetric Modes:4 Umbrella Mode:1 Number of Bands in Experimental Spectrum:2 (1, 2/3) Only asymmetric stretches involve a change in dipole moment, so show up on the spectrum. 2 and 3 are degenerate so only result in one peak. 4 is symmetric and doesn't have a change in dipole moment so no peak is seen. And, 5/6 have signals with a very weak intensity so are indistinguishable from noise. Expected:Negative charge on N and positive charge on H Charge on N:-1.125 Charge on H:0.375
N2
Calculation Method:RB3LYP Basis Set:6-31G(D,P) Final Energy E(RB3LYP:-109.52412868au RMS Gradient:0.00000060au Point Group:D<sub>∞h</sub> N-N Bond Distance:1.10550Å Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000001 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000001 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000000 0.001200 YES
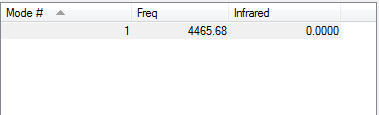
N2 |
The optimisation file is liked to here
H2
Calculation Method:RB3LYP
Basis Set:6-31G(D,P)
Final Energy E(RB3LYP:-1.17853936au
RMS Gradient:0.00000017au
Point Group:D<sub>∞h</sub>
H-H Bond Distance:0.74279Å
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000000 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000000 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000000 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000001 0.001200 YES
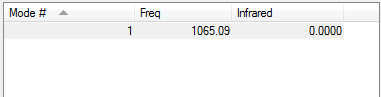
H2 |
The optimisation file is liked to here
