Rep:MOD:mjr116
NH3
Molecule: NH3
Calulation Method: RB3LYP
Basis Set: 6-31G(d,p)
Final Energy E(RB3LYP) in au: -56.55776873
RMS Gradient: 0.00000485
Point Group: C3V
N-H Bond Distance: 1.01798
H-N-H Bond Angle: 105.741
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000004 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000004 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000072 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000035 0.001200 YES
The optimisation file is linked to here
test molecule |
how many modes do you expect from the 3N-6 rule?
12
which modes are degenerate (ie have the same energy)?
2 and 3 5 and 6
which modes are "bending" vibrations and which are "bond stretch" vibrations?
1 - bending 2 - bending 3 - bending 4 - stretch 5 - stretch 6 - stetch
which mode is highly symmetric?
4
one mode is known as the "umbrella" mode, which one is this?
1
how many bands would you expect to see in an experimental spectrum of gaseous ammonia?
6
N - atom charge: -1.125 H - atom charge: 0.375
N2
Molecule: N2
Calculation Method: RB3LYP
Basis Set: 6-31G(d,p)
Final energy E(RB3LYP) in au: -109.52412868
RMS gradient: 0.00000365
Point Group: D*H
N-N bond length: 1.10550
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000006 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000006 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000002 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000003 0.001200 YES
Frequencies: 2457.31
The optimisation file is linked to here
test molecule |
H2
Molecule: H2
Calculation Method: RB3LYP
Basis Set: 6-31G(d,p)
E(RB3LYP): -1.09691172
RMS Gradient: 0.05487992
Point Group: D*H
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000211 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000211 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000278 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000393 0.001200 YES
The optimisation file is linked to here
test molecule |
Energy for the reaction
N2 + 3H2 -> 2NH3
E(NH3)= -56.55776873
2*E(NH3)= -113.11553746
E(N2)= -109.52412868
E(H2)= -1.09691172
3*E(H2)= -3.29073516
ΔE=2*E(NH3)-[E(N2)+3*E(H2)]= -113.11553746 - (-109.52412868 + -3.29073516) = -0.30067362
Energy for converting hydrogen and nitrogen gas into ammonia gas in kJ/mol = -789.418649445
The ammonia product is therefore more stable.
F2
Molecule: F2
Calculation Method: RB3LYP
Basis Set: 6-31G(d,p)
E(RB3LYP): -199.48874381
RMS Gradient: 0.06248728
Point Group: D*H
Item Value Threshold Converged? Maximum Force 0.000250 0.000450 YES RMS Force 0.000250 0.000300 YES Maximum Displacement 0.000308 0.001800 YES RMS Displacement 0.000435 0.001200 YES
The optimisation file is linked to here
test molecule |
Frequency 1063.53
Charge: 0.0000
Orbitals
This is the 2σ_g F2 orbital. One electron from each of the 2s atomic orbitals on the Fluorine atoms combine in-phase to make the 2σ_g molecular orbital. This molecular is an occupied orbital and it is a bonding MO. The electron density is spread between the two atoms and therefore this MO will have a stabilising effect on the bonding between the two F atoms.
This is the 2σ_u* orbital. Two electrons contribute to this molecular orbital, one from each of the 2s atomic orbitals of the fluorine atoms. This is an occupied molecular orbital and it is a result of the out of phase combination of orbitals, therefore this is an antibonding molecular orbital. This reduces the stability of the bond between the F atoms as the electron density is over the atoms but there is a node (gap) between the two atoms of lower electron density.
This is the 3σ_g F2 molecular orbital. It is the result of the in-phase combination of the 2p orbitals on the fluorine atoms, therefore this is an occupied bonding MO. The electron density is in between the two nuclei therefore this MO contributes to the stability of the bonding.
This is the 1π_u F2 molecular orbital. It is the result of in-phase combination of the 2p orbitals, and is therefore an occupied bonding MO which contributes to the stability of the molecule.
This is the 1π_g* F2 molecular orbital. It is an anti-bonding orbital resulting from the out of phase combination of the 2p atomic orbitals. This is the HOMO (Highest Occupied Molecular Orbital) of the F¬2 molecule.
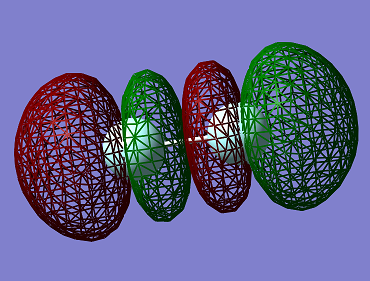 This is the 3σ_u* F2 molecular orbital. It is an anti-bonding MO resulting from the out of phase combination of the 2p atomic orbitals of the fluorine atoms. It is the LUMO (Lowest Unoccupied Molecular Orbital) of the F2 molecule.
This is the 3σ_u* F2 molecular orbital. It is an anti-bonding MO resulting from the out of phase combination of the 2p atomic orbitals of the fluorine atoms. It is the LUMO (Lowest Unoccupied Molecular Orbital) of the F2 molecule.