Haber-Bosch process
N2 + 3H2 -> 2NH3
E(NH3)=-56.55776873 au
2*E(NH3)=-113.11553750 au
E(N2)=-109.52412868 au
E(H2)=-1.17893936 au
3*E(H2)=-3.53681808 au
ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]=-0.05579070 au
ΔH=-146.47848290 KJ/mol
Literature Value:ΔH=-45.7KJ/mol [1]
- ↑ Modak JM. Haber process for ammonia synthesis. Resonance. 2011 Dec 1;16(12):1159-67..
For the standard enthalpy change of reaction, to form one mole of ammonia. To form two moles, the ΔH=-91.4KJ/mol. The value calculated using computational methods was -146.47848290 KJ/mol, this is relatively close to the experimental value. Ammonia product is more stable as the reaction is exothermic.
F2
Calculation Method:RB3LYP
Basis Set:6-31G(D,P)
Final Energy E(RB3LYP:-199.49825218 au
RMS Gradient:0.00007365 au
Point Group:D<sub>∞h</sub>
F-F Bond Distance:1.40281Å
Item Value Threshold Converged?
Maximum Force 0.000128 0.000450 YES
RMS Force 0.000128 0.000300 YES
Maximum Displacement 0.000156 0.001800 YES
RMS Displacement 0.000221 0.001200 YES
Expected:F2 is homodinuclear so no expected charge on either F.
Charge on F:0
F2 |
The optimisation file is liked to here
Molecular Orbitals
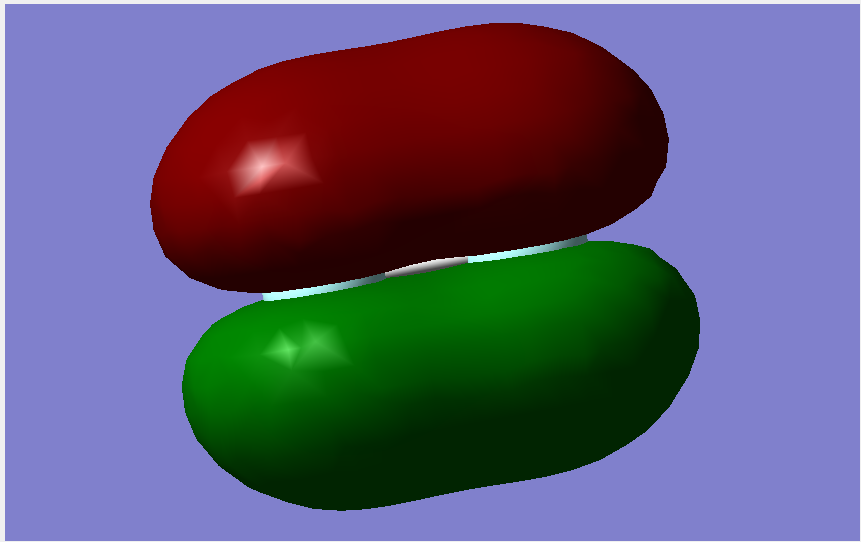
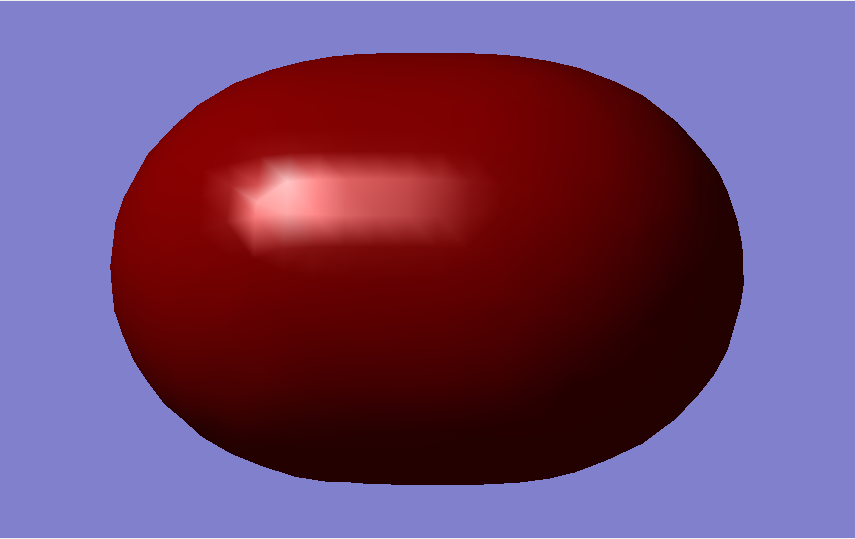
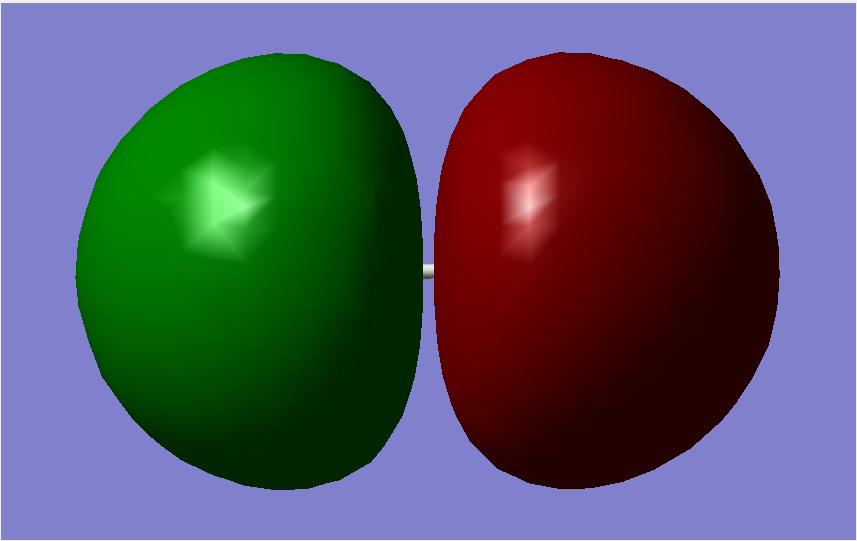
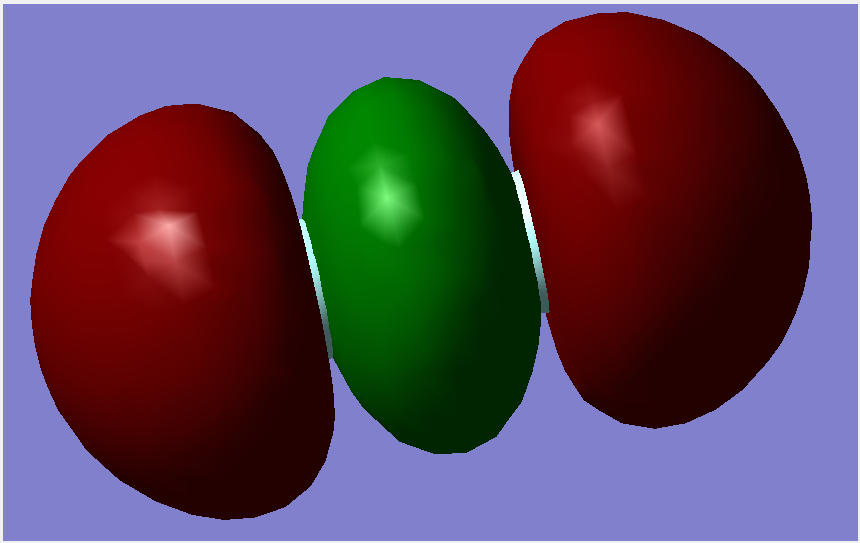

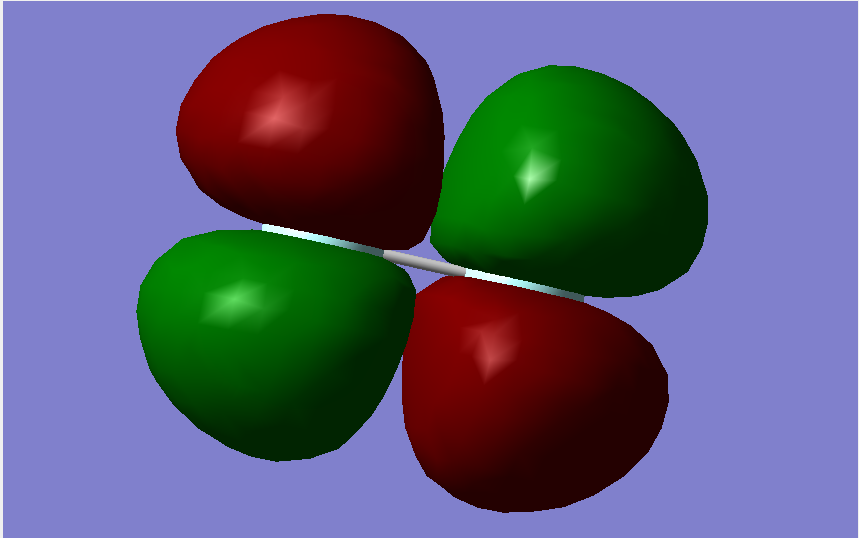
The overall bond order is 1, as there is a single sigma bond